Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
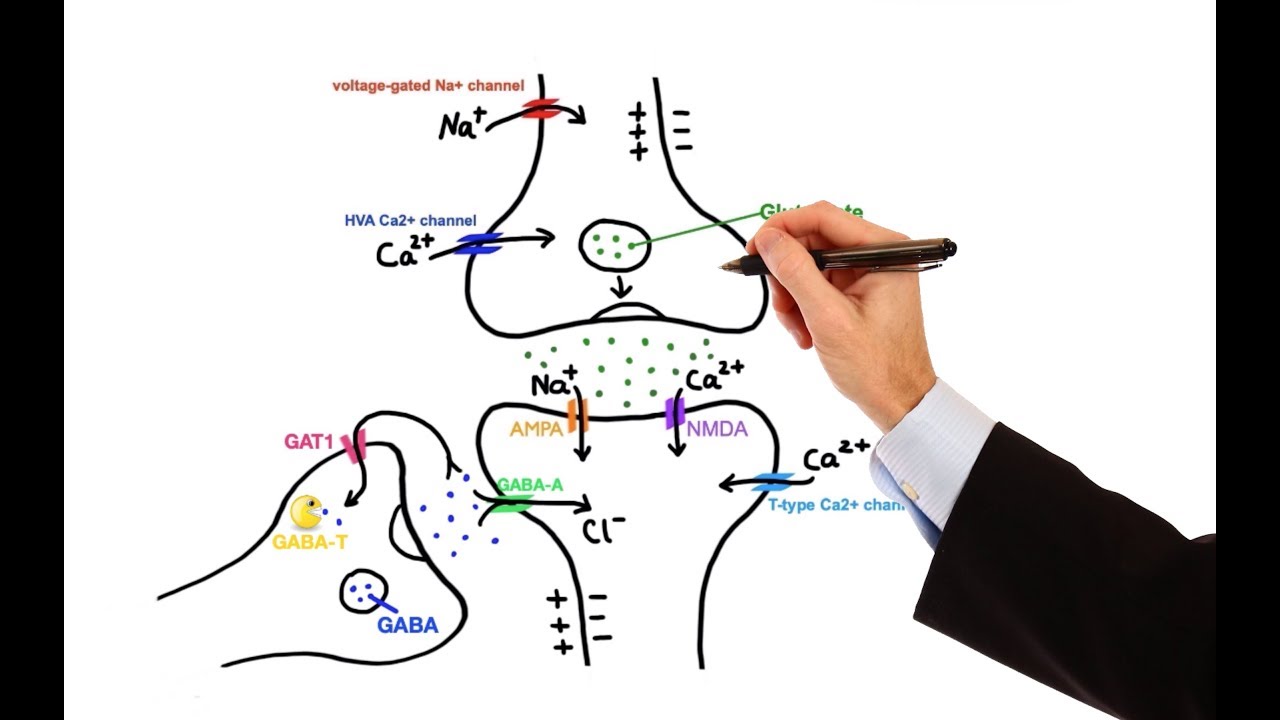
Gabapentin is an antiepileptic drug used in the treatment of partial and generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Its antiepileptic mechanism of action is not known. The transport of gabapentin across membranes and its demonstrated effects on voltage-gated ion channels (sodium, calcium), presynaptic mecha Mechanism of Action. Although the exact mechanism of action with the GABA receptors is unknown, researchers know that gabapentin freely passes the blood-brain barrier and acts on neurotransmitters. Gabapentin has a cyclohexyl group to the structure of the neurotransmitter GABA as a chemical structure. Mechanisms of action. Gabapentin and pregabalin do not bind to GABA receptors despite their structural similarity but have a high affinity for the α2δ-1 subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs). 19 VGCCs are composed of multiple subunits: α 1, β, γ and α 2 δ. Gabapentin is an antiepileptic drug (AED) by design expected to mimic the action of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). However, its principal proposed mechanism of action is the interaction with the alpha 2-delta subunit of L-type voltage-regulated calcium channels. Gabapentin poss Summary This chapter contains section titled: Introduction and chemistry Mechanisms of action Pharmacokinetics Clinical efficacy Side-effects Place of gabapentin in the therapy of epilepsy Administ As with many other agents, GBP was licensed for the treatment of epilepsy with little or no understanding of its mechanism of action. Continued research and the parallel development of PGB have contributed to a contemporary pharmacological view of GBP (and PGB) as drugs with multiple modest cellular effects at therapeutic concentrations, but with a single predominant mechanism of action that Gabapentin's mechanism of action involves binding to the α2δ subunit of voltage gated calcium channels, modulating neurotransmitter release and dampening excessive neuronal excitability. Furthermore, gabapentin exhibits a favorable safety profile, with most adverse effects being mild to moderate in nature. Despite a decade of clinical use both as an antiepileptic and antinociceptive agent, the mechanism by which gabapentin (GBP) exerts its pharmacologic effects remains to be determined. Gabapentin is 1 of many antiseizure medications available for the treatment of epilepsy in adults; however, there are potential risks associated with its use. Therefore, it is important to determine the place of therapy of gabapentin in the treatment of epilepsy. Gabapentin's mechanism of action involves binding to the α2δ subunit of voltage gated calcium channels, modulating neurotransmitter release and dampening excessive neuronal excitability. Furthermore, gabapentin exhibits a favorable safety profile, with most adverse effects being mild to moderate in nature. Mechanisms of action of antiepileptic drugs GRAEME J. SILLS Department of Molecular and Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool _____ Introduction The serendipitous discovery of the anticonvulsant properties of phenobarbital in 1912 marked the foundation of the modern pharmacotherapy of epilepsy. The subsequent 70 years saw the As with many other agents, GBP was licensed for the treatment of epilepsy with little or no understanding of its mechanism of action. Continued research and the parallel development of PGB have contributed to a contemporary pharmacological view of GBP (and PGB) as drugs with multiple modest cellular effects at therapeutic concentrations, but with a single predominant mechanism of action that Medline and EMBASE database searches were conducted to identify studies relating to mechanisms of action and effects in experimental animal models of inflammatory and postoperative pain and human models of experimental pain. The effects of gabapentinoids may be attributed to depression of dorsal horn sensitivity through a multitude of mechanisms. The precise mechanism of action of gabapentin is not fully understood (McClean 1995; Morris 1999; Pfizer 2016). By its chemical structure, gabapentin is related to the neurotransmitter gamma‐aminobutyric acid (GABA). Although its mechanism of action remains to be defined gabapentin is effective in a number of seizure models which predict its efficacy in partial and tonic-clonic seizures. Clinical studies support the clini cal efficacy of gabapentin as adjunctive therapy in adults with epilepsy with partial and secondarily generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Synopsis Gabapentin is an antiepileptic drug with an unknown mechanism of action apparently dissimilar to that of other antiepileptic agents, and possessing some desirable pharmacokinetic traits. The drug is not protein bound, is not metabolised and does not induce liver enzymes, diminishing the likelihood of drug interactions with other antiepileptic agents and drugs such as oral The chemical structure of gabapentin (Neurontin) is derived by addition of a cyclohexyl group to the backbone of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin prevents seizures in a wide variety of models in animals, including generalized tonic-clonic and partial seizures. Sancho-Rieger J and López-Trigo J 28 showed that gabapentin is an efficient, favorably tolerated drug utilized as monotherapy in partial epilepsy. Deciphering the genetics that underpins the mechanisms that generate seizures is one of the promising areas in the field. 104 Many epilepsy genes have been identified, including genes that increase the risk of different types of epilepsy, such as generalized and focal epilepsy and developmental and epileptic encephalopathies. These genes have a Gabapentin is ineffective in absence seizures and should be used in caution in patients with mixed seizure disorders involving absence seizures. Gabapentin has been associated with drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), otherwise known as multi-organ hypersensitivity.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |