Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
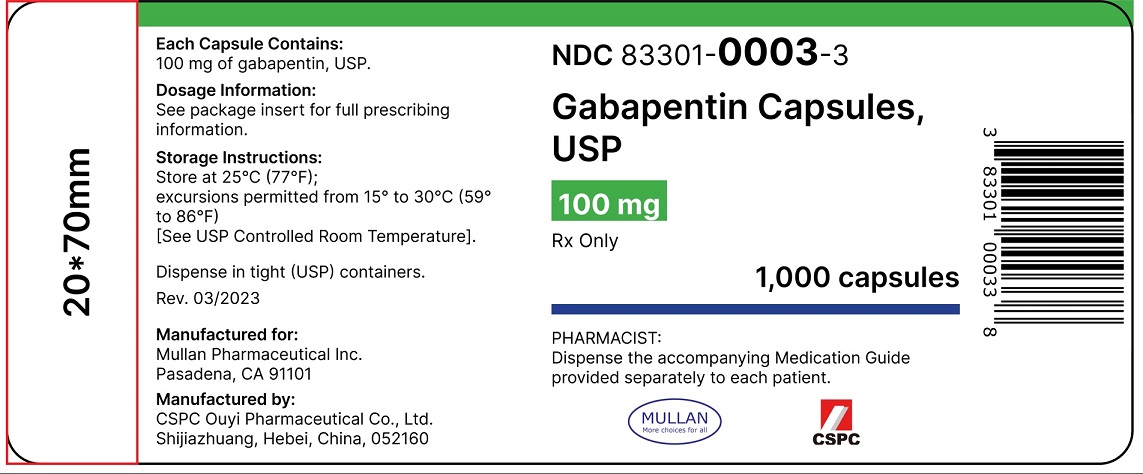
Neurontin was evaluated for the management of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) in 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter studies; N=563 patients in the intent-to-treat (ITT) FDA-Approved Indications. Gabapentin: Gabapentin is indicated for postherpetic neuralgia and serves as adjunctive therapy for managing partial seizures (with or without secondary generalization) in adults and pediatric patients aged 3 or older. 1. Indications and Usage for Gabapentin. Gabapentin is indicated for: • Management of postherpetic neuralgia in adults • Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures, with and without secondary generalization, in adults and pediatric patients 3 years and older with epilepsy ----- INDICATIONS AND USAGE-----gabapentin products because of differing pharmacokinetic profil with the evening meal. GRALISE alternative medication, this should be done gradually over a mi function. GRALISE should not be us hypersensitivity to the drug ----- RECENT MAJOR CHANGES----- Indication. In the United States, gabapentin is officially indicated for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia in adults and for the adjunctive treatment of partial-onset seizures, with or without secondary generalization, in patients 3 years of age and older. 16 In Europe, gabapentin is indicated for adjunctive therapy in the treatment of Gabapentin is FDA-approved as Neurontin to treat partial seizures in adults and children with epilepsy. Partial seizures are convulsions that originate from a single location in the brain. Neurontin is also approved to treat a type of nerve pain called postherpetic neuralgia, or PHN. During the controlled epilepsy trials in patients older than 12 years of age receiving doses of gabapentin up to 1,800 mg daily, somnolence, dizziness, and ataxia were reported at a greater rate in patients receiving gabapentin compared to placebo: i.e., 19% in drug versus 9% in placebo for somnolence, 17% in drug versus 7% in placebo for Elimination: Gabapentin is eliminated from the systemic circulation by renal excretion as unchanged drug. Gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Gabapentin elimination half-life is 5 to 7 hours and is unaltered by dose or following multiple dosing. Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal hypersensitivity to the drug HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION . These highlights do not include all the information needed to use GRALISE safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for GRALISE. GRALISE™ (gabapentin) tablets Initial U.S. Approval: 1993 -----INDICATIONS AND USAGE ----- This label may not be the latest approved by FDA. For current labeling information, please visit particular, gabapentin prevents pain-related responses in Table 1: FDA-Approved Indications for Pregabalin and Gabapentin: Indications. Pregabalin. Gabapentin. Neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. x. Gabapentin is a prescription medication approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of neuropathic pain and epileptic disorders. This drug is currently marketed in capsule, tablet, and oral solution formulations. In recent years, however, gabapentin has been increasingly encountered by law enforcement, The authors concluded that gabapentin is associated with reduction in acute pain associated with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy (the later indication is not approved by the FDA), and that there is limited evidence to support the use of gabapentin for other types of neuropathic pain and pain disorders. 1 This Editorial During the controlled epilepsy trials in patients older than 12 years of age receiving doses of gabapentin up to 1800 mg daily, somnolence, dizziness, and ataxia were reported at a greater rate in patients receiving gabapentin compared to placebo: i.e., 19% in drug versus 9% in placebo for somnolence, 17% in drug versus 7% in placebo for -----INDICATIONS AND USAGE----- NEURONTIN is indicated for: •Postherpetic neuralgia in adults (1) •Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures, with and without secondary Gabapentin tablets are indicated for: In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). Different brands of gabapentin are not interchangeable and they are FDA approved for different conditions. Use only the brand and form of gabapentin your doctor has prescribed. Check your medicine each time you get a refill to make sure you receive the correct form. 2.3 Dosage Adjustment in Patients with Renal Impairment Dosage adjustment in patients 12 years of age and older with renal impairment or undergoing hemodialysis is recommended, as follows (see dosing recommendations above for effective doses in each indication): TABLE 1. NEURONTIN Dosage Based on Renal Function Renal Function Total Daily 5.6 Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)/Multiorgan Hypersensitivity . 5.7 Discontinuation of HORIZANT 5.8 Tumorigenic Potential . 6 ADVERSE REACTIONS . 6.1 Clinical Trials Experience 6.2 Adverse Events Associated With Gabapentin . 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS . 8.1 Pregnancy 8.2 Labor and Delivery 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE . NEURONTIN ® is indicated for: Management of postherpetic neuralgia in adults Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures, with and without secondary . generalization, in adults and pediatric patients 3 years and older with epilepsy . 2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION . 2.1 Dosage for Postherpetic Neuralgia
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |