Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
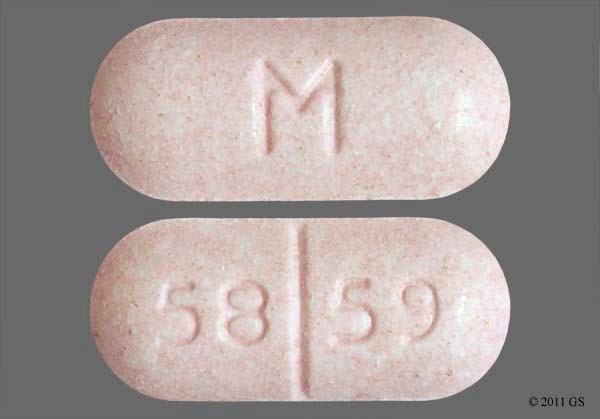
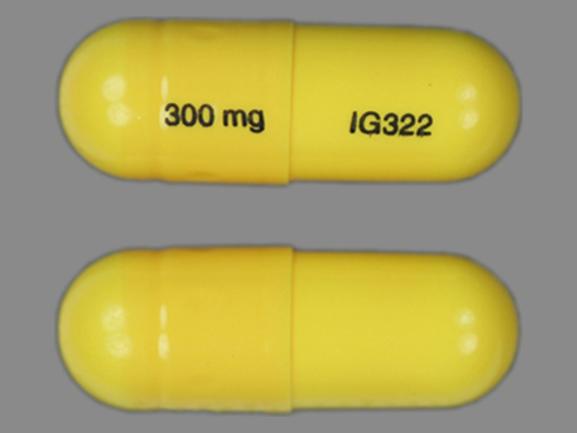
Taking gabapentin with other drugs that make you drowsy or slow your breathing can cause dangerous side effects or death. Ask your doctor before taking opioid medication, a sleeping pill, a muscle relaxer, or medicine for anxiety or seizures. Tell your doctor about all your current medicines. Many drugs can affect gabapentin, especially: naproxen; Muscle relaxer side effects: Find out more about what you can expect when taking muscle relaxers, including the most common side effects. Alcohol and muscle relaxers don’t mix. Learn why this can be a dangerous combination that should be avoided. Common muscle relaxer dosing: Wondering if you’re on a low dose? Combining muscle relaxers and gabapentin can increase the risk of overdose, especially when taken in high doses or with other central nervous system depressants. It's crucial to follow your healthcare provider's instructions and never exceed the recommended dosage. Skeletal Muscle Relaxants Table 1. Skeletal Muscle Relaxants (Antispasmodic Agents) Drug Recommended dosage Most common adverse effects Comments Monthly cost* Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that is primarily used to treat seizures and nerve pain. It was initially developed as a muscle relaxer and anti-spasmodic medication, but its anticonvulsive properties were discovered later. Can You Take Gabapentin as a Muscle Relaxer? This medication, which can relieve nerve pain and is helpful for seizures, is an anticonvulsant. Here’s what that means. Taking Flexeril (cyclobenzaprine) and gabapentin together may result in an increase in CNS side effects like drowsiness, respiratory depression, confusion, balance problems or weakness. Gabapentin and muscle relaxers are commonly prescribed medications for pain relief. While each medication is effective on its own, patients may wonder if it is safe to take them together. The answer is not simple and depends on the individual’s medical history and the specific medications being taken. Taking a muscle relaxer with gabapentin can be safe when done under medical supervision. These medications may interact, leading to increased sedation, dizziness, and cognitive impairment. Gabapentin’s Indirect Effects on Relaxation; Understanding the Difference: Muscle Relaxers vs. Gabapentin; Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Gabapentin. 1. What kind of pain is gabapentin good for? 2. Does gabapentin make you feel relaxed? 3. Is gabapentin mainly prescribed for epilepsy? 4. What are the serious risks with gabapentin? 5. When taken together, gabapentin and muscle relaxers can cause a very strong high that can be dangerous. In adults, the Food and Drug Administration has approved gabapentin to treat shingles postherpetic neuralgia, which causes pain after shingles. Gabapentin’s initial development focused on its ability to act as a muscle relaxer and anti-spasmodic, but its potential as an anticonvulsant quickly overshadowed these initial uses. It operates by modulating the activity of neurotransmitters, specifically by interacting with voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system. What are the more common side effects of gabapentin? Common side effects of gabapentin include: Feeling tired. Dizziness. Headache. Nausea and vomiting. Fever. Difficulty speaking. Recurring infections. Memory loss. Weight gain. Movement problems: coordination problems, being unsteady, tremors, jerky movements. Consulting a healthcare professional is essential before combining a muscle relaxer with Gabapentin due to potential interactions and side effects. Gabapentin is commonly prescribed for nerve pain and seizures, while muscle relaxers are often used to treat muscle spasms and discomfort. Yes, combining gabapentin with a muscle relaxer is generally possible, but it requires careful consideration and medical guidance. Gabapentin, a medication primarily used for nerve pain and seizures, often finds itself in discussions about pain management. 350 moderate drug interactions (1398 brand and generic names) 6 minor drug interactions (13 brand and generic names) A total of 270 drugs are known to interact with Gabapentin: 28 major drug interactions (148 brand and generic names) 232 moderate drug interactions (1026 brand and generic names) 10 minor drug interactions (52 brand and generic You should not take gabapentin with other drugs that can cause drowsiness, such as: benzodiazepines (e.g., Xanax, Valium), barbiturates (e.g., phenobarbital), narcotics (e.g., codeine, oxycodone), certain antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline, trazodone), muscle relaxants (e.g., carisoprodol, cyclobenzaprine), or antihistamines (e.g Find patient medical information for Gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin) on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings, and user ratings Is it safe to mix gabapentin with muscle relaxants? While there are no known specific interactions between gabapentin and most muscle relaxants, there can be additive side effects like increased drowsiness and confusion.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |