Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
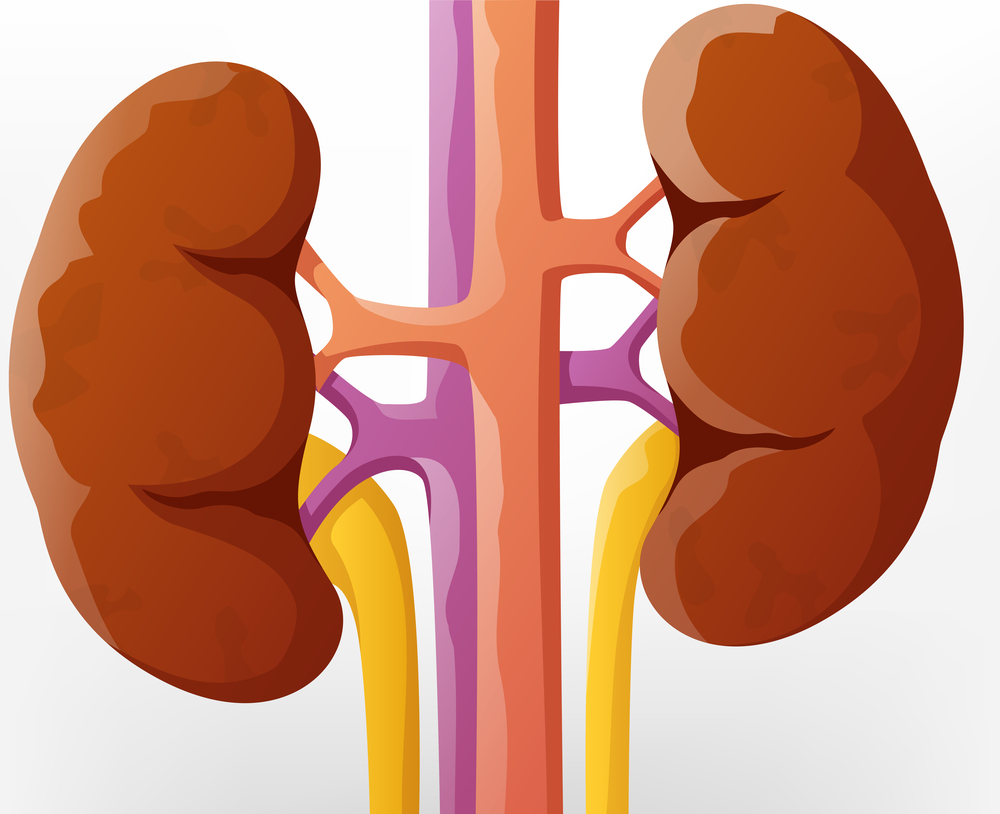
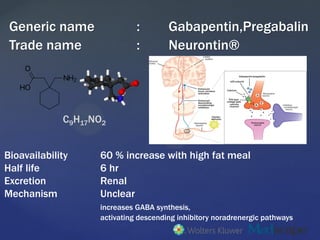
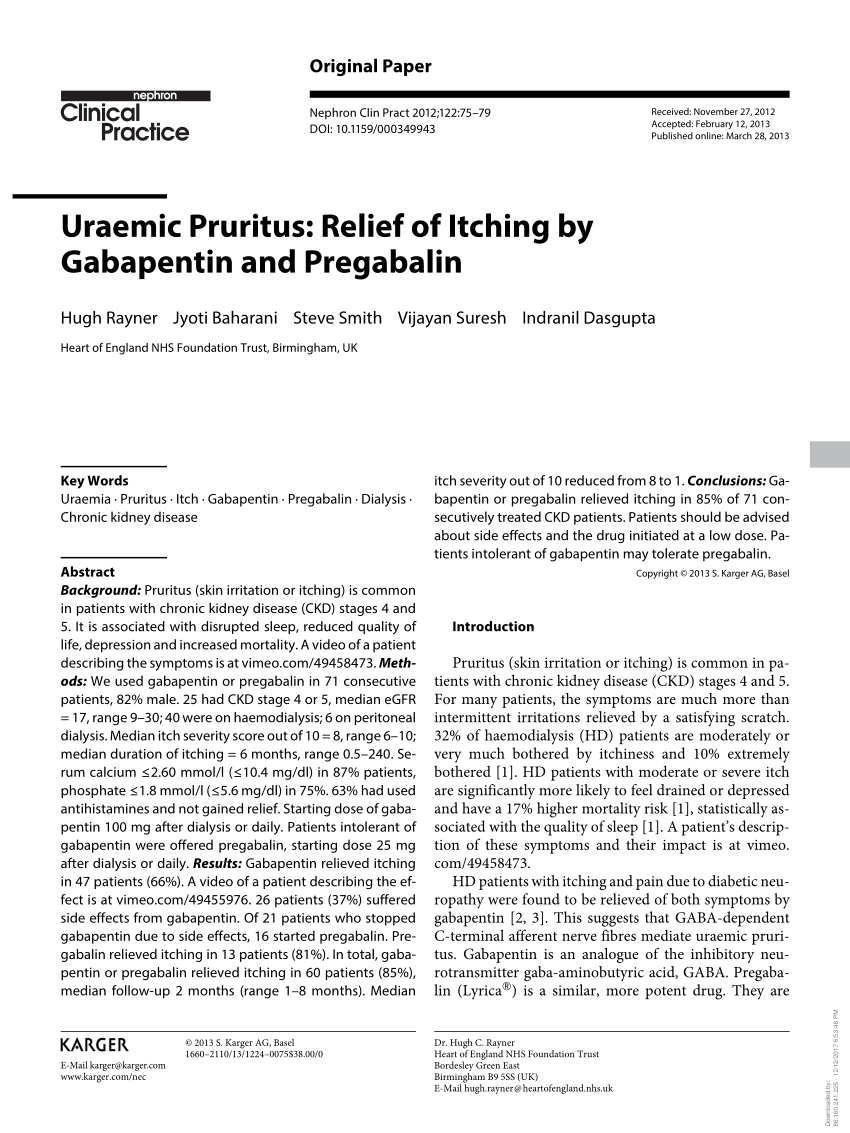
Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Patients receiving higher gabapentinoid doses with decreased kidney function may be at an increased risk of adverse effects (AEs), but limited evidence exists evaluating gabapentinoid dosing and AEs in this population. Introduction. Renal dose adjustments for gabapentin and pregabalin are ubiquitously evident in the medical literature. All manufacturers for these branded and generic dosage forms list dosing recommendations relative to creatinine clearance (CrCl) for both medications (Table 1). People with kidney disease. As gabapentinoids are predominantly excreted by the kidney, cautious starting doses and careful dose adjustments are required for people with acute or chronic kidney disease. When creatinine clearance is below 30 mL/minute, the half-lives of both gabapentin and pregabalin are prolonged. 8 Rational dosing of gabapentin and pregabalin in chronic kidney disease. Rational dosing of gabapentin and pregabalin in chronic kidney disease J Pain Res. 2017 Jan Kidney Function: If a child has kidney problems, the dose needs to be lower. Ages ≥12 years : Adjust based on creatinine clearance and weight. Dosage Adjustment : Lower doses required; consult a paediatric specialist. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used for neuropathic pain in CKD patients but are not fully understood as this population remains excluded from efficacy and safety trials. Renal adjustments for the gabapentinoids are prodigiously recommended in the literature. Rational dosing of gabapentin and pregabalin in chronic kidney disease normal renal function on maximum recommended dosing yielded concentrations of 5–8 mg/L for gabapentin and ~ 2.8–8.2 mg/L for pregabalin. 22–25 The elimination half-lives of gabapentin and pregabalin are prolonged with renal impairment leading up to accumulation with Gabapentin and pregabalin are often used in patients with CKD primarily to treat neuropathic pain and restless leg syndrome and given the high prevalence of diabetes in this population, the proportion who receive these drugs is very high. In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. With a growing chronic kidney disease epidemic,22, 23 an increasing number of patients with chronic kidney disease will be exposed to gabapentin. This study demonstrates that gabapentin dosage for patients with chronic kidney disease has been insufficiently adjusted and that the risk of gabapentin toxicity has been underrecognized. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Furthermore, the impact of gabapentin accumulation can be particularly pronounced in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD), where kidney function is severely impaired or virtually absent. Dialysis may help to some extent, but it often doesn’t clear gabapentin as effectively as healthy kidneys. Rationale & Objective: Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kid-neys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Use of gabapentinoids outside of the approved indications is common, but evidence for this is limited, especially for chronic nonspecific back pain and nonradicular leg pain. Some effects of gabapentinoids encourage their nonmedical use (e.g. euphoria, sedation, disinhibition). Here’s a scenario of using gabapentin in chronic kidney disease. A 42 year old African American man with a history of coronary artery disease and decompensated heart failure s/p heart transplant and chronic kidney disease presented to a hospital on 9/29/16 complaining of shortness of breath, dyspnea upon exertion and LE edema. In patients with stable renal function, creatinine clearance can be reasonably well estimated using the equation of Cockcroft and Gault. The use of gabapentin capsules in patients less than 12 years of age with compromised renal function has not been studied. Pharmacology. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used first-line agents for diabetic peripheral neuropathy and other common neuropathies. Pharmacologically, both agents inhibit alpha-2-delta (α2δ) subunit of N-type voltage-gated calcium channels, a key receptor involved in regulating the excitability of neurons. 3 Peripheral nerve injury results in the upregulation of α2δ-1 receptors Discussion: Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |