Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | /GettyImages-1043917898-a7919e52eed44d1cb330f36623135db3.jpg) |
 |  |
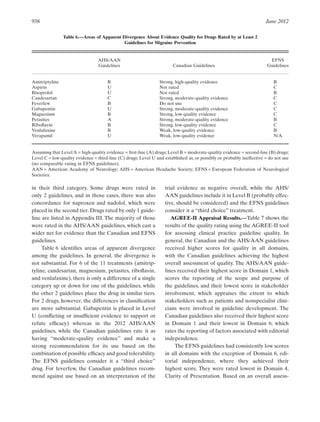
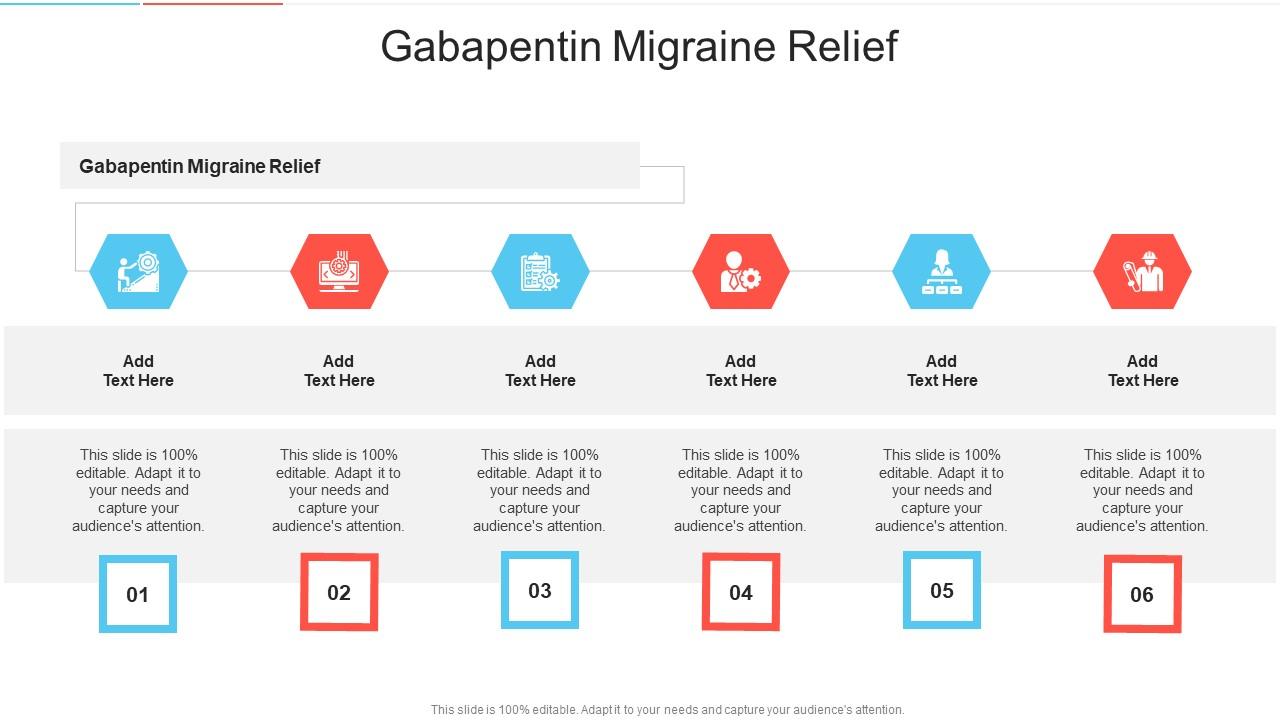
Discover the potential of gabapentin for preventing migraine attacks and headaches. While not a first-line treatment, it can be effective in combination with other options. Gabapentin is an anti-seizure drug that is sometimes prescribed to help prevent migraines. However, there is conflicting research on whether it's effective for this use. It may also be prescribed for conditions such as diabetic neuropathy, restless leg syndrome, and fibromyalgia. Petasites is established to be effective in migraine prevention. 64, 65 CoQ10 is possibly effective for migraine prevention, 27 while riboflavin is probably effective. 66 Percutaneous estradiol is possibly effective for migraine prevention, 67 as is a combination of soy isoflavones (60 mg), dong quai (100 mg), and black cohosh (50 mg). 67 Gabapentin is used "off-label" for migraine prevention and treatment, including migraines with or without aura, vestibular migraines. It reduces the frequency of headaches, pain intensity, and the use of symptomatic medications 1 , 2 . Evidence for acute migraine treatment medications is summarized in Table 3. Medication Gabapentin (Neurontin) is minimally effective at high doses, and adverse effects are common. Gabapentin for Migraine User Reviews Brand names: Neurontin, Gralise, Gabarone, Fanatrex Gabapentin has an average rating of 7.9 out of 10 from a total of 111 reviews for the off-label treatment of Migraine. Guidance from NICE and SIGN agrees that gabapentin should not be considered as a prophylactic treatment for migraine [NICE, 2021; SIGN, 2023]. Gabapentin is no better than placebo for prophylactic treatment of migraine in adults, is commonly associated with adverse events and there is an increased risk of addiction . Recurrent migraines can be functionally disabling and can impair quality of life. The disabling nature of migraine headaches leads to frequent visits to outpatient clinics and emergency department facilities, causing significant health and financial burdens. Headaches fall in the top five causes of emergency department visits and the top twenty reasons for outpatient visits.[1] The overall Gabapentin is an effective prophylactic agent for patients with migraine. In addition, gabapentin appears generally well tolerated with mild to moderate somnolence and dizziness. Gabapentin for migraine prevention can be taken with or without food and comes in an extended release tablet, an immediate release tablet, or an oral solution. One trial each of gabapentin 900 mg (53 patients), and gabapentin titrated to 1200 mg (63 patients) and 1800 mg (122 patients) failed to show a statistically significant reduction in headache frequency in the active treatment group as compared to the placebo group, whereas one trial of gabapentin titrated to 1800 to 2400 mg (113 patients Identifying and managing environmental, dietary, and behavioral triggers are useful strategies for preventing migraines. First-line medications established as effective based on clinical evidence Objective. Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. Annual medical expenditures and lost productivity associated with migraine is estimated to exceed $78 billion, making the prevention of migraine an important unmet clinical and societal need. In 1996, Mathew and Lucker reported results of an open-label study that demonstrated reduced severity and frequency of headaches in patients with migraine (with and without aura) after treatment with gabapentin at 900 to 1800 mg/day. 5 This study provided the basis for further evaluation of gabapentin in migraine prophylaxis. The results of a Does gabapentin (Neurontin) help prevent episodic migraine? Evidence-Based Answer Gabapentin does not decrease the frequency of migraine headaches and is not recommended for prophylactic migraine, episodic migraine, monotherapy, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (lisinopril), angiotensin II–receptor blockers, antiseizure medications, beta-blockers, β-blockers, calcitonin gene-related peptide antagonist-gepants, CGRP monoclonal antibodies, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and serotonin and norepinephrine A treatment plan should consider not only the patient’s diagnosis, symptoms, and coexistent or comorbid conditions, but also the patient’s expectations, needs, and goals.1 Effective migraine treatment begins with making an accurate diagnosis, ruling out alternate causes, ordering appropriate studies, and addressing the headache’s impact We found moderate certainty evidence that beta-blockers, valproate, and amitriptyline increase the proportion of patients who experience a 50% or more reduction in monthly migraine days, and low certainty evidence that gabapentin may not be different from placebo. There are many different types of migraine — getting a proper diagnosis from a Headache Specialist is crucial to making sure you get an appropriate treatment plan. Fifty percent of people living with migraine go undiagnosed. Many people, especially those who are chronic, can have more than one type
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | /GettyImages-1043917898-a7919e52eed44d1cb330f36623135db3.jpg) |
 |  |