Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
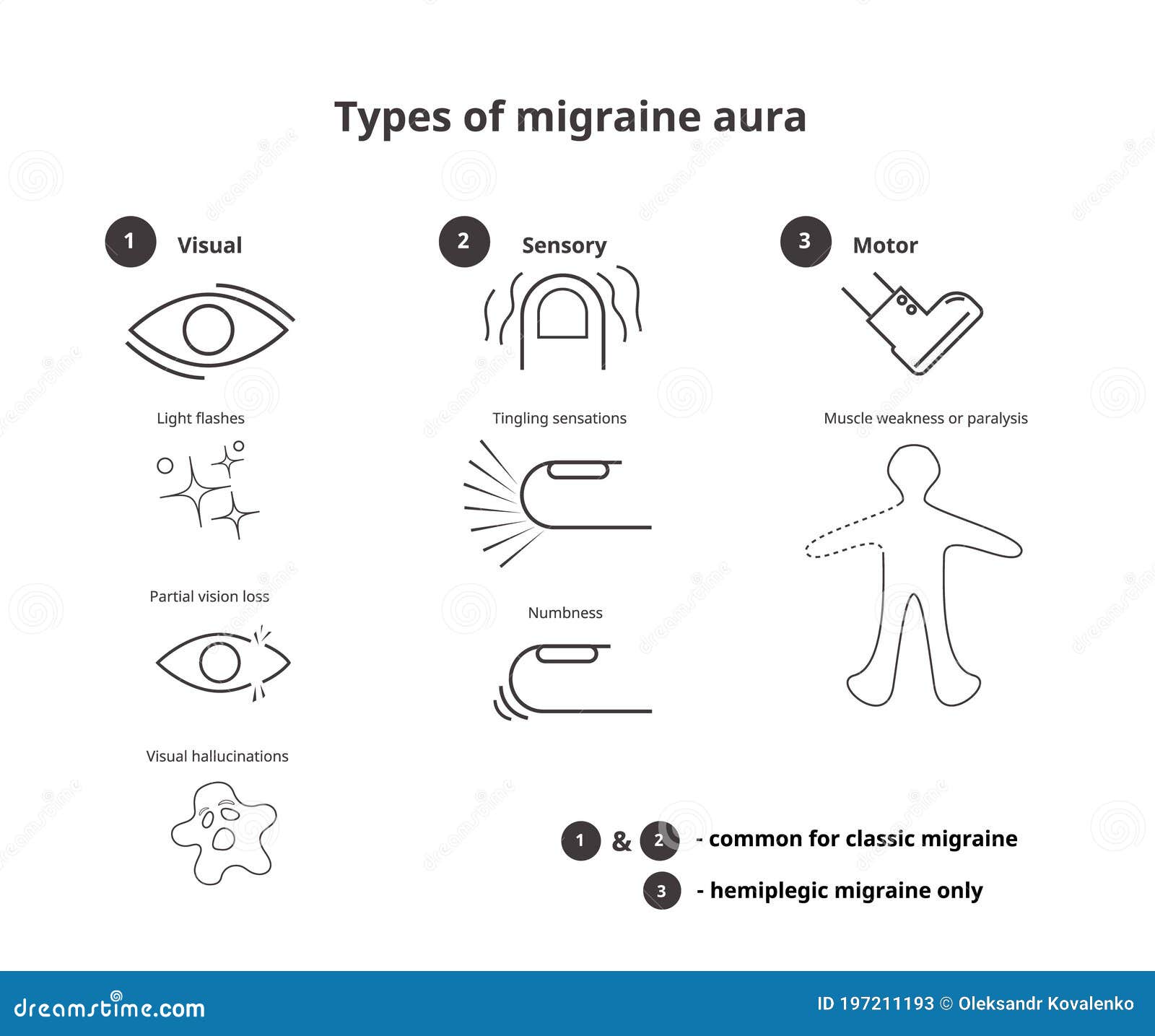
Hemiplegic migraine (HM) is a clinically and genetically heterogeneous condition with attacks of headache and motor weakness which may be associated with impaired consciousness, cerebellar ataxia and intellectual disability. HM can occur as a sporadic HM or familiar HM with an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance. Mutations in CACNA1A, ATP1A2 and SCN1A encoding proteins involved in ion. Since my first two aren’t controlling my migraines enough to get me more than barely-functional I’m supposed to start gabapentin. I’ve never had an anti-seizure medication before and I don’t know what to expect. I looked it up online and the reviews were from people with a wide array of disorders, most of which I don’t have. A hemiplegic migraine is a rare type of migraine that happens with one-sided muscle weakness. While this type of migraine isn’t a medical emergency, it can look and feel similar to a stroke. Contact emergency services right away if you notice any stroke-like symptoms. In clinical practice, acetazolamide has been used off-label for headache disorders such as IIH, vestibular migraine and hemiplegic migraine. IIH associated with headaches that can overlap symptomatically with migraine. Acetazolamide is an effective treatment both for the headaches and the increased intracranial pressure (Nye & Thadani, 2015). Hemiplegic migraine is a rare and serious type of migraine headache. Many of its symptoms mimic those common to stroke. For example, muscle weakness can be so extreme that it causes a Not with hemiplegic migraine, migraine with brainstem aura, stroke, heart disease, or uncontrolled hypertension, or pregnancy: Anti-seizure medications: gabapentin Migraine disorders are further classified into migraine without aura, migraine with aura, familial or sporadic hemiplegic migraine, and basilar-type migraine. Complications of migraines include chronic migraine, status migrainosus, persistent aura without infarction, migrainous infarction, and migraine-triggered seizures. Hemiplegic migraine is a rare subtype of migraine with aura, characterized by the presence of motor weakness as an aura manifestation at the time of migraine attack. Typically, migraine aura has visual symptoms as aura, but occasionally impairment in sensation or speech may also be seen. Migraine is subdivided into migraine with or without aura, and is defined as either episodic or chronic. Migraine with aura consists of visual symptoms (zigzag or flickering lights, spots, lines, or loss of vision), sensory symptoms (pins and needles, or numbness), or dysphasia, which usually precede the onset of headache. Symptoms usually Hemiplegic migraine (HM) is a subtype of migraine with aura that includes motor weakness; such headaches can be excruciating. The presence of not only headache but also aura symptoms of HM increase the burden on patients, and the treatment of HM is sometimes challenging. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) The recommendations on what information and self-care advice should be given to people with migraine are based on clinical guidelines National headache management system for adults [], Headaches in over 12s: diagnosis and management [], Primary care management of headache in adults [Becker, 2015] and Pharmacological management of migraine [], the American Headache Society updated consensus In 2022, a trial (Head-to-Head Study of Erenumab Against Topiramate in Patients with Episodic and Chronic Migraine [HERMES]) comparing erenumab and topiramate for the prevention of migraine was published. 38 The HER-MES study was a 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted in adults (n = 777); most patients had Migraine relief medications that combine caffeine, aspirin and acetaminophen (Excedrin Migraine) may be helpful, but usually only against mild migraine pain. Triptans. Prescription drugs such as sumatriptan (Imitrex, Tosymra) and rizatriptan (Maxalt, Maxalt-MLT) are used to treat migraine because they block pain pathways in the brain. Migraine is a common episodic disorder, the hallmark of which is a disabling headache generally associated with nausea and/or light and sound sensitivity. The acute treatment of migraine in adults is reviewed here. Preventive treatment of migraine in adults is discussed separately. (See "Preventive treatment of episodic migraine in adults".) Triptans and other vasoconstrictors are contraindicated in patients with coronary artery disease and in specific migraine syndromes, such as hemiplegic and basilar migraines. Gabapentin is an effective prophylactic agent for patients with migraine. In addition, gabapentin appears generally well tolerated with mild to moderate somnolence and dizziness. Gabapentin or pregabalin for the prophylaxis of episodic migraine in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013(6):CD010609. Xu XM, Liu Y, Dong MX, Zou DZ, Wei YD. Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. Due to this ambiguity, a clinical evidence literature review was performed investigating GBP's efficacy in headache disorders. Learn more about this rare type of migraine, its different forms and why it’s important to get an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment. Hemiplegic migraine is a rare form of migraine where people experience weakness on one side of their body (hemiplegia) along with headache and other symptoms that are often the same as seen in migraine.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |