Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
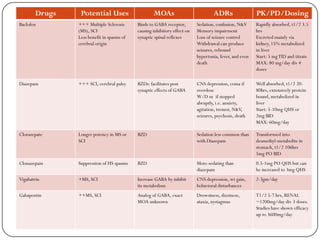
Gabapentin enacarbil and gabapentin are associated with a low rate of transient serum enzyme elevations during treatment and with rare instances of clinically apparent liver injury. Gabapentin enacarbil is a long acting form of gabapentin that is used for restless leg syndrome and for painful postherpetic neuropathy. Gabapentin therapy is not associated with serum aminotransferase elevations, but several cases of clinically apparent liver injury have been reported. Gabapentin is not metabolized by the liver and is excreted unchanged in the kidneys after circulating in the blood. It affects nerves and chemicals involved in pain and seizures. Several studies demonstrated that chronic treatment with gabapentin may alter liver and renal homeostasis As no surrogate parameter is available to predict hepatic metabolism of drugs, dose Gabapentin has no appreciable liver metabolism, yet, suspected cases of gabapentin-induced hepatotoxicity have been reported. Per literature review, two cases of possible gabapentin-induced liver injury have been reported. In clinical trials in diabetic neuropathy and epilepsy, therapy with gabapentin was not associated with an increased frequency of serum aminotransferase elevations or liver toxicity. Gabapentin (Neurontin) usually isn’t bad for your liver or kidneys. In most cases, it has little effect on these organs. In rare instances, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome. Gabapentin lacks liver metabolism; the mechanism by which it produces liver injury is still unknown; however, there are reports of hepatotoxicity associated with its administration, so its use must be individualized for each patient. Hepatic metabolism converts OXC to its active metabolite monohydroxylated derivative. 32 Liver disease has no effect on the pharmacokinetics of OXC and monohydroxylated derivative. 33 OXC has not been associated with hepatotoxicity except for anecdotal case reports, but it can cause a modest elevation of liver enzymes. 34, 35, 36 Gabapentin is eliminated from the systemic circulation by renal excretion as unchanged drug. Gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Gabapentin elimination half-life is 5 to 7 hours and is unaltered by dose or following multiple dosing. Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance are directly Gabapentin has no appreciable liver metabolism and there are only rare case reports about possible hepatotoxicity. Some of these reports describe patients taking multiple drugs, so the association remains unclear. 139 , 140 , 141 , 142 P53 gene expression, histological, and immunohistochemical examinations were performed in liver and kidney tissue samples. Key findings: Gabapentin increased AST, ALT, LDH, ALP, urea, creatinine, MDA, and p53 gene expression and it reduced GSH. Moreover, gabapentin administration caused structural changes in the hepatic and renal architecture Gabapentin-Induced Liver Toxicity Am J Ther. 2022 Nov-Dec;29(6):e751-e752. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0000000000001208. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Authors Japjot Chahal 1 Gapentin has no appreciable liver metabolism, but suspected cases of gabapentin-induced hepatotoxicity have been reported. Even high doses of gabapentin (400mg/kg) for 30 days do not produce deleterious adverse effects on the liver or haematological parameters. Gabapentin is not protein-bound. A high volume of distribution indicates greater concentration in tissue than in plasma. It is not metabolized and does not induce hepatic enzymes or inhibit metabolism of other antiepileptic drugs. This class, which includes gabapentin and pregabalin, is not metabolized by the liver. Therefore, risks in patients with advanced liver disease are not greatly increased. However, there are case reports of pregabalin‐induced hepatoxicity.4 Gabapentin and pregabalin are renally excreted, so dosages need to be adjusted for renal failure. - Carbamazepine - gabapentin - all undergo liver metabolism - valproic acid gabapentin A patient experiencing tonic-clonic seizures should be managed by: - having the patient place his or her head between the knees - lowering the patient's head in the dental chair until it is even with the heart - tilting the patient's head to one side to Generic Name Gabapentin DrugBank Accession Number DB00996 Background. Gabapentin is a structural analogue of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid that was first approved for use in the United States in 1993. 16 It was originally developed as a novel anti-epileptic for the treatment of certain types of seizures 14,5 - today it is also widely used to treat neuropathic pain. 8 Gabapentin, a water-soluble amino acid, is eliminated unchanged by the kidneys and there is no appreciable metabolism by the liver. However, there are a few descriptions of gabapentin-related Gabapentin is not metabolized by the liver. Instead, it is excreted unchanged in your kidneys after circulating in your blood. Gabapentin affects nerves and chemicals in your body that are involved in some types of pain and in seizures. They are not metabolised by the liver and do not affect the cytochrome P450 system, major cytochrome P450 system isoenzymes; however, drug-induced hepatotoxicity has been described in case reports. 16 Elimination is mostly done by the kidney and is proportional to the creatinine clearance. Accumulation can cause renal failure resulting in
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |