Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 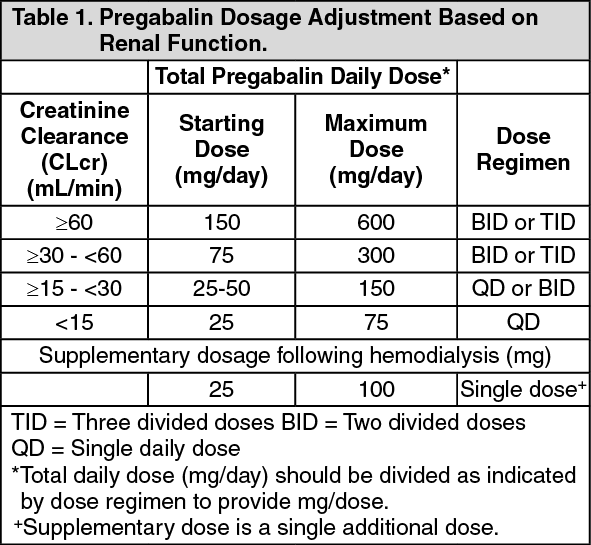 |
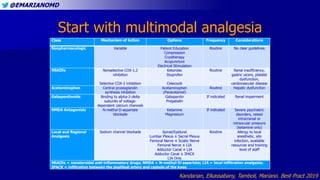
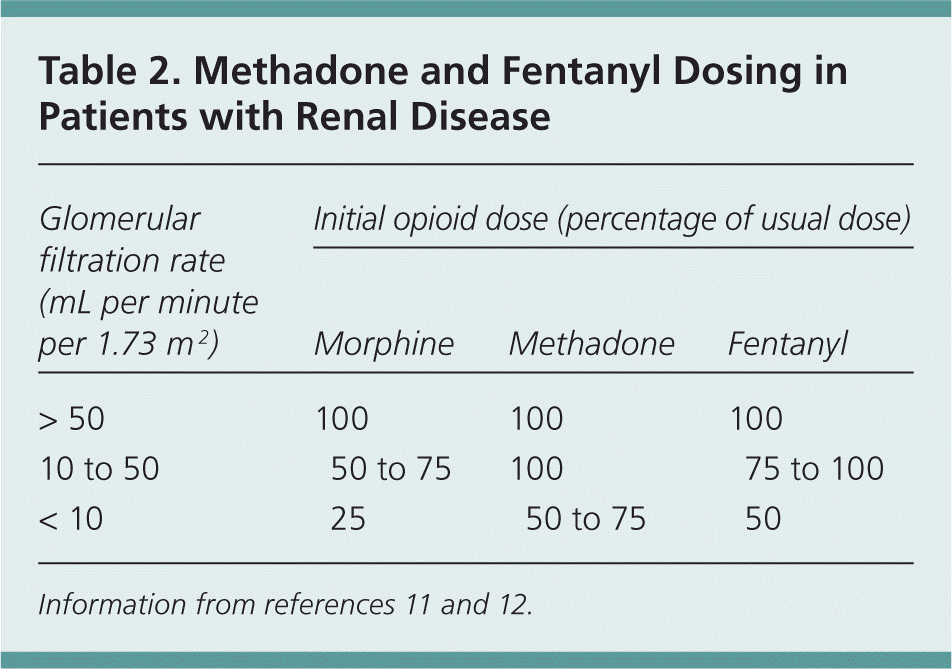
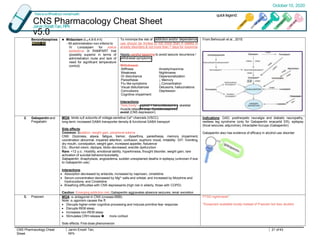
Therapeutic dosing targets of both medications have been established in clinical trials for neuropathic pain (gabapentin 1800–3600 mg/day; pregabalin 150–600 mg/day). However, patients with renal impairment were often excluded from these studies. Dosage adjustment in patients 12 years of age and older with renal impairment or undergoing hemodialysis is recommended, as follows (see dosing recommendations above for effective doses in each indication): Gabapentin was first conceptualised in the early 1970s during efforts to discover drugs for treating neurological disorders. 7 Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) was known to be a key inhibitory neurotransmitter, whose inhibition could cause seizures. Challenges in pain management in patients with kidney disease. Pain assessment. This should start with assessment of a) pain severity using various standardized tools, most common of which is the numerical rating scale []; b) pathophysiologic evaluatio n into mechanism of injury and type of pain; c) psychosocial evaluation of co-occurring factors that contribute to pain or make treatment of Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Gabapentin is eliminated in urine unmetabolized at a rate proportional to creatinine clearance. 24 In patients with renal impairment, with unaltered gastrointestinal absorption, gabapentin half-life can be prolonged up to 132 hours (without dialysis), 30 placing patients with chronic kidney disease at an increased risk for toxicity. Pain is one of the most common and distressing symptoms among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) . The prevalence of pain has been associated with substantially lower health-related quality of life and greater psychosocial distress, insomnia, and depressive symptoms [ 2-9 ]. The half-life of gabapentin immediate-release formulation is 5–7 hours in patients with normal renal function and is prolonged up to 52 hours in patients with CrCl<30 mL/min. 26 The half-life of pregabalin is 16.7 hours in patients with CrCl 30–59 mL/min, 25 hours in patients with CrCl 15–29 mL/min, and 48.7 hours in patients with CrCl<15 This study addresses specified outcomes in patients taking gabapentinoids with impaired kidney function compared to patients with normal kidney function. Minimal exclusion criteria allowed for the inclusion of patients with a wide range of CrCl and gabapentinoid dosing. Take 900-1200 gabapentin daily over past 20 years. Experiencing severe side effects of gabapentin that Im beginning to think correlate with decreased kidney function. It’s becoming cyclic. Take normal dose of gabapentin until start to become confused and lethargic. Taper gabapentin and start to return to normal. Renal impairment (Neurontin) CrCl >60 mL/min: 300-1200 mg PO TID; Renal impairment: Gabapentin dose reduction may be required, depending on renal function. Kidney Function: If a child has kidney problems, the dose needs to be lower. Ages ≥12 years : Adjust based on creatinine clearance and weight. Dosage Adjustment : Lower doses required; consult a paediatric specialist. Rational dosing of gabapentin and pregabalin in chronic kidney disease normal renal function on maximum recommended dosing yielded concentrations of 5–8 mg/L for gabapentin and ~ 2.8–8.2 mg/L for pregabalin. 22–25 The elimination half-lives of gabapentin and pregabalin are prolonged with renal impairment leading up to accumulation with Loading dose of 300–400 mg in patients who have never received gabapentin. Maintenance dose of 100–300 mg after each HD : session and increase according to tolerability. Gabapentin Dosage Guidelines in Adults, Adolescents 12 Years of Age and Older with Renal Impairment 1-5. Doses often need to be reduced in renal impairment to prevent accumulation and toxicity. Examples of drugs that should be reduced in renal impairment are the gabapentinoids: gabapentin and pregabalin. Table 1 shows maximum recommended dose of gabapentin in renal impairment: Table 2 shows the maximum recommended dose of pregabalin in renal
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |