Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
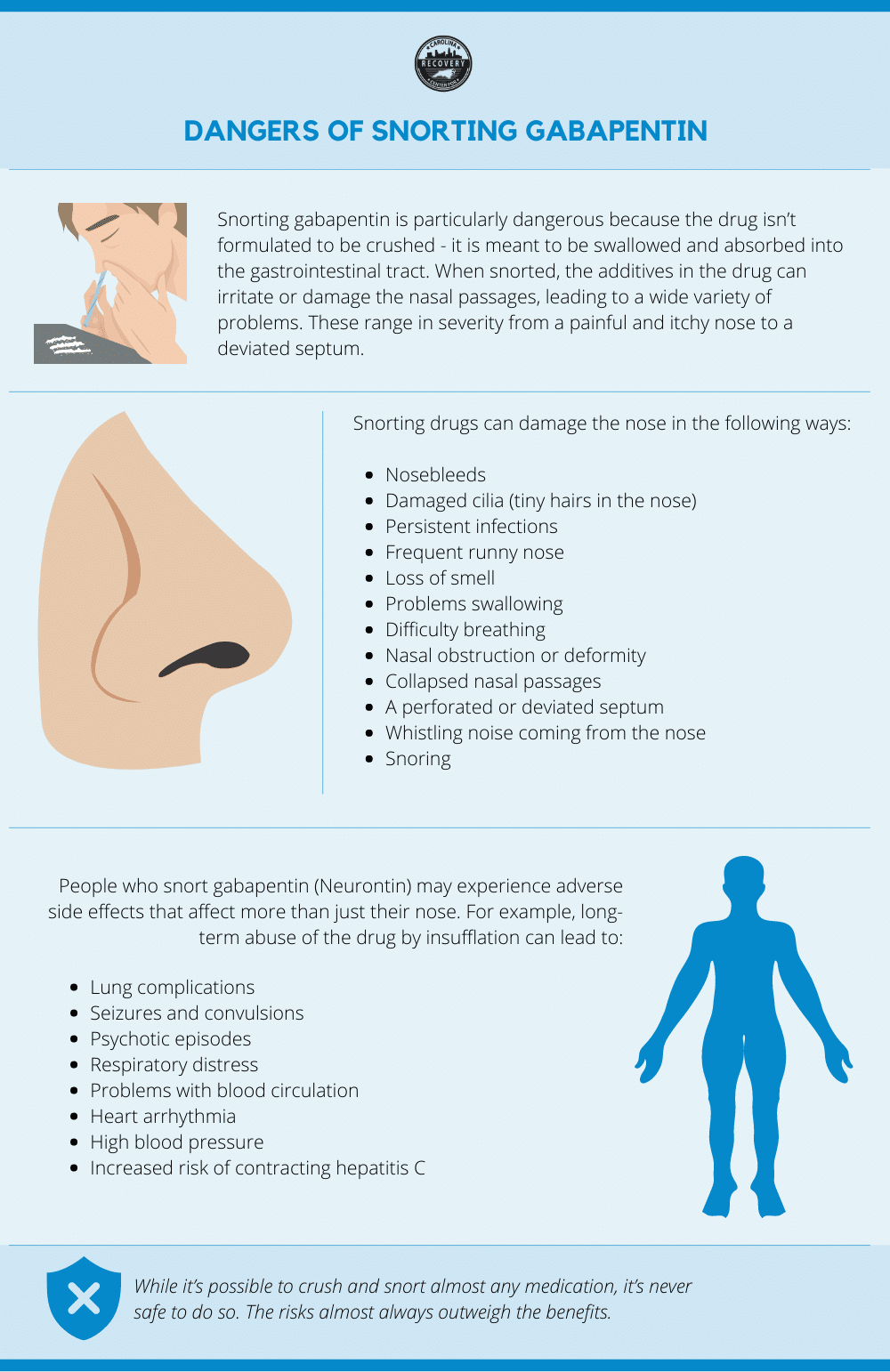 |  |
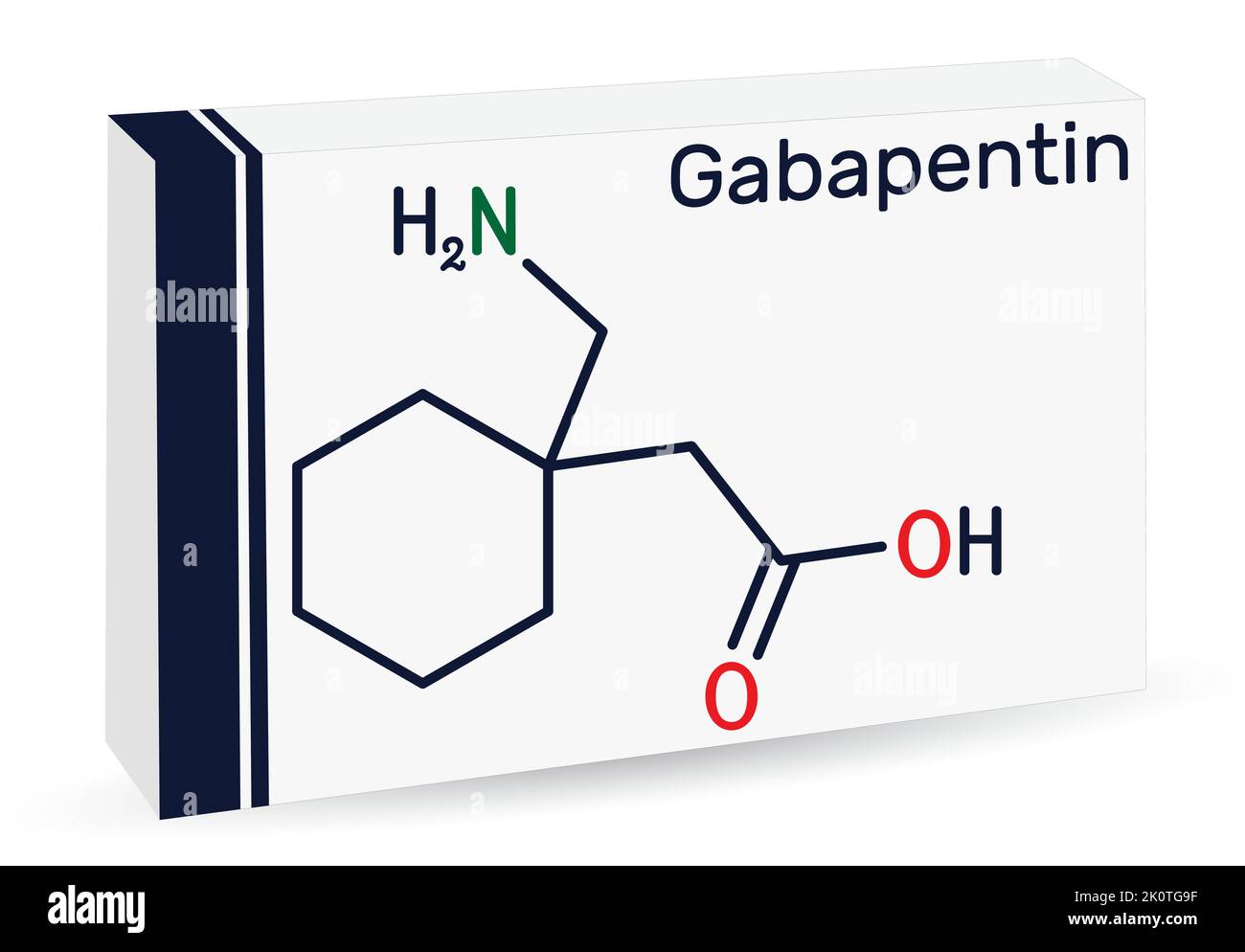
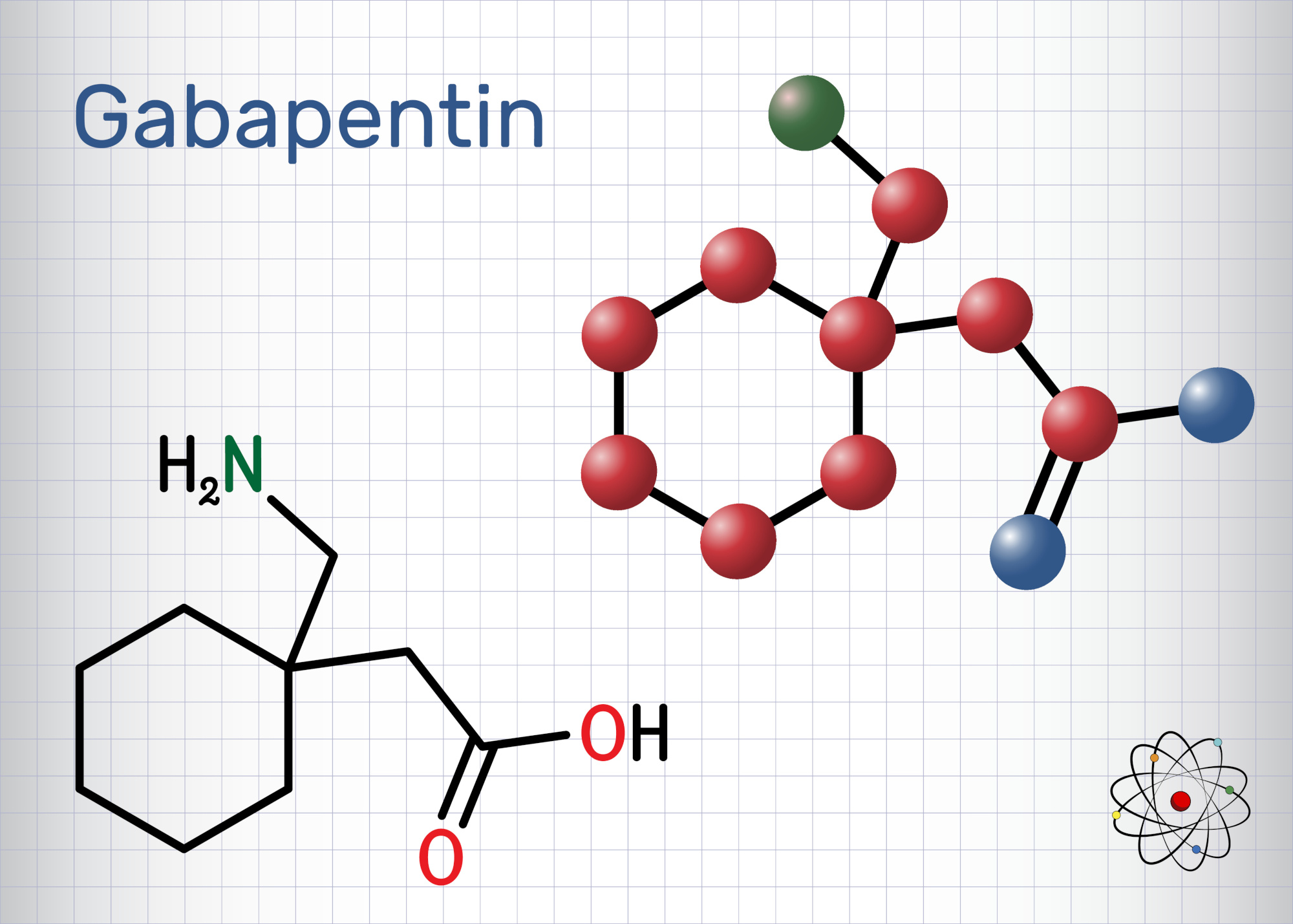
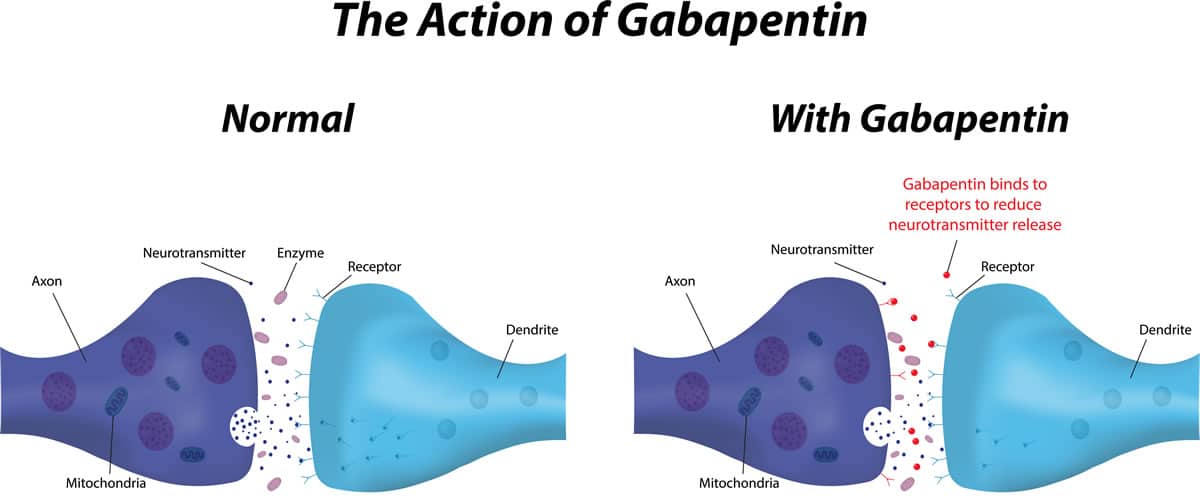
Gabapentin (often prescribed under its brand name Neurontin) is an anti-convulsant/sedative medication used to treat a wide range of medical issues, ranging from partial seizures to shingles-related nerve pain and restless leg syndrome. 1 It is also commonly used off-label to treat an even wider variety of physical and mental health concerns, including fibromyalgia, neuropathic pain, and And while gabapentin is reported to have low addictive liability levels (Brockbrader et al., 2010), key informants expressed some concern about gabapentin misuse as a first indication of relapse. Limiting access to and controlling the administration of gabapentin and other medications during treatment will likely limit the opportunities for Risky or illegal behavior to get more gabapentin is a major red flag of addiction. Gabapentin can potentially amplify the sedative effects of other central nervous system depressants like alcohol, benzodiazepines, or opioids. Signs and Symptoms of Gabapentin Addiction. Gabapentin addiction can cause behavioral changes similar to those of opioid addiction. These include: 12. Compulsive use of gabapentin despite adverse consequences; Experiencing cravings for gabapentin and increasing the dose without a doctor's recommendation Gabapentin has been increasingly associated with drug abuse, particularly in people who mix it with opioids, alcohol or other substances. Illegal diversion of gabapentin has led to its illicit availability on the streets, as well. Using gabapentin with opioids can be dangerous. Yes, it can be a highly addictive substance. However, it may be tough to figure out if you have an addiction to Gabapentin—mainly because it is a prescription pill and may seem like a safe medication at first. In this article, we’ll be examining some risk factors for Gabapentin addiction. Gabapentin is one of the recommended mainstays of evidence-based treatment. 3. Unfortunately, our clinical experience suggests that gabapentin is now prevalent as a drug of abuse. The drug’s effects vary with the user, dosage, past experience, psychiatric history, and expectations. When taken as prescribed for an intended medical condition, gabapentin is well-tolerated and not considered addictive. However, addiction can occur or worsen when misused illicitly, at higher doses, or combined with opioids. While gabapentin is not inherently addictive, misuse can elevate the risk of developing a dependency. Gabapentin is an FDA-approved medication sold under the brand names Neurontin, Gralise, and Horizant. [3] . Gabapentin is not likely to cause addiction, but it may lead to dependence or misuse under certain conditions. As such, doctors prescribe gabapentin carefully to avoid withdrawal Gabapentin may be used to treat addictions to other substances, but it can also be addictive. If you or someone you know may be abusing gabapentin or struggling with a gabapentin addiction, knowing the side effects, risks, and treatment options may be beneficial. It is entirely possible to abuse Neurontin, but many people mistake this as indicating that addiction is highly likely. That is not the case, as this medicine does not bind to similar receptors as the most addictive substances after use, reducing the likelihood of it resulting in addiction. Though an off-label use, gabapentin has also been found useful in treating certain mental health disorders. 3 So, during addiction treatment, a person could be prescribed gabapentin to help with symptoms of cannabis, opioid, or alcohol use disorders or to help with co-occurring mental disorders such as anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder Is Gabapentin Addictive? An important concern surrounding Gabapentin is whether it is addictive. While Gabapentin is not classified as a controlled substance, evidence suggests that it may lead to misuse or dependency in some individuals. Gabapentin is a prescription Painkiller that is less addictive than Opioids. Still, addiction and abuse occur; overdosing is possible. Before we answer the question, Is gabapentin addictive, let’s first take a look at what this medication is and what types of conditions it treats. Gabapentin is a prescription medication that is classified as an anticonvulsant. Despite those warnings, gabapentinoids — gabapentin in particular — are still being promoted as a treatment for all sorts of things, from dental pain to alcoholism to improving your sex life. Gabapentin has been pitched for so many different conditions that a drug company executive infamously called it “snake oil.” Gabapentin can be addictive and prone to misuse in certain individuals, primarily those with current or past substance use disorders. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used to treat seizures by decreasing abnormal excitement in the brain that.While gabapentin is not typically considered highly addictive, it can be misused or lead to dependence in some cases. Overall, gabapentin is not considered a highly addictive drug. Many cases of gabapentin abuse occur in people who already have addictions to opioids and other drugs. In response to increased abuse of gabapentin, some states are classifying gabapentin as a Schedule V controlled substance.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |