Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
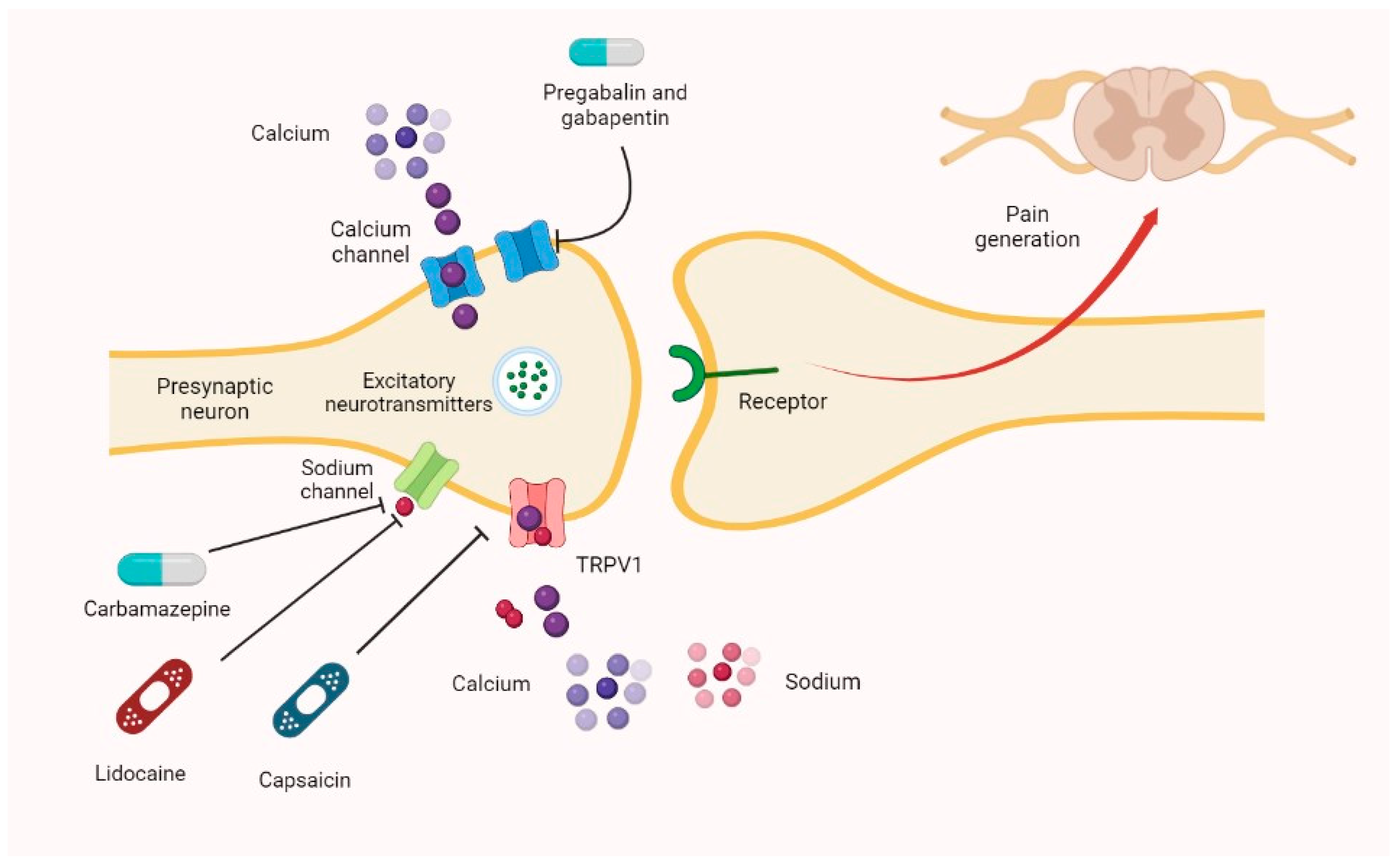 |  |
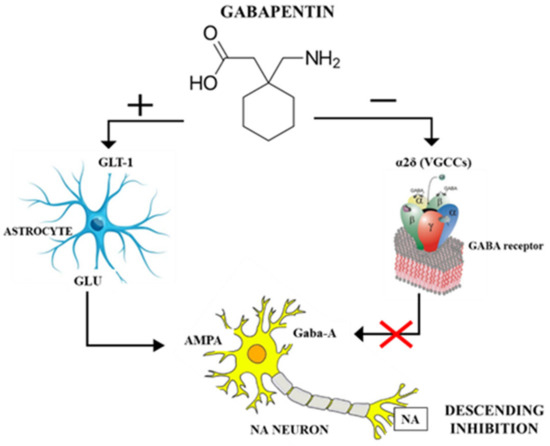
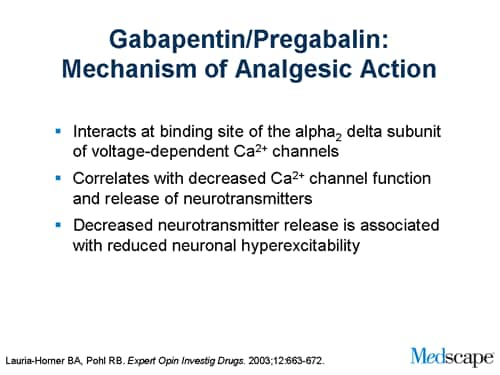
However, one consideration is the addictive potential of gabapentin. Clinical trials testing the efficacy of gabapentin at various doses from 900 to 3600 mg have found mixed results in treatment for alcohol use disorder . Gabapentin caused a marked decrease in neuronal synapse formation in brains of intact mice and abnormal neuronal synapse formation in a mouse model of synaptic repair. Gabapentin has been shown in vitro to interfere with activity of the α2β subunit of voltage-activated calcium channels, a receptor involved in neuronal synaptogenesis. Mechanism of action. ↑ the frequency of Cl-channel opening and thus facilitating GABAA action . via its binding to the α and γ subunit of the GABAA receptor . Antiepileptic drugs (AED) can be separated by mechanism of action (MOA) affecting the following Gabapentin Mechanism of action. Gabapentin does not act directly on GABA receptors in spite of their close structural resemblance to GABA. They may, however, modify the synaptic or nonsynaptic release of GABA. An increase in brain GABA concentration is observed in patients receiving gabapentin. While sharing a common property of suppressing seizures, antiseizure medications have many different pharmacologic profiles that are relevant when selecting and prescribing these agents in patients with epilepsy and other conditions. Gabapentin is a neurologic drug that works by blocking calcium channels and preventing the release of neurotransmitters. This in turn blocks the generation and propagation of action potentials. Antiepileptic drugs (AED) can be separated by mechanism of action (MOA) affecting voltage-gated Na + channels. affecting Ca 2+ channels. affecting GABA activity. Mechanism of action and get 5 days of unlimited access to over 1,100 medical articles and 5,000 USMLE and NBME exam-style questions. gabapentin) and as . mood Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what are the 3 drugs that treat absence seizures, what is the first line for absence seizures, MOA of ethosuximide and more. Gabapentinoids are a class of drugs that includes gabapentin and pregabalin. They work by blocking voltage-dependent calcium channels. Clinically, gabapentinoids are used as narrow-spectrum antiepileptic drugs to treat focal seizures. They are also effective at treating neuropathic pain. Gabapentin: Gabapentin is indicated for postherpetic neuralgia and serves as adjunctive therapy for managing partial seizures (with or without secondary generalization) in adults and pediatric patients aged 3 or older. Gabapentin is a medication indicated for use in to treat different seizure presentations, peripheral neuropathic pain and migraine prophylaxis. Other uses include bipolar disorder and post-herpetic neuralgia, though these are off-label uses. Mechanism of beta-‐blocker mortality benefit in heart failure: decreased RAAS; decreased catecholamine binding reduces cardiac remodelling; Only beta-‐blockers shown to improve mortality in heart failure: carvedilol, bisoprolol, metoprolol-‐XR · Contraindications to verapamil: Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. ANTIEPILEPTICS, PART 2: DRUG NAME: vigabatrin (Sabril) gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise) CLASS: GABA inhibitors: GABA analogues: MECHANISM OF ACTION: Prevent GABA reuptake into presynaptic neurons; ↑ GABA concentration in synapse; ↓ seizure activity Gabapentin's mechanism in RLS is unclear, but it is known to bind strongly to α2δ-subunits of voltage-activated calcium channels. This binding likely inhibits calcium entry, normalizing neurotransmitter release, including excitatory glutamate; however, the precise mechanism remains unknown. Generic name (trade name): gabapentin. MOA: blocks voltage-dependent calcium channels, modulating excitatory neurotransmitters release. Indications: Contradictions/precautions: elderly, depression, respiratory impairment, alcohol, CNS depressants, abrupt withdrawal. Interactions: binds to polyvalent cations, CNS depression, antileptic drugs By blocking the transmission of nerve impulses, gabapentin can be used to treat peripheral neuropathy, especially post-herpetic neuropathy. This blockade of nerve impulses also makes gabapentin useful as a narrow spectrum antiepileptic, used to treat focal or partial seizures. Gabapentin and pregabalin block voltage gated Ca2+ channels, thereby inhibiting calcium currents and subsequently reducing neurotransmitter release. This unique mechanism make them particularly effective in addressing neuropathic pain conditions, with notable success in managing postherpetic neuralgia and painful diabetic neuropathy.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |