Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
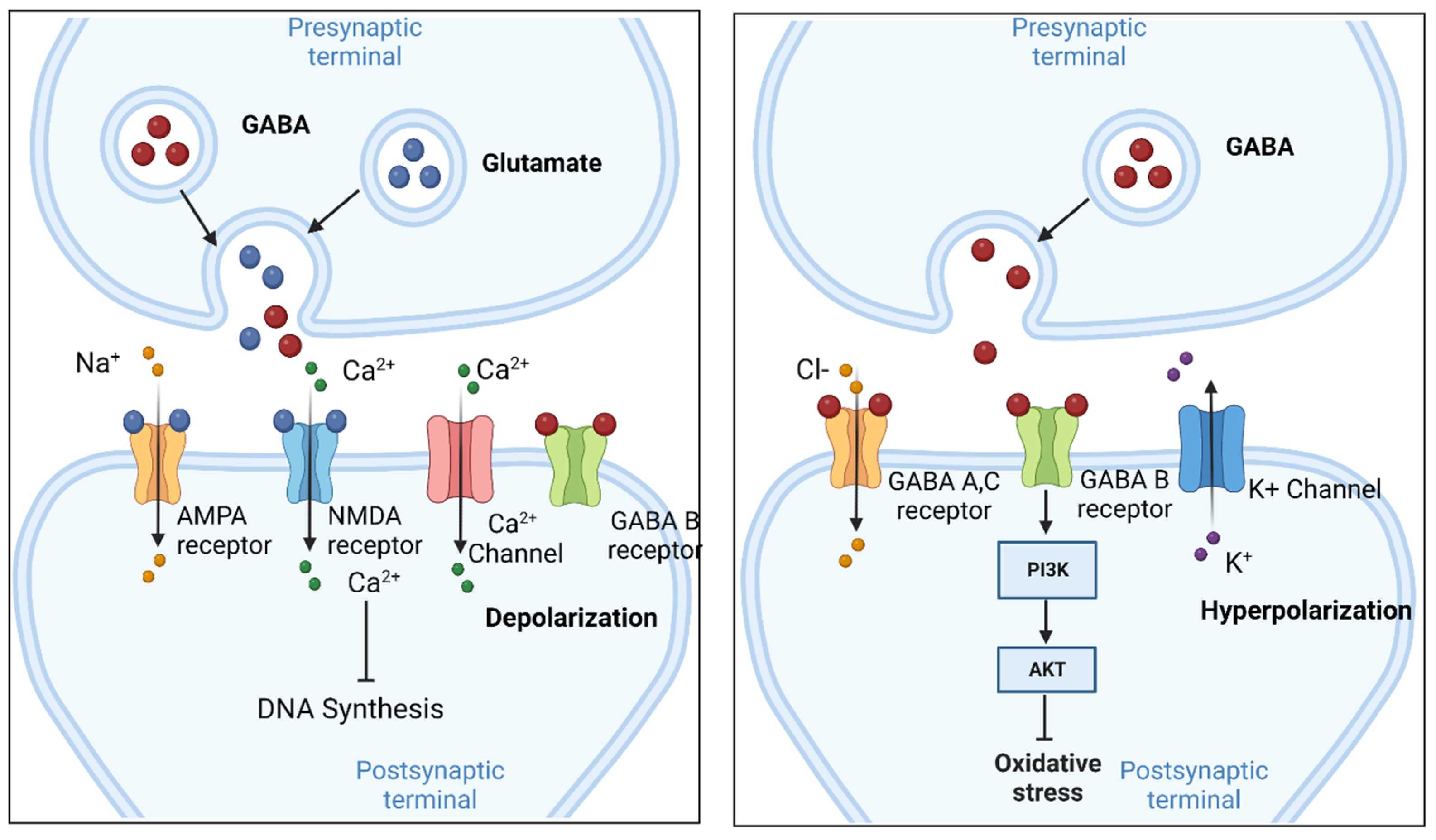
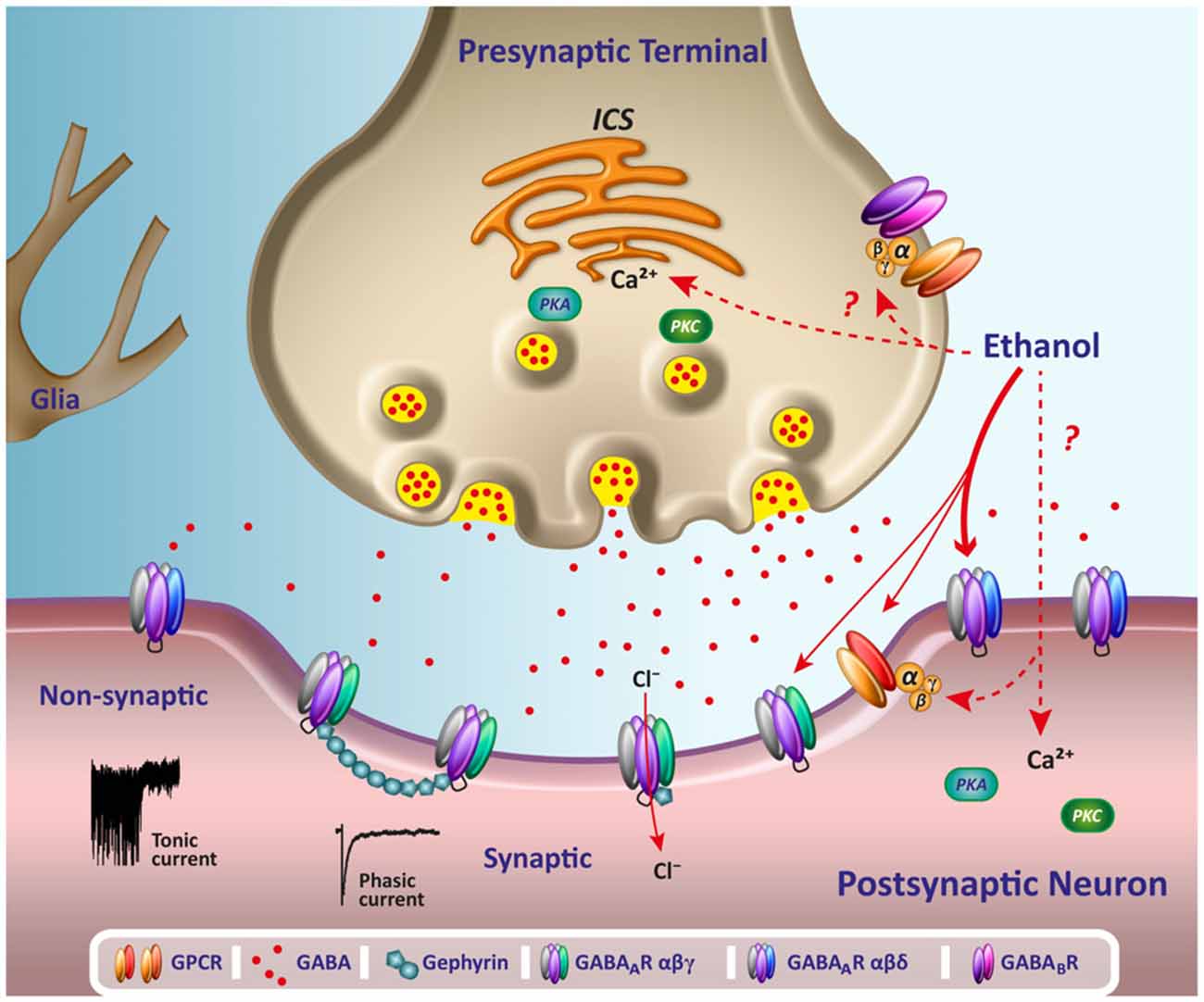
Gabapentin enhanced expression of δGABA A receptors and increased a tonic inhibitory conductance in neurons. This increased expression likely contributes to GABAergic effects as gabapentin caused ataxia and anxiolysis in wild-type mice but not δ subunit null-mutant mice. In human and rat studies, gabapentin was found to increase GABA biosynthesis, and to increase non-synaptic GABA neurotransmission in vitro. As the GABA system is the most prolific inhibitory receptor set within the brain, its increase in biosynthesis results in the sedating and anxiolytic (or calming effects) of gabapentin on the nervous system. While gabapentin was designed as a GABA analogue, its GABA-like properties are not as straightforward as initially believed. The drug does not directly bind to GABA receptors or increase GABA levels in the brain. However, it may indirectly enhance GABAergic neurotransmission through its effects on calcium channels and other neuronal processes. Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABA A) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. Although GABA concentration changes were small both within day (average 5.6%) and between day (average 4.8%), gabapentin administration was associated with an average increase in GABA GABA was elevated in patients taking gabapentin compared with 14 complex partial epilepsy patients, matched for antiepileptic drug treatment. Brain GABA levels appeared to be higher in patients taking high-dose gabapentin (3,300-3,600 mg/day) than in those taking standard doses (1,200-2,400 mg/day). A dose of 2000 mg or more of glutamine a day when taken on an empty stomach with vitamin B6 (2mg or more), will increase your natural level of GABA and probably reduce your pain levels. Pure GABA is available as a tablet, capsule or in sublingual (under-the tongue) form in most health food stores or online. Foods and Supplements to Increase GABA . You may be able to increase the production of GABA by increasing glutamate, since your body uses glutamate to produce GABA. To increase glutamate production, it may help to add precursors of glutamate (the things your body uses to make it) to your diet or supplement regimen. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter found in the central nervous system (CNS) that regulates its excitability. Gabapentin functions by modulating enzymes involved in GABA synthesis. It differs in chemical structure from GABA and its half-life is much longer (McLean, 1994). One MRS study in humans has found that the administration of gabapentin increased brain GABA levels by 55.7% (Cai et al., 2012). Treatment of mice with gabapentin resulted in an increase in surface, but not total, expression in cerebellum and hippocampus. There was no change in expression of α1- or α5-subunits. Treatment of mice with gabapentin did not increase GABA, taurine, or alanine levels, or neurosteroids in the brain. Daily GBP therapy increased GABA (0.5 mM; 95% CI, 0.2-0.9), homocarnosine (0.3 mM; 95% CI, 0.2-0.4), and pyrrolidinone (0.10 mM; 95% CI, 0.06-0.14). Rechallenging patients taking GBP daily increased median brain GABA by 0.4 mM (range, 0.3-0.5) within 1 h. Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABA A) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. Sprouting grains, seeds, and legumes may increase GABA content. Some studies suggest that the germination process can lead to an accumulation of GABA in sprouted products. It's important to note that the GABA content in food can be influenced by factors such as processing, cooking methods, and the specific cultivar or variety of the food. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Gabapentin increased GABA turnover in 11 out of 12 brain regions tested, but the temporal effect of the drug varied from region to region (Loscher et al, 1991).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |