Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
.jpg) |  |
 |  |
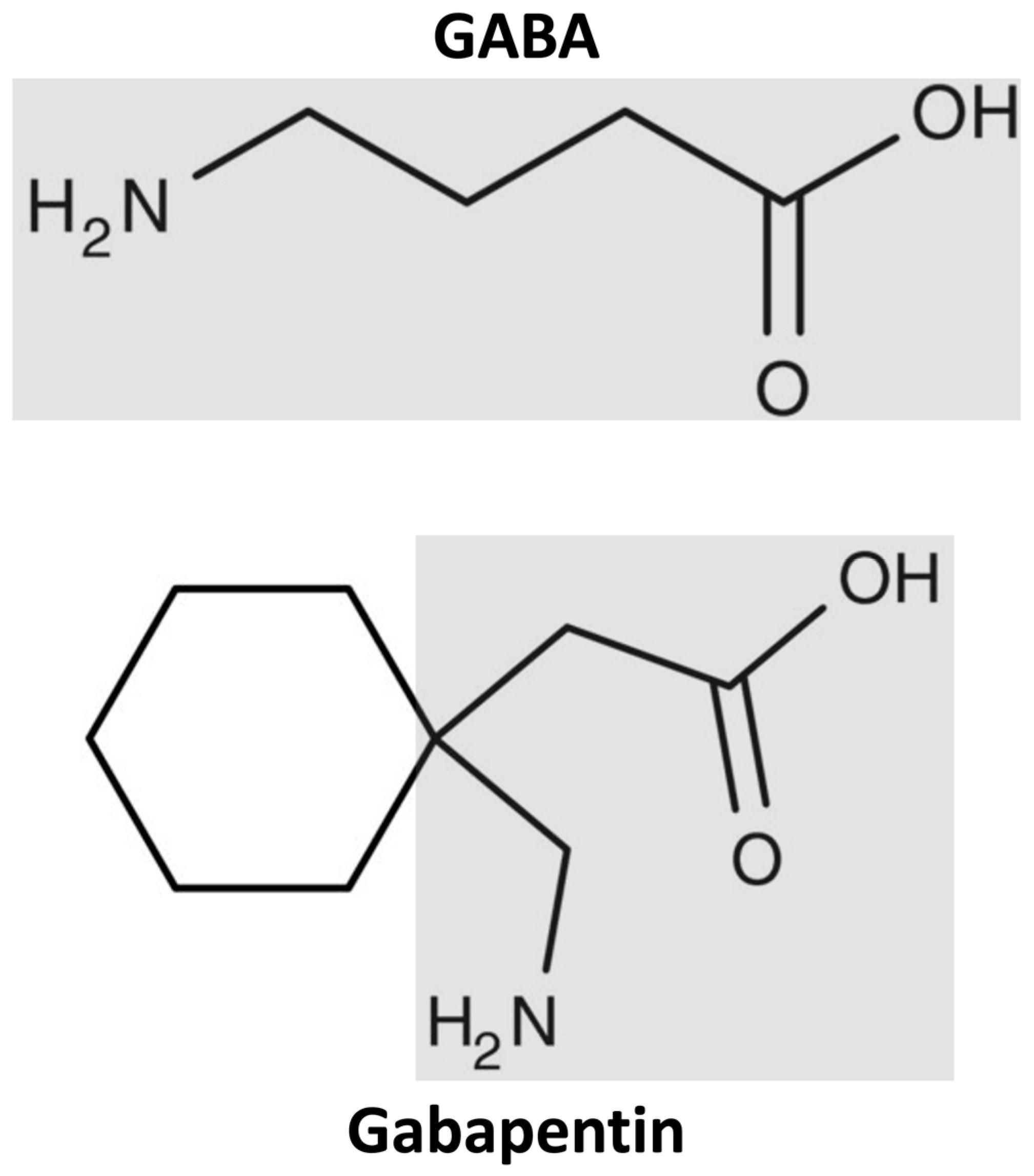 |  |
For some, these feelings can become overwhelming, interfering with daily life. Enter gabapentin. Studies have shown promising results in using this medication to treat various anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), social anxiety, and panic disorder. But gabapentin’s potential doesn’t stop at anxiety. Gabapentin isn’t usually used to treat anxiety alone. More often, it’s given to ease anxiety symptoms for someone who also has depression or bipolar disorder. (Anxiety is commonly comorbid Gabapentin may be effective for anxiety, but it’s usually not a first-choice medication for this use. Other medications have been studied more for anxiety, and they’re typically tried first. The recommended gabapentin dosage for anxiety and other conditions can range from 300 mg to 3,600 mg per day. Off-label gabapentin (Neurontin) got a bad rep when it missed the mark in bipolar disorder, but there may be something worth salvaging in this drug. Here, we weigh its pros and cons for anxiety, substance use disorders, sleep, pain, and hot flashes, and compare it to its underutilized cousin, pregabalin (Lyrica). There are currently no known ongoing trials of gabapentin for anxiety disorders. Another anticonvulsant, tiagabine, is FDA-approved for the treatment of partial seizures and has been shown to have potential anxiolytic effects in preclinical studies . Preclinical data suggest the potential anxiolytic effect of gabapentin ().Recently, Beauclair et al. reported reduction in anxiety symptoms and syndromes in 18 patients with primary psychotic disorders and in one patient with generalized anxiety disorder treated adjunctively with gabapentin, 200–1800 mg/day. Whether you’re already taking gabapentin for an anxiety disorder or are curious if you might benefit from it, you may be wondering how effective it is, how it works, and if there are side effects. Here we’ll cover everything you need to know about gabapentin for anxiety. Research also indicates that gabapentin works better than disorders like bipolar illness, panic disorder, or panic attacks to lessen the effects of alcohol withdrawal and some forms of anxiety. The precise mechanism of gabapentin’s action is not entirely understood. Preclinical data suggest the potential anxiolytic effect of gabapentin ().Recently, Beauclair et al. reported reduction in anxiety symptoms and syndromes in 18 patients with primary psychotic disorders and in one patient with generalized anxiety disorder treated adjunctively with gabapentin, 200–1800 mg/day. Gabapentin appears to have some benefit for anxiety disorders but failed to show benefit in bipolar disorder trials. In the individual patient with a mixed psychiatric disorder, benefits are most likely due to anxiolytic effects. Gabapentin is thought to work by affecting neurotransmitters in the brain, like gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). GABA helps regulate anxiety and stress responses in the brain, so increasing levels can cause a calming effect, reducing feelings of anxiety and promoting relaxation. Gabapentin is frequently used in the treatment of anxiety disorders. However, there are no randomized controlled trials on the effectiveness of this medication in generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), and there are only a few case reports. A small randomized, controlled trial suggested that adjunctive gabapentin accelerates therapeutic response to fluoxetine in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. 32 In a randomized, controlled trial of 420 breast cancer survivors with nonspecific anxiety symptoms, 8 weeks of treatment with gabapentin 300 mg produced significant In recent years, gabapentin has gained attention for its potential role in managing anxiety disorders, particularly for individuals who do not respond well to traditional anxiety medications like SSRIs or benzodiazepines. In this review, the author examines the evidence for psychopharmacologic treatments among adults for generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder derived from clinical trials. For each disorder, major categories of drugs are reviewed, and then the evidence-based medications in each category are discussed. The author reviews key safety and tolerability Although evidence is limited, some studies show gabapentin can help with anxiety symptoms. One 2020 review suggests gabapentin may help with different types of situational anxiety, For these reasons, gabapentin has been embraced as a possible treatment for anxiety disorders. Anxiety is a common mental health challenge that features an outsized response to feeling threatened or afraid. The fear response is out of proportion to the actual threat, resulting in a rush of stress hormone production. Previously presumed to have a low abuse and misuse potential, gabapentin has been commonly prescribed for the treatment of anxiety disorders. 10, 11 While pregabalin has shown efficacy for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) in two RCTs, 12, 13 the authors could find no such RCTs done for gabapentin. 9 One randomized, double-blind, placebo There is mounting evidence that Gabapentin may be an effective intervention for various types of anxiety including: generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, and panic disorder. Gabapentin for Anxiety Disorders: The Research. There is considerable research documenting the efficacy and safety of Gabapentin for anxiety disorders. The potential benefits of gabapentin for various sleep issues are wide-ranging. It has shown promise in addressing insomnia, particularly in individuals with chronic pain conditions or anxiety disorders. Gabapentin may also be helpful for those experiencing restless leg syndrome (RLS), a condition that can significantly disrupt sleep.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |