Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
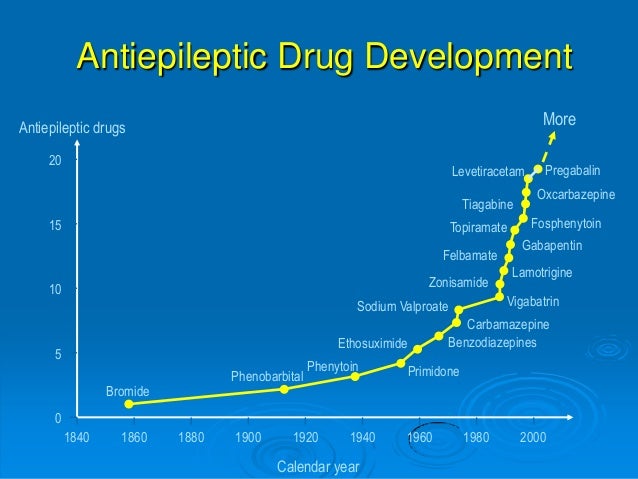
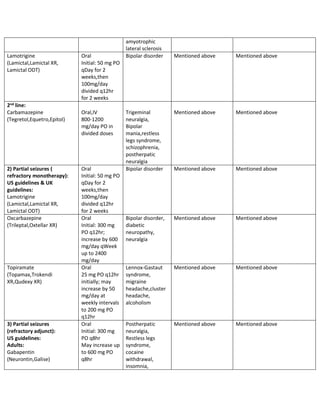
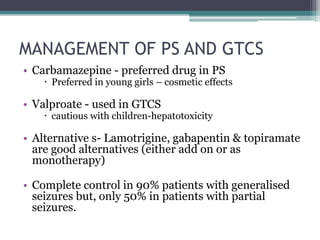
The Swedish MPA (2022) 18 guideline recommends gabapentin as a possible alternative to first-line options (lamotrigine and levetiracetam) for use as monotherapy for focal-onset seizures in older adults based on a single study with possible methodological flaws. Gabapentin as monotherapy probably controlled seizures no better and no worse than comparator AEDs (lamotrigine, carbamazepine, oxcarbazepines, and topiramate) and gabapentin was probably better in retaining people in studies and preventing withdrawals due to adverse events. BACKGROUND Epilepsy is one of the most common chronic neurological disorders, affecting more than 50 million people Most people with epilepsy are treated with a single antiepileptic drug (monotherapy) and current guidelines from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) in the United Kingdom for adults and children recommend carbamazepine or lamotrigine as first-line treatment for focal onset seizures and sodium valproate for generalised Gabapentin Effectiveness as Initial Monotherapy for Epileptic Seizures and Syndromes. Adults with partial-onset seizures: Derived from existing evidence, GBP is effective as initial monotherapy for adults with recently diagnosed or untreated partial-onset seizures. 38, 42, 43 Additionally, gabapentin possesses adequate evidence for confident use as monotherapy in treatment of partial-onset seizures, although it lacks formal FDA approval for this indication [10,17]. Among the second-generation AEDs approved for monotherapy use, few comparator trials have been conducted. Gabapentin is recommended as a possible alternative to first-line options (lamotrigine and levetiracetam) for use as monotherapy for focal-onset seizures in older adults. Supporting evidence: A single study with possible methodological flaws. Focal (partial) epilepsy: Focal epilepsy, also known as partial epilepsy, originates from a specific region of the brain. Seizures in focal epilepsy are characterized by abnormal electrical discharges localized in a specific area, which may result in motor, sensory, autonomic, or cognitive symptoms. Focal seizures can be Epilepsy is one of the most common chronic neurological disorders, affecting more than 50 million people globally. In this review we summarised the evidence from randomised controlled trials of gabapentin used as monotherapy for the treatment of focal epilepsy, both newly diagnosed and drug-resistant, with or without secondary generalisation. Gabapentin, lamotrigine, oxcarbazepine, and vigabatrin have been compared with conventional AEDs in patients with newly diagnosed epilepsy in randomized active-control trials. In patients with partial-onset (focal) seizures, levetiracetam (Keppra), lamotrigine (Lamictal), and carbamazepine (Tegretol) were associated with the longest time to treatment withdrawal (i.e In this review we summarised the evidence from randomised controlled trials of gabapentin used as monotherapy for the treatment of focal epilepsy, both newly diagnosed and drug-resistant, with or without secondary generalisation. Beydoun A, Fischer J, Labar DR, et al. Gabapentin monotherapy: II A 26-week, double-blind, dose-controlled, multi-center study of conversion from polytherapy in outpatients with refractory complex partial or secondarily generalized seizures. In this review we summarised the evidence from randomised controlled trials of gabapentin used as monotherapy for the treatment of focal epilepsy, both newly diagnosed and drug-resistant, with or without secondary generalisation. Request PDF | Gabapentin monotherapy for epilepsy: Reviews | This is a protocol for a Cochrane Review (Intervention). The objectives are as follows: To assess the effects of gabapentin monotherapy In this review we summarised the evidence from randomised controlled trials of gabapentin used as monotherapy for the treatment of focal epilepsy, both newly diagnosed and drug-resistant, with or without secondary generalisation. To investigate the efficacy of gabapentin administered as monotherapy in patients with newly diagnosed partial epilepsy, a randomized double-blind trial was performed. Request PDF | Gabapentin monotherapy for epilepsy: A review | Background: Epilepsy is one of the most common chronic neurological disorders, affecting more than 50 million people globally. In this The efficacy and safety of gabapentin as monotherapy for treatment of partial onset seizures were evaluated in three large multicenter, double-blind, parallel-group, dose-controlled trials. In the first trial, 275 outpatients with refractory partial epilepsy maintained on stable doses of one or two antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) were switched to Based on three multicentre studies that directly compared gabapentin monotherapy versus carbamazepine monotherapy in focal epilepsy, we found evidence suggesting that there is a reduced risk of withdrawal from treatment due to adverse events with gabapentin monotherapy compared to carbamazepine monotherapy (GBPSG, Chadwick et al. [75–78 The International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) recommended gabapentin as initial monotherapy of newly diagnosed, not yet treated focal seizures in adults; for focal seizures in the elderly; and for idiopathic focal epilepsy in children (Glauser 2006; Glauser 2013).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |