Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
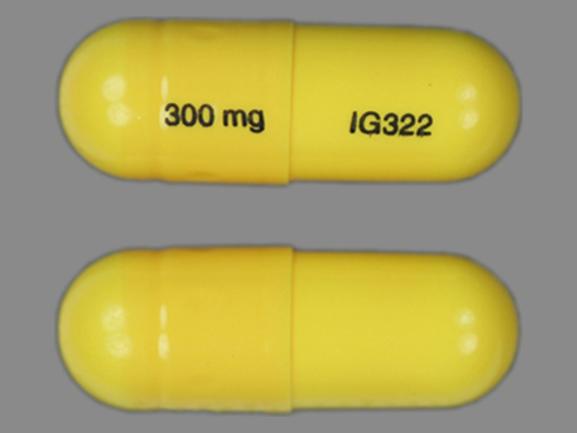
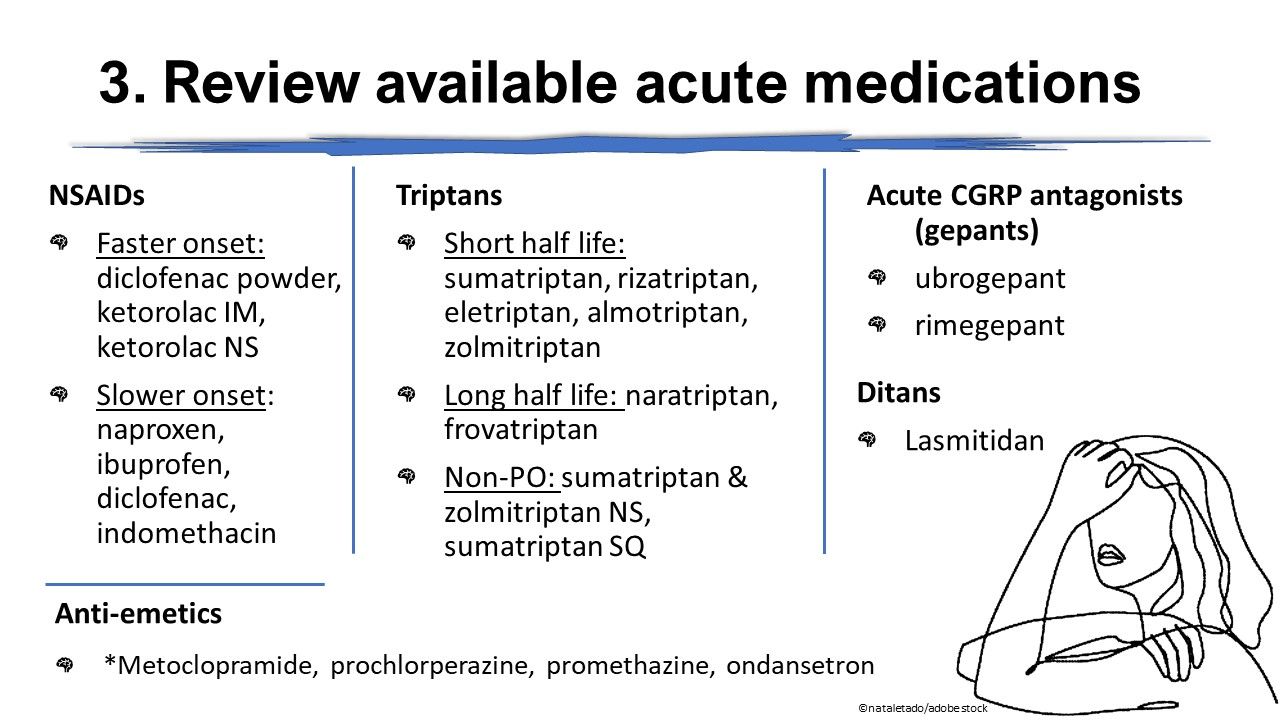
Objective: Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. Neurontin may be prescribed off-label to treat migraines. Neurontin is also referred to by its drug name, Gabapentin. Neurontin is an anticonvulsant, or drug that controls seizures. Neurontin is believed to work on certain types of pain by reducing pain signals sent by damaged nerves. How do I take it? Discover the potential of gabapentin for preventing migraine attacks and headaches. While not a first-line treatment, it can be effective in combination with other options. However, researchers weren't able to tease out the sequence of when people took the drugs. And with anti-nausea drugs, it's not clear if people were rating their helpfulness on nausea rather than headache, Dr. Loder points out. But it's a good reminder that for many people who have migraines, nausea and vomiting are a big problem. Gabapentin is an anti-seizure drug that is sometimes prescribed to help prevent migraines. However, there is conflicting research on whether it's effective for this use. It may also be prescribed for conditions such as diabetic neuropathy, restless leg syndrome, and fibromyalgia. In people experiencing nerve pain after having had shingles, gabapentin is thought to change the way pain signals are sent through the body and brain. It's not entirely clear how gabapentin works to treat restless legs syndrome. Side effects of gabapentin. Common side effects of gabapentin include: drowsiness or dizziness; headache or blurred Experimental research 11 suggests that gabapentin reduces neuronal excitability in spinal trigeminal nuclei and prevents central sensitization during migraine attack. Gabapentin dosage: 1,200 mg to 2,400 mg per day divided in three doses. Migraines impose significant health and financial burdens. Approximately 38% of patients with episodic migraines would benefit from preventive therapy, but less than 13% take prophylactic medications. Does gabapentin (Neurontin) help prevent episodic migraine? Gabapentin does not decrease the frequency of migraine headaches and is not recommended for prophylactic therapy. (Strength Headache subtype Diagnostic criteria Nonpharmacologic treatment options Gabapentin (Neurontin) is minimally effective at high doses, and adverse effects are common. Gabapentin is believed to work by affecting certain neurotransmitters in the brain, including GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), which plays a role in regulating nerve activity. By modulating these neurotransmitters, Gabapentin may help reduce the frequency and intensity of migraine attacks. [1,2] I wish to share my clinical perspective of chronic daily headache (CDHA) and my treatment protocol, which gives very successful results. I think that many headaches referred to as rebound headache or transformed migraine, are actually variants of fibromyalgia, consisting of recurrent muscle spasms and non-restorative sleep. GBP has some efficacy in migraine headache, but not sufficient evidence to suggest primary therapy. When primary headache treatments fail, a GBP trial may be considered in the individual patient. Gabapentin’s role in migraine prevention isn’t well known. It’s believed that it may influence electrical activity in the brain through neurotransmitters and block calcium channels. Gabapentin is an effective prophylactic agent for patients with migraine. In addition, gabapentin appears generally well tolerated with mild to moderate somnolence and dizziness. Reviews and ratings for Gabapentin when used in the treatment of migraine. 121 reviews submitted with a 7.9 average score.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |