Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
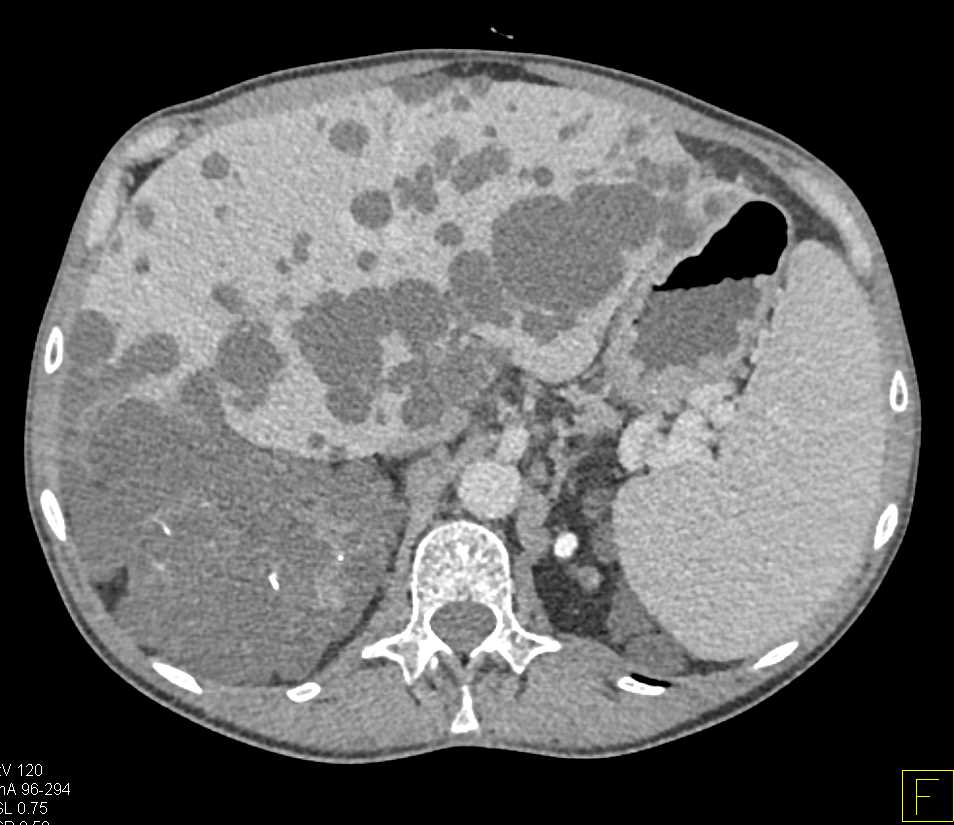
Changes in liver function may be attributed to free radical damage induced by gabapentin, as documented in this study, where the drug enhanced antioxidant defense systems and elevated liver NO Gabapentin and Cirrhosis of the Liver - Fatty Liver Disease Gabapentin (GPN) is a new antiepileptic agent currently in used as add-on therapy in adult patients suffering from partial seizures. The extent of liver damage at different dosage and long term treatment with GPN is not yet clear. Gabapentin (Neurontin) usually isn’t bad for your liver or kidneys. In most cases, it has little effect on these organs. In rare instances, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome. Rare cases of liver and kidney damage have been reported with Gabapentin use. Individuals with pre-existing liver or kidney conditions may be at a higher risk. Regular monitoring of liver and kidney function is essential while taking Gabapentin. Gabapentin enacarbil and gabapentin are associated with a low rate of transient serum enzyme elevations during treatment and with rare instances of clinically apparent liver injury. Gabapentin enacarbil (gab" a pen' tin) enacarbil (en" a kar' bil) is a prodrug of and long acting form of gabapentin. We study 323,232 people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin) or have Elevated liver enzymes. No report of Elevated liver enzymes is found in people who take Gabapentin. The phase IV clinical study is created by eHealthMe based on reports from the FDA, and is updated regularly. Gabapentin was held and patient’s liver function tests improved, with ALP 1058 IU/L, AST 158 IU/L, and ALT 149 IU/L, and remained stable. Patient discontinued gabapentin and was advised to follow up outpatient, unfortunately he was lost to follow-up. Gapentin has no appreciable liver metabolism, but suspected cases of gabapentin-induced hepatotoxicity have been reported. Even high doses of gabapentin (400mg/kg) for 30 days do not produce deleterious adverse effects on the liver or haematological parameters. Gabapentin is an uncommon cause of DILI reported to cause a hepatocellular, cholestatic, or mixed picture of liver injury. Given the limitations of prior cases, we feel our report most closely ties gabapentin use to the resultant transaminase elevation. Gabapentin induced cholestasis was thought likely and the drug was stopped. After this, clinical symptoms and liver function tests improved gradually (figure). A liver biopsy showed normal liver architecture with evidence of portal tract expansion by a chronic inflammatory cell infiltrate that incorporated eosinophils and neutrophils. Other AEDs with rising and currently highest prescription rates were associated with few or no cases of liver injury including gabapentin (45.3 million), clonazepam (18.8 million), pregabalin (10.6 million), topiramate (9.3 million), and levetiracetam (7.7 million) and many of cases were judged as only “probable”. When it comes to gabapentin and kidney disease, kidney disease sufferers should be aware of the risks that are involved in taking gabapentin with kidney disease. Gabapentin is actually toxic to the kidneys. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Our previous and several other studies shows that long term treatment with old or new anti epileptic drugs affect liver function from transient state to a fatal liver damage (1,8-10). But when considered GPN such an effect is quite less and no report of death or fatal liver damage. Gabapentin is a unique anticonvulsant that is used as adjunctive therapy in management of epilepsy and for neuropathic pain syndromes. Therapy with gabapentin is not associated with serum aminotransferase elevations, but several cases of clinically apparent liver injury from gabapentin have been reported. Gabapentin affects nerves and chemicals in your body that are involved in some types of pain and in seizures. There is insufficient data to estimate incidence for these or establish whether gabapentin is the sole cause of elevated liver function tests, notes Pfizer. Liver enzymes are proteins your liver uses for normal liver functions. When your liver is damaged, these enzymes leak out into your blood and can be measured with blood testing called liver function testing. There are several liver enzymes, but the ones that show liver damage from medications are aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine Herein, we report a gabapentin-induced hepatocellular injury in a patient without another identifiable cause for acute liver injury. Discontinuing gabapentin resulted in rapid reversal improvement in hepatocellular injury. Question. I have a patient with trigeminal neuralgia who was taking 1600 mg of gabapentin and had serious elevations of liver function tests (aspartate transaminase 258 U/L, alanine transaminase
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |