Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
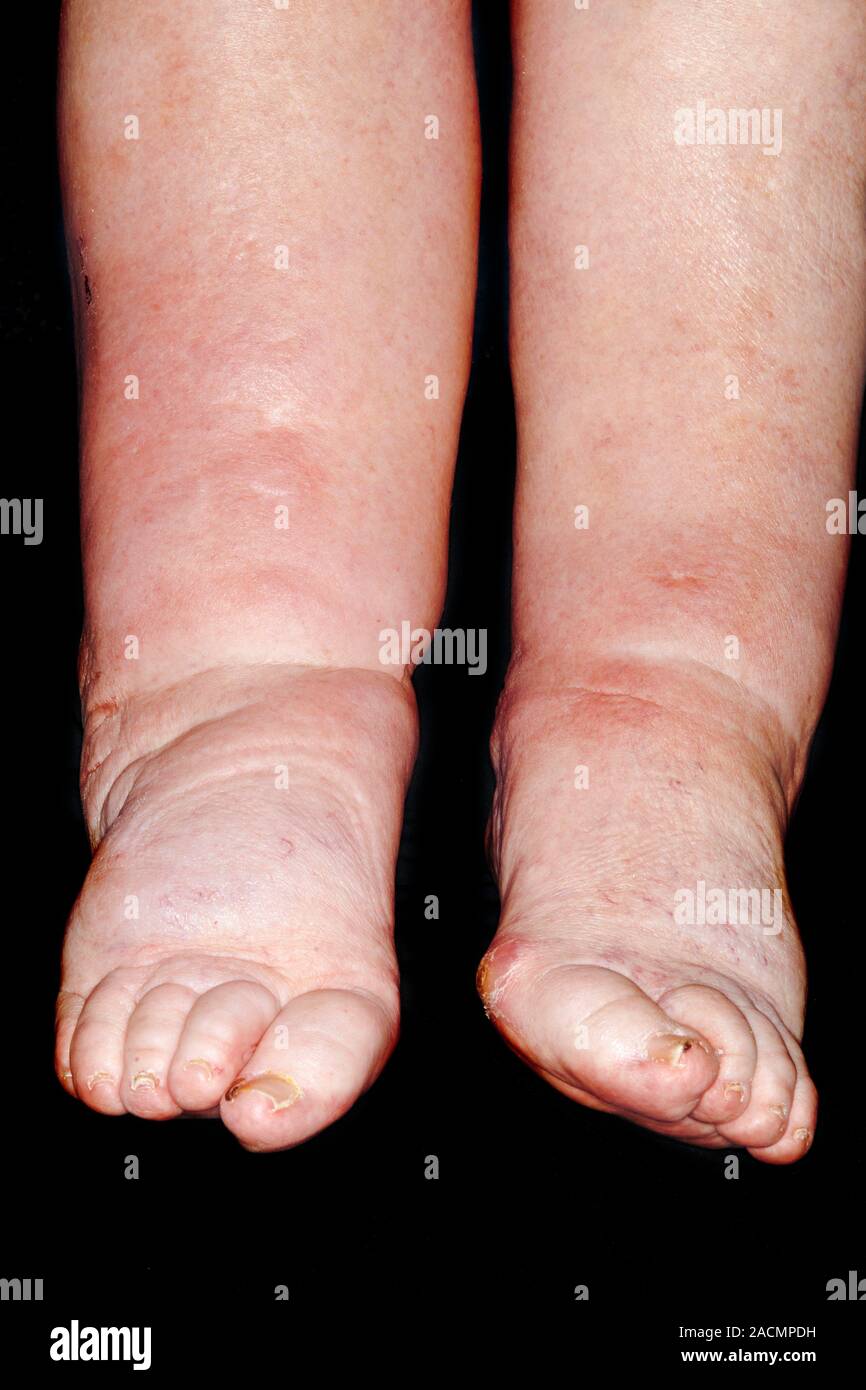
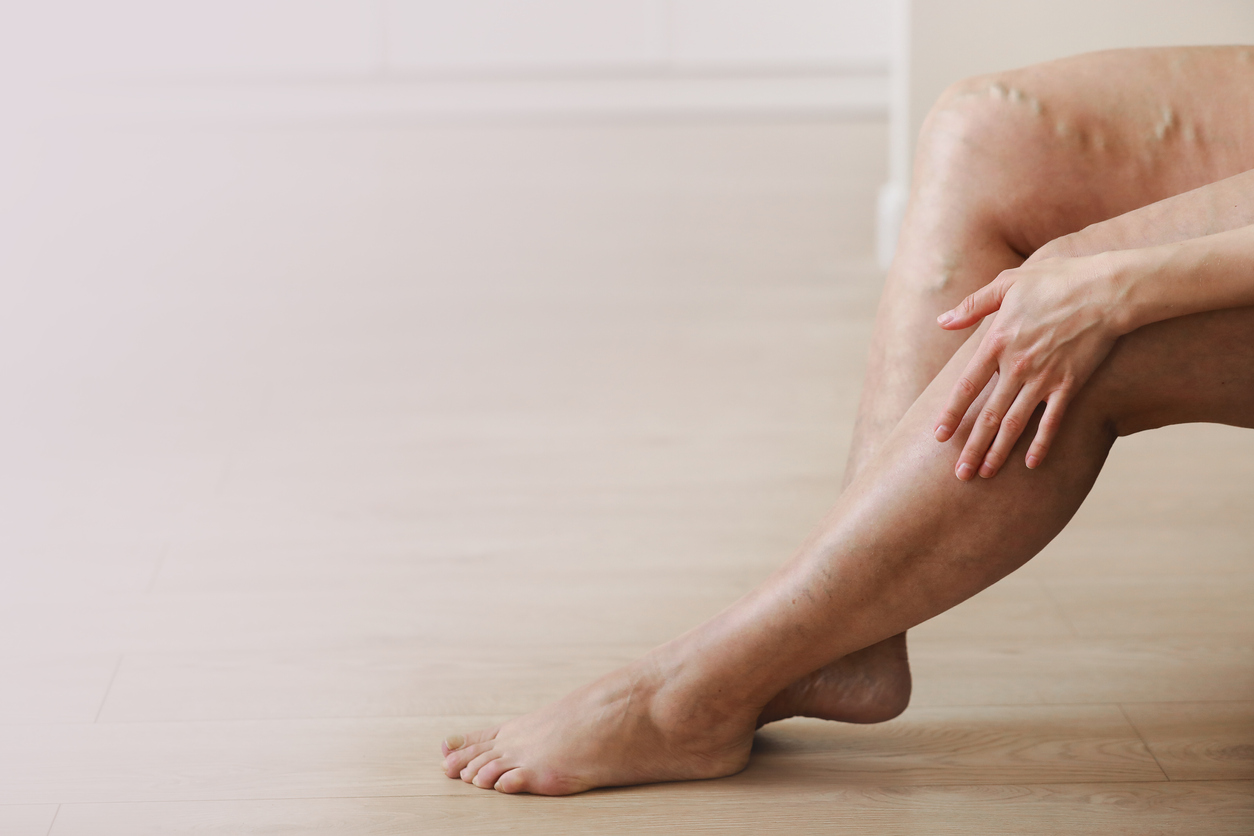
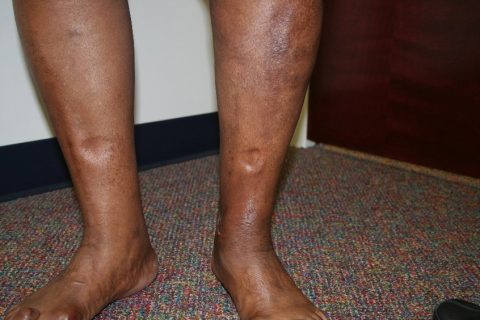
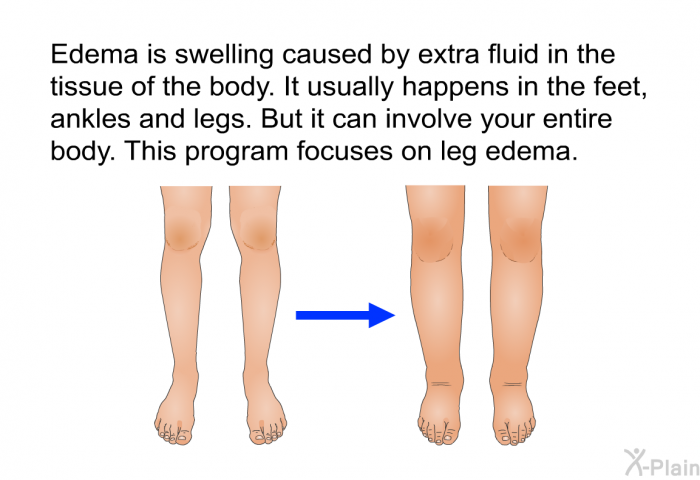
Furthermore, experimental data have shown an indirect inhibitory effect of gabapentinoids (ie, gabapentin, pregabalin) on the Cav1.2 channel pore of arterial myocytes, leading to vasodilatory effects and inhibition of the myogenic tone. 96-98 These data suggest that gabapentinoid-related peripheral edema 94, 95 may exhibit the same This is a case of painful, 4+ pitting bilateral edema with a probable association to gabapentin (Naranjo score 5) and a clear dose relationship in a patient with pervasive developmental disorder and schizoaffective disorder utilizing gabapentin for mood stabilization. Similarly, the incidence of peripheral edema caused by CCB is dose related and common in the elderly, comparable to reports of gabapentin induced edema. This case illustrates that gabapentin induced leg swelling can confound the clinical picture and it is thus important to recognize this side effect of gabapentin. Swelling in the feet and ankles. Patients taking Neurontin may experience swelling in the feet and ankles. The presence of lower leg swelling may cause discomfort and impair walking. My mother-in-law was unable to wear regular shoes because of swelling of her feet and ankles, so we found her socks and soft slippers that fit her feet comfortably. Fluid retention, or edema, can occur when gabapentin affects vascular permeability or alters kidney function. Edema refers to swelling caused by excess fluid accumulation in tissues. It can occur in various parts of the body but is most commonly seen in the legs, ankles, and feet. Edema is a well-described side effect of gabapentinoid drugs (i.e., gabapentin and pregabalin). In this study from Ontario, Canada, researchers used provincial databases to examine whether gabapentinoid use was followed by diuretic prescriptions — a so-called “prescribing cascade” in which a drug is prescribed to treat an adverse effect of another drug. Gabapentin binds to the alpha-2-delta subunit of presynaptic voltage-gated calcium channels and is used for a wide variety of on- and off-label indications. Gabapentin is dosed at total daily doses ranging from 300 to 3600 mg/d, which is generally divided into 3 doses. Although gabapentin is general I take 600 mg of gabapentin, 300 mg twice daily. No swelling in my feet. I still get some cramping and stabbing. I hope everything is going well with others. diabetic neuropathy, which is associated with multiple co-morbidities that can give rise to bilateral leg swelling. Presence of gabapentin induced leg swelling can thus confound the clinical picture. Key words: Gabapentinoids can cause concentration-dependent peripheral edema of early onset. Reduced myogenic tone is the main mechanism of these non-cardiogenic edemas. In case of peripheral edema or heart failure, a drug etiology should be considered. The Edema is in her hands and feet and when they swell it’s very painful but not pitting. Has anyone heard of this? We have seen several doctors and they are just shake their heads and say it’ll probably go away. The authors reported bilateral pretibial edema after 3 weeks of gabapentin 300 mg/d for neuropathic pain. Within 3 days of discontinuation of gabapentin, the edema resolved. When the patient was rechallenged with gabapentin, the edema returned after 5 days, suggesting the authors' suspicions of an adverse effect from gabapentin was likely correct. He noticed significant leg swelling almost immediately upon starting treatment; this persisted for nearly three weeks before gradually improving after his doctor reduced his dosage. These cases highlight how individual responses vary widely based on dosage levels and personal health backgrounds while using gabapentin. Gabapentin is a common medication-related cause of peripheral edema. This is when you experience swollen tissues in the body, often in the arms and legs. Up to 8% of people report edema with gabapentin clinical studies. But it’s more likely to occur in older adults. This is clinically important as gabapentin is a very commonly prescribed medication to patients with neuropathies, especially in diabetic neuropathy who may also have other co-morbid condition such as heart failure, malnutrition, nephropathy, that can give rise to bilateral leg swelling. Managing gabapentin-induced edema requires a multi-faceted approach, considering both lifestyle modifications and potential medication adjustments. Our article will provide practical tips and strategies that can help alleviate and manage the swelling effectively. Sorry to say, but my swelling lead to weight gain.I was prescribed Gabapentin for nerve pain. I started at 200 mgs once daily at bedtime. I couldn't stay on it for longer than two weeks. Amlodipine (Norvasc), gabapentin (Neurontin, Horizant, Gralise), and pregabalin (Lyrica) can cause puffy legs and ankles. Birth control pills, certain over-the-counter pain medications, and steroids are a few other culprits. Leg edema might be occurred in systemic and local types. Systemic edema could be caused by congestive cardiac failure, renal failure, hypoalbuminemia, protein losing neuropathy. For localized edema we can note following reasons such as primary and secondary lymphedema, lipedema, deep vein thrombosis and chronic venous disease.[ 13 , 14 ]
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |