Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
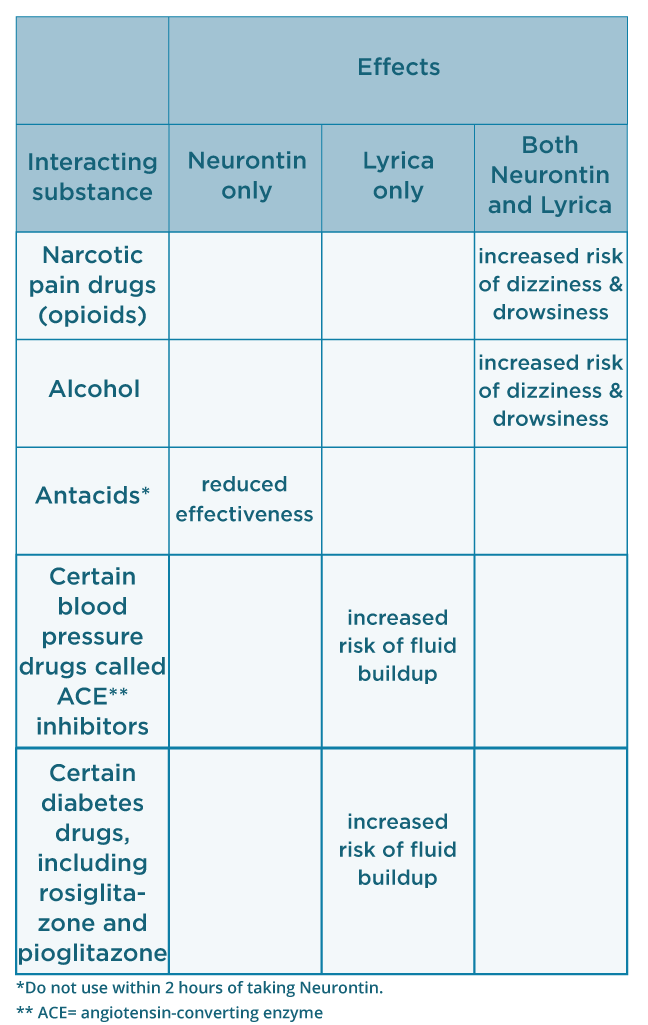
According to the American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention (AMPP) Study, 38.8% of patients with migraine should be considered for (13.1%) or offered (25.7%) preventive migraine therapy.16 Unfortunately, the underutilization of migraine preventive medications is underscored by the fact that only 13% of all patients with migraine currently use Acute migraines respond to nonsteroidal medications and triptans. Ibuprofen appears to be slightly more effective than naproxen, aspirin, and acetaminophen. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is minimally Gabapentin is an effective prophylactic agent for patients with migraine. In addition, gabapentin appears generally well tolerated with mild to moderate somnolence and dizziness. Recurrent migraines can be functionally disabling and can impair quality of life. The disabling nature of migraine headaches leads to frequent visits to outpatient clinics and emergency department facilities, causing significant health and financial burdens. Headaches fall in the top five causes of emergency department visits and the top twenty reasons for outpatient visits.[1] The overall Migraine is a common episodic disorder, the hallmark of which is a disabling headache generally associated with nausea and/or light and sound sensitivity. The acute treatment of migraine in adults is reviewed here. Preventive treatment of migraine in adults is discussed separately. (See "Preventive treatment of episodic migraine in adults".) Migraine relief medications that combine caffeine, aspirin and acetaminophen (Excedrin Migraine) may be helpful, but usually only against mild migraine pain. Triptans. Prescription drugs such as sumatriptan (Imitrex, Tosymra) and rizatriptan (Maxalt, Maxalt-MLT) are used to treat migraine because they block pain pathways in the brain. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug that may help prevent migraine attacks, but it’s not well studied or recommended as a primary therapy. Learn about its dosage, side effects, and how it works. Gabapentin for Migraine User Reviews Brand names: Neurontin, Gralise, Gabarone, Fanatrex Gabapentin has an average rating of 7.9 out of 10 from a total of 111 reviews for the off-label treatment of Migraine. In 1996, Mathew and Lucker reported results of an open-label study that demonstrated reduced severity and frequency of headaches in patients with migraine (with and without aura) after treatment with gabapentin at 900 to 1800 mg/day. 5 This study provided the basis for further evaluation of gabapentin in migraine prophylaxis. The results of a Gabapentin is a medication that can be used off-label for migraine prevention and treatment, as well as other types of headache. Learn about its effectiveness, side effects, and how it compares to other options. Gabapentin is commonly used to treat and prevent seizures in people with epilepsy or to treat nerve pain (postherpetic neuralgia) that can occur after a viral infection called shingles. Migraine attacks can not only cause severe throbbing head pain or pulsing sensations, but also nausea, vomiting, and extreme sensitivity to light and sound.There are as-needed treatments to stop symptoms of a migraine attack (acute treatment) and long-term treatments to decrease the frequency and severity of migraine attacks (preventive treatment). Migraines. Gabapentin is used "off-label" for migraine prevention and treatment, including migraines with or without aura, vestibular migraines. It reduces the frequency of headaches, pain intensity, and the use of symptomatic medications 1, 2. However, gabapentin is not helpful for migraine aura, vertigo, or other accompaing symptoms. sign in; Don't have an account ? Create one now; Enjoy faster checkout, create ideaboards, earn My Funds and become a Beyond+ member! track order; my offers A systematic review of five studies found no evidence that gabapentin reduces the frequency or severity of migraine headaches. Gabapentin is not recommended for migraine prevention and may cause adverse effects. This article reviews the evidence and recommendations for preventive therapy of migraines, including medications, complementary treatments, and nonpharmacologic therapies. Gabapentin is not included as an effective or probably effective option, and its use is not supported by clinical evidence.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |