Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
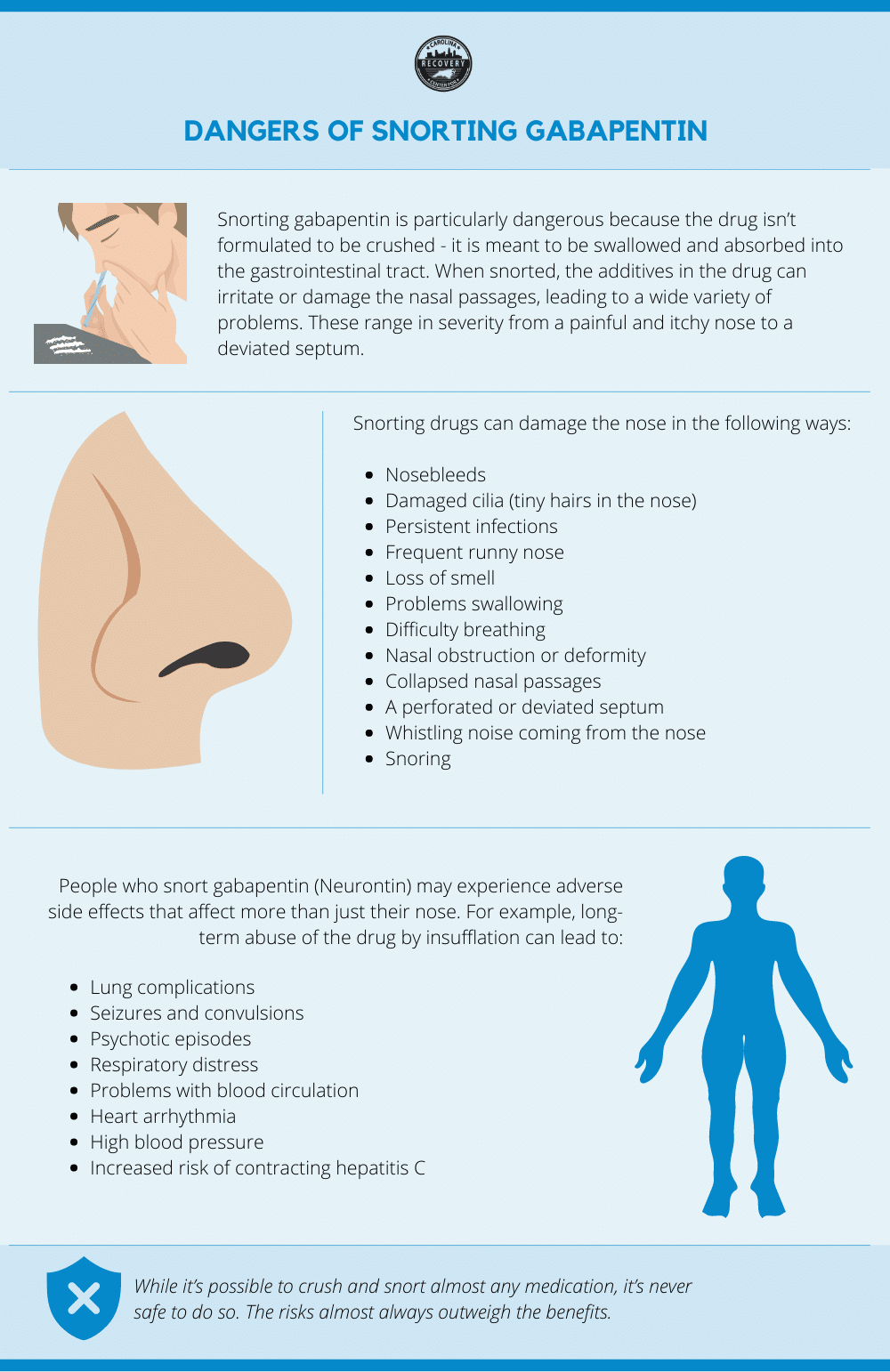
Not everyone who takes gabapentin will experience changes in blood pressure. However, certain factors may increase your risk, including: * Age: Older adults may be more susceptible to blood pressure changes. * Existing blood pressure issues: If you already have high or low blood pressure, gabapentin may exacerbate these issues. Research on rats has shown that gabapentin may lower blood pressure in those with high blood pressure (hypertension). Then, unilateral microinjection of gabapentin into the NTS before and after N(ω)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) treatment whether to change blood pressure and heart rate. Results: Unilateral microinjection of gabapentin into the NTS produced prominent dose-related depressor and bradycardic effects in SHR rats. The cardiovascular Some studies suggest that gabapentin may raise blood pressure in certain individuals, which could be a concern for people with high blood pressure. The Risks of Taking Gabapentin for High Blood Pressure. Research indicates that gabapentin can cause blood pressure to rise in some cases, which may be due to its effects on the body’s blood vessels. We have explained how gabapentin can cause high blood pressure. However, not every individual taking gabapentin would experience high blood pressure or the same side effects. Other factors can increase one’s risk of high blood pressure besides gabapentin. 2. Can Gabapentin cause high blood pressure? While some studies suggest gabapentin may have therapeutic benefits for individuals with hypertension, it does not typically cause high blood pressure. It is important to monitor blood pressure when taking gabapentin, especially in patients with a history of hypertension, but gabapentin is not a Background Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications to treat pain in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Gabapentin and pregabalin can cause fluid retention, which is hypothesized to be associated with cardiovascular diseases. However, whether long-term use of gabapentin and pregabalin is associated with adverse cardiovascular diseases remains unknown. This study aims to Gabapentin is used to control seizures, to treat nerve pain that can happen after having had shingles, and to treat a condition called restless legs syndrome. In addition to these FDA-approved uses, doctors sometimes prescribe gabapentin off-label. High blood pressure is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Tylenol, and have Rheumatoid arthritis. Pain and blood pressure appear to be strictly related. According to available evidence, both pain and analgesic therapies may induce a clinically significant destabilization of blood pressure values. The subsequent implications on hypertension incidence and blood pressure control remain unclear and should be explored in future studies. Funding Blood Pressure Monitoring: Regularly monitor blood pressure to detect any increases. Cholesterol Monitoring: Gabapentin may increase LDL cholesterol, so regular monitoring is important. Open Communication: Inform your doctor about any changes you experience, such as swelling, palpitations, or chest pain. Oral and intravenous gabapentin can markedly attenuate blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive rats. The nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) is the primary integrative center for cardiovascular control and other autonomic functions in the central nervous system. Ligands of auxiliary α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs) decrease elevated L-type VDCCs surface expression in arterial myocytes and arterial constriction in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). However, their effect on blood pressure (BP) is unclear. In this study, we investigated the hemodynamic response to acute and chronic administration of gabapentin, a ligand of This is true for all gabapentin products, which can cause withdrawal symptoms like anxiety, agitation, and nausea or vomiting. More seriously, stopping treatment with gabapentin abruptly can lead to seizures. If you want to stop taking gabapentin, don’t make any changes without talking to your prescriber. Yes, it can cause High Blood Pressure (hypertension) Cardiovascular side effects including hypertension have been reported to occur in more than one percent of patients taking gabapentin. Read more at: Gabapentin side effects may make you want to stop taking the drug. But don’t stop taking it without first talking with your doctor. losartan, a medication used to treat high blood pressure Can gabapentin cause high blood pressure? Yes, abruptly stopping gabapentin can lead to rebound hypertension , a withdrawal symptom. Additionally, while not a direct cause, the cardiovascular risks associated with long-term use can indirectly affect blood pressure. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin and pregabalin can cause fluid retention, which is hypothesized to be associated with cardiovascular diseases. However, whether long-term use of gabapentin and pregabalin is associated with adverse cardiovascular diseases remains unknown. Summary: Low blood pressure is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Aspirin, and have High blood pressure.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |