Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
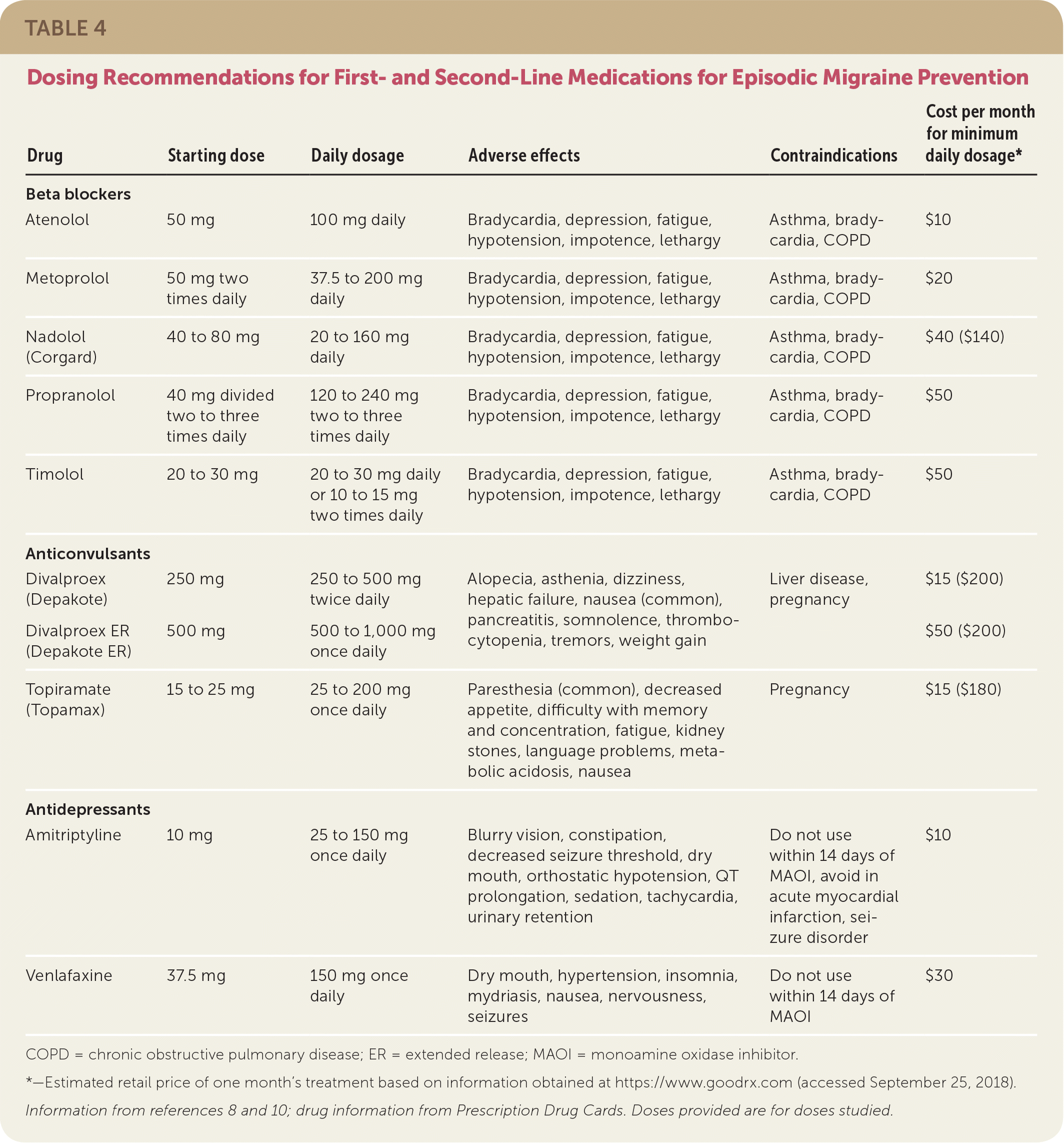
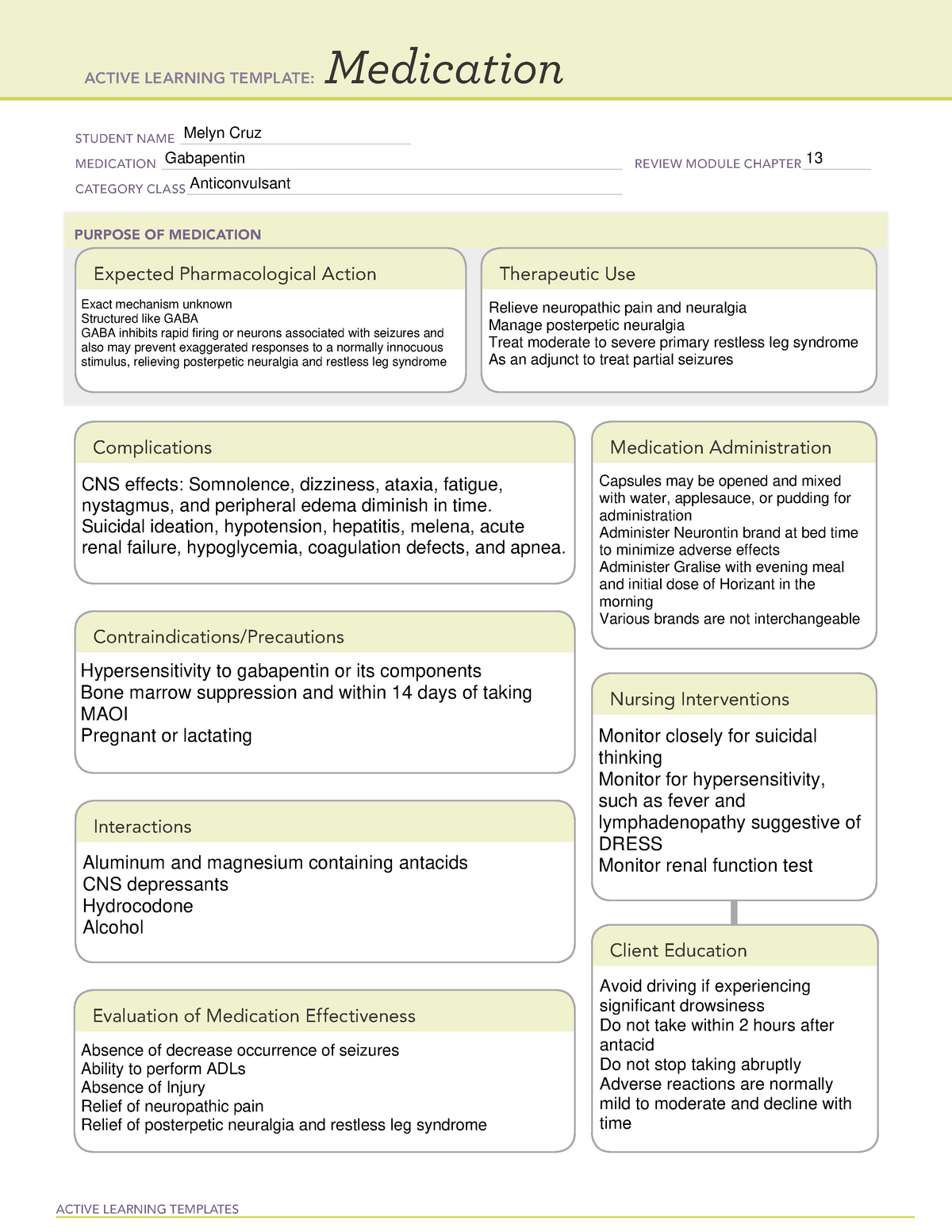
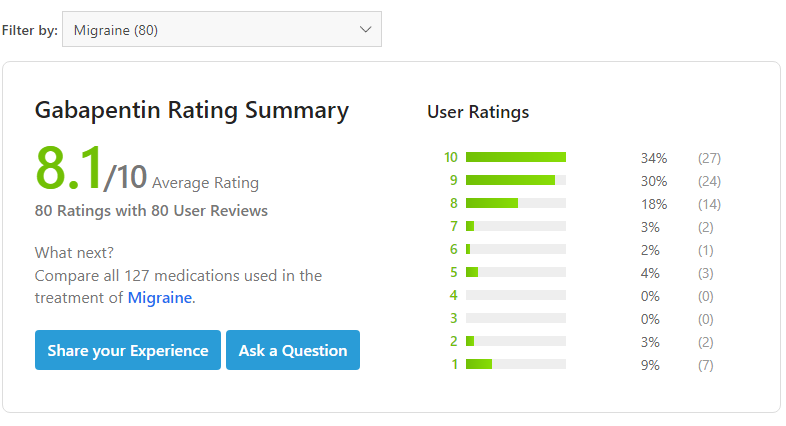
Does gabapentin (Neurontin) help prevent episodic migraine? Evidence-Based Answer Gabapentin does not decrease the frequency of migraine headaches and is not recommended for However, little evidence is available on the effects and mechanisms of action of gabapentin during the migraine attack period. Gabapentin's analgesic effect may result from the antagonism of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and central nervous system calcium channels[5,6]. Migraine is a common, multifactorial neurovascular disorder. Objective.—To compare gabapentin with placebo for use as a prophylactic agent in patients with migraine (with or without aura). Study Design and Treatment.—After screening, a 4-week, single-blind, placebo baseline period was followed by a 12-week, double-blind, treatment period. Discover the potential of gabapentin for preventing migraine attacks and headaches. While not a first-line treatment, it can be effective in combination with other options. The American Academy of Neurology (AAN) and the American Headache Society (AHS) do not list gabapentin as "effective" or "probably effective" for preventing migraines in their 2012 guidelines. Instead, gabapentin is given a level U rating, which means the evidence is conflicting or inadequate to support or refute its use for migraine prevention. The objective of our study was to assess the efficacy and safety of gabapentin in the prophylaxis of migraine in patients refractory to other prophylactic treatments. The study included 67 migraine patients, 55 women and 12 men; 52 patients completed this prospective, open-label study. This double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter study in patients with migraine (with or without aura) was conducted to determine the efficacy and safety of gabapentin in migraine prophylaxis. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used off-label to help prevent migraine attacks. Learn about why it’s used and how it works. According to the American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention (AMPP) Study, 38.8% of patients with migraine should be considered for (13.1%) or offered (25.7%) preventive migraine therapy.16 Unfortunately, the underutilization of migraine preventive medications is underscored by the fact that only 13% of all patients with migraine currently use In 2022, a trial (Head-to-Head Study of Erenumab Against Topiramate in Patients with Episodic and Chronic Migraine [HERMES]) comparing erenumab and topiramate for the prevention of migraine was published. 38 The HER-MES study was a 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted in adults (n = 777); most patients had Gabapentin (Neurontin) for prophylactic treatment of migraines and headaches, how it works, dosage, review of clinical trials on the effectiveness of gabapentin. Migraine triggers are specific to individuals. A headache diary is a helpful tool to aid patients in identifying particular triggers, monitoring the number of headache days, and documenting Gabapentin shows to have an effective therapeutic action in the prophylactic treatment of migraine. Our observations indicate that gabapentin is well tolerated by patients and that reduces headache frequency and use of symptomatic drugs in both groups. The recommendations on what information and self-care advice should be given to people with migraine are based on clinical guidelines National headache management system for adults [], Headaches in over 12s: diagnosis and management [], Primary care management of headache in adults [Becker, 2015] and Pharmacological management of migraine [], the American Headache Society updated consensus Petasites is established to be effective in migraine prevention. 64, 65 CoQ10 is possibly effective for migraine prevention, 27 while riboflavin is probably effective. 66 Percutaneous estradiol is possibly effective for migraine prevention, 67 as is a combination of soy isoflavones (60 mg), dong quai (100 mg), and black cohosh (50 mg). 67 Gabapentin is an effective prophylactic agent for patients with migraine. In addition, gabapentin appears generally well tolerated with mild to moderate somnolence and dizziness. GBP has some efficacy in migraine headache, but not sufficient evidence to suggest primary therapy. When primary headache treatments fail, a GBP trial may be considered in the individual patient. Gabapentin , Headache , Migraine , Chronic Daily Headache Objective While there are several trials that support the efficacy of various drugs for migraine prophylaxis against placebo, there is limited evidence addressing the comparative safety and efficacy of these drugs. We conducted a systematic review and network meta-analysis to facilitate comparison between drugs for migraine prophylaxis. Methods We searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, CENTRAL, and Gabapentin Gabapentin’s mode of action in migraine is unclear (66). It interacts with the α 2δ-subunit of the calcium channel and increases the concentration and probably the syn-thesis of brain γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin binds to gabapentin-binding protein—a novel, membrane-associated protein in the outer layers of the Studies were required to be prospective, controlled trials of gabapentin/gabapentin enacarbil or pregabalin taken regularly to prevent the occurrence of migraine attacks, to improve migraine‐related quality of life, or both. Two review authors independently selected studies and extracted data.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |