Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
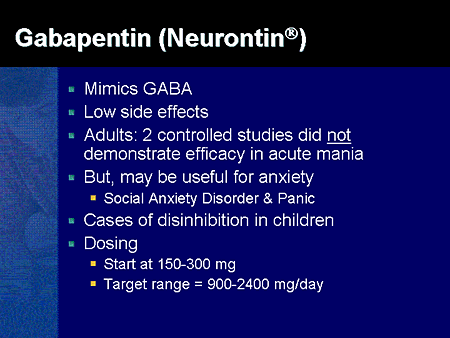
A recent survey using the US-based TriNetX electronic health records network showed that gabapentin had been prescribed at least once in 13.6% of patients with bipolar disorder (BD), 11.5% Despite of the lack of evidence, reviews of gabapentin prescribing patterns in the United States show that this medication is still being used with alarming frequency for bipolar disorder. There are now five medications with specific, FDA approval for acute bipolar depression. A recent survey using the US-based TriNetX electronic health records network showed that gabapentin had been prescribed at least once in 13.6% of patients with bipolar disorder (BD), 11.5% with anxiety disorders, and 12.7% with insomnia disorder; for pregabalin, the figures were 2.9%, 2.6%, 3.0% respectively (PJH, unpublished observations). Gabapentin, a medication commonly used to treat seizures and nerve pain, has also been explored as a potential treatment for bipolar disorder. Research suggests that gabapentin may help alleviate symptoms of bipolar disorder, particularly in patients who have not responded to traditional treatments. What is Bipolar Disorder? Bipolar disorder is Two new anticonvulsants, lamotrigine and gabapentin, have been used increasingly for bipolar disorder in the past several years. Despite this array of options, bipolar disorder remains a difficult disorder to treat. Some subtypes, such as those characterized by rapid cycling or mixed episodes, have been especially resistant to lithium treatment. Researchers found that gabapentin does not help people with bipolar disorder. Learn more about the history of why some doctors prescribe gabapentin for bipolar as an adjunct therapy, even though there’s no evidence that it works for bipolar treatment or maintenance. RESULTS. Bipolar Disorder. The randomized controlled trials 19 –21 investigating gabapentin for treating bipolar disorder indicate it is likely to be ineffective. Data interpretation is difficult: dosing varies by trial, gabapentin is used as both monotherapy and adjunctive therapy, patients have heterogeneous diagnoses, and primary outcomes differ between studies. We identified 40 open-label studies on the use of GBP in at least 600 patients with bipolar disorder (BP), manic, depressed, or mixed episodes and unipolar depression and four controlled studies. Abstract. Despite its prevalence and disease burden, several chasms still exist with regard to the pharmacotherapy of bipolar disorder (BD). Polypharmacy is commonly encountered as a significant proportion of patients remain symptomatic, and the management of the depressive phase of the illness is a particular challenge. Conclusions: The findings of this study did not demonstrate that gabapentin is an effective adjunctive treatment when administered to outpatients with bipolar disorder. Independent assessment of manic and depressive symptoms by self-rating. Scale characteristics and implications for the study of mania. Gabapentin appears to have acute anti-manic and anti-depressant properties as an adjunctive agent for refractory bipolar illness. Prospective double-blind studies are needed to further delineate its acute efficacy when used as monotherapy and its prophylactic efficacy as monotherapy or in conjuction Gabapentin may be a useful drug for the add-on treatment of bipolar patients with poor response to other mood stabilizers. Gabapentin may improve depressive residual symptoms such as irritability, social withdrawal or anxiety. These results should be confirmed in randomized clinical trials. Gabapentin for Bipolar Disorder User Reviews Brand names: Neurontin, Gralise, Gabarone, Fanatrex. Gabapentin has an average rating of 8.5 out of 10 from a total of 138 reviews for the off-label treatment of Bipolar Disorder. 81% of reviewers reported a positive experience, while 9% reported a negative experience. Gabapentin has less likely benefit adjunctively for bipolar disorder. Gabapentin has clearer efficacy for alcohol craving and withdrawal symptoms and may have a role in adjunctive treatment of opioid dependence. There is no clear evidence for gabapentin therapy in depression, PTSD prevention, OCD, or other types of substance abuse. is more gabapentin prescribed for bi-polar disorder than lamotrigine, even though there is little compelling evi-dence for gabapentin’s efficacy in bipolar disorder and the FDA has approved lamotrigine for the treat-ment of bipolar disorder.1,2 Thus, up to half of bipolar patients receiving combination therapy are given anti- Right now, there is no good evidence that gabapentin can be used for treating people with bipolar disorder. High-quality, randomized controlled studies found that Gabapentin is a new adjunctive medication to antiseizure therapies. Anecdotal evidence suggests that it may also help to alleviate mood symptoms in patients with bipolar illness. An open-label study examined the effects of adjunctive gabapentin in bipolar patients with mixed symptoms who had previou The use of gabapentin in bipolar disorder (BPD) treatment provides an informative case of off-label uptake and abandonment of a new medication. Gabapentin was patented by Warner-Lambert in 1977 and FDA-approved in December1993 for the adjunctive treatment of epilepsy and in 2002 for postherpetic neuralgia (see Appendix 1 for timeline). Fifty-five double-blind randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and 15 open-label studies were identified. For bipolar disorder, four double-blind RCTs investigating gabapentin, and no double-blind RCTs investigating pregabalin, were identified. Evidence does not support the use of gabapentin for bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder (MDD), posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), stimulant use disorder, or opioid withdrawal.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |