Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
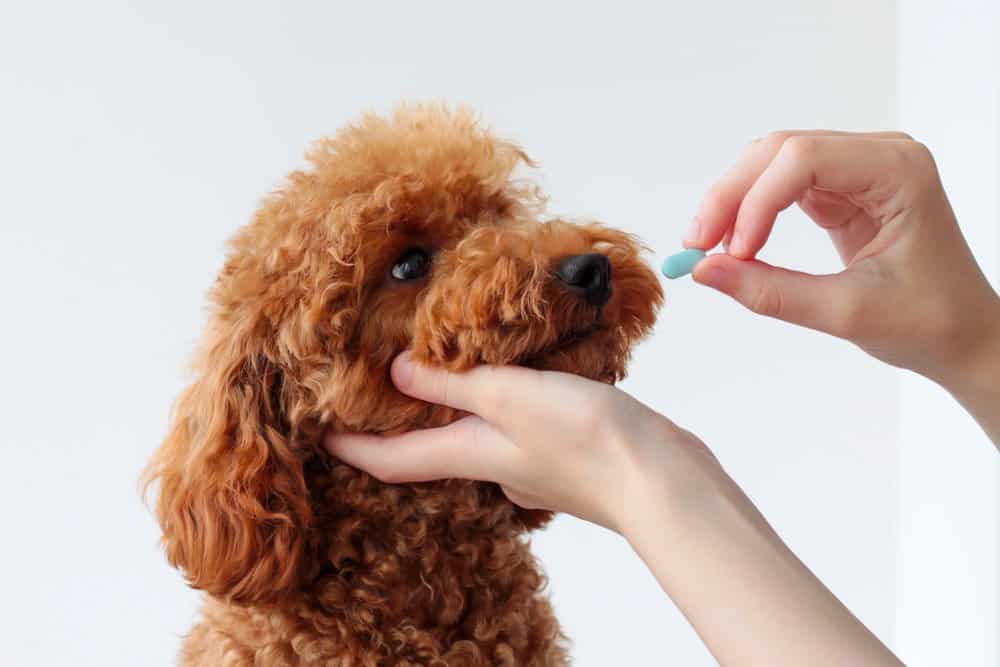
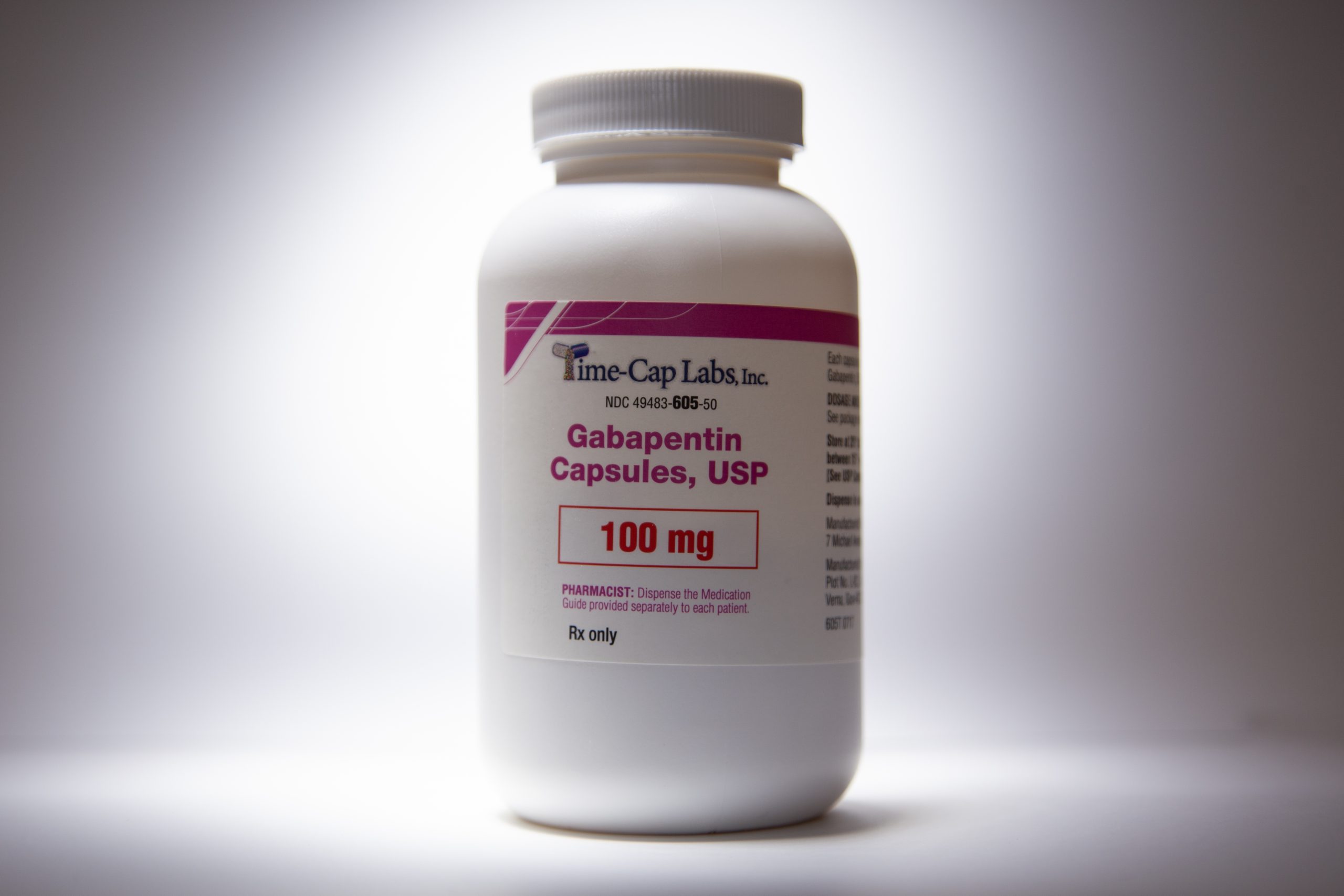
This article will give you a vet’s guide for administering a specific medication, called Gabapentin*, that is used to treat chronic or neuropathic (peripheral or central nerve) pain in dogs, as well as seizures. Gabapentin can treat and reduce the frequency of seizures and is commonly used as an anticonvulsant to treat or prevent seizures in dogs. Gabapentin may also be used to provide pain relief for dogs, particularly when other medications have proved ineffective or are not well tolerated. Whatever oral medication that you would want to use, that may be gabapentin that may be tramadol, anything that you would want to treat these [with]. We also want to treat the inflammation that's inside the eye. Because these things can get worse from a pain perspective, just from the inflammation and the uveitis that's inside the eye. For this reason, always wean your dog off gabapentin gradually. VETERINARY FAN Odin was prescribed gabapentin as an adjunct to a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) to treat pain from a chronic eye condition. After the problematic eye was removed, gabapentin was given post-surgically and then tapered off. As you can probably tell, I am Gabapentin is extremely safe for dogs, and it has the potential to alleviate pain for our dogs and improve their quality and enjoyment of life. If you’ve been wondering why so many veterinarians are prescribing this medication more and more, there’s your answer. Gabapentin dosage in dogs varies depending on the specific condition being treated. Anticonvulsant: Every eight hours, give your dog 4.5 to 9 mg per pound of weight. Neuropathy: Initially, administer 2.3 to 6.8 mg per pound every 12 hours. 8. Can Gabapentin be used to manage pain in dogs with arthritis? Yes, Gabapentin can be used to manage pain in dogs with arthritis. It can help alleviate discomfort and improve your pet's quality of life. However, it is important to work closely with your veterinarian to determine the appropriate dosage for your dog. 9. Gabapentin for dogs is commonly prescribed for pain, anxiety, or seizures. It's generally safe, but there are some known side effects to be aware of. Vets use gabapentin in dogs to treat a number of conditions, including situational anxiety, chronic pain, and (less commonly) seizures or muscle tremors. This medication is very affordable and low in side effects, making it a low-risk option for many dogs. Gabapentin is commonly prescribed for dogs with chronic pain from conditions like osteoarthritis, spondylosis, intervertebral disc disease, and many more. It’s particularly effective when used in combination with other pain-relievers, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications like meloxicam, firocoxib, and carprofen. Gabapentin works best for managing neuropathic pain – pain that stems from issues like extruded discs and nerve injuries. It is also very efficient in managing joint pain and postoperative pain. When used together with NSAIDs and opioids, it boosts their efficacy and allows lowering their doses. As gabapentin appears to be useful drug in attenuation of increased IOP associated with intubation, its administration can be reliably advised when performing ocular procedures in dogs with deep ulcer or laceration in which increased IOP may result in ocular complications, such as perforation of the globe. Can gabapentin help dog with eye pain? Gabapentin is a commonly prescribed medication for dogs dealing with chronic pain, seizures, or anxiety. However, understanding the right dosage and how to use it safely can be challenging for pet owners. Gabapentin is commonly prescribed to dogs for pain management, particularly for conditions like arthritis, neuropathic pain, or to control seizures. While it’s an effective treatment for many dogs, it’s essential to understand the potential side effects that may occur, especially with long-term use. In this guide, we’ll explore the most common side effects, how to manage them, and what Veterinarians commonly prescribe gabapentin to treat pain, seizures, and anxiety in dogs. Gabapentin is a human medication, and its use in veterinary medicine is “off-label,” meaning it is not FDA-approved for pets. Side effects of stopping gabapentin in dogs. It is important to note that if your vet does want to take your dog off gabapentin, he or she may recommend gradually decreasing the dose rather than stopping cold turkey. Rapidly stopping gabapentin can cause increased seizure activity if your dog is taking gabapentin as an anti-seizure medication.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |