Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
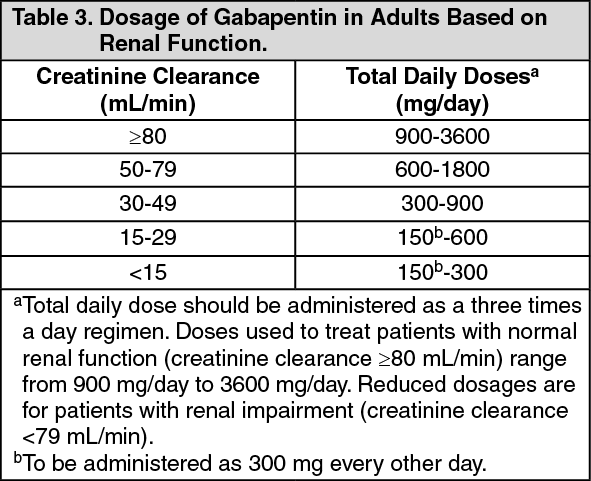
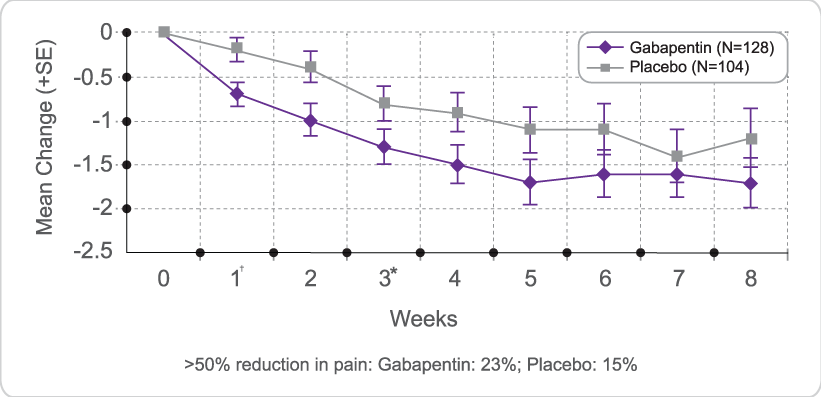
We aimed to identify trends in gabapentin utilization among infants hospitalized in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) across the United States and to evaluate the associations between clinical diagnoses and gabapentin treatment. Gabapentin is used for neurologic pain in adult and children. Gabapentin is thought to decrease central sensitisation, therefore reducing pain recognition.(8) Gabapentin usage in neonates is increasing despite no prospective studies evaluating the dosing, efficacy and safety in neonatal period.(2, 5, 9) Gabapentin is Gabapentin was well tolerated in infants. Initial gabapentin dosing of 5 mg/kg/dose every 24 hours appears safe and consistent with other published studies in infants. The improvement in outcomes with few adverse events suggests a beneficial role for gabapentin. After clinical evaluation, if pharmacological intervention with gabapentin is recommended, dosing is typically started at 5 mg/kg/day divided two or three times per day. The dose is titrated to desired effect by 5 mg/kg/day every 2–4 days to a maximum dose of 35 mg/kg/day. There was a statistical improvement in weight-for-age Z scores from 24 hours prior to gabapentin initiation to 2 weeks after the maximum dose of gabapentin (−2.23 ± 1.78 to −1.66 ± 1.91, p Median maximum dose was 25 mg/kg/day (IQR 15–35 mg/kg/day) and 84% were discharged home on gabapentin. The majority required equipment at discharge (64% gastrostomy or nasogastric tube feeds, 54% supplemental oxygen or mechanical ventilation, and 40% both). The dose was titrated to effect by administering gabapentin at 5 mg/kg/d by mouth at night on days 1 and 2, 10 mg/kg/d divided twice daily on days 3 and 4, and 15 mg/kg/d divided 3 times daily from day 5 onward. Gabapentin use increased from 0% in 2005 to 0.39% in 2016. Treatment was prescribed to neonates at 31 of 48 studied hospitals; 73% of total treated infants localized to five neonatal intensive care units. Term (0.16%) and ≤28 weeks' gestation preterm infants (0.22%) were most likely to receive gabapentin. We included patients discharged from 2005 – 2018 who received ≥ 1 gabapentin dose during their hospitalization. We describe infant clinical characteristics, as well as timing of gabapentin exposure. Gabapentin is used for neurologic pain in adult and children. Gabapentin is thought to decrease central sensitisation, therefore reducing pain recognition.(8) Gabapentin usage in neonates is increasing despite no prospective studies evaluating the dosing, efficacy and safety in neonatal period.(2, 5, 9) Gabapentin is Initial gabapentin dosing of 5 mg/kg/dose every 24 hours appears safe and consistent with other published studies in infants. The improvement in outcomes with few adverse events suggests a beneficial role for gabapentin. Keywords: gabapentin, infants, irritability, neonates, pain, visceral hyperalgesia. Initial gabapentin dosing of 5 mg/kg/dose every 24 hours appears safe and consistent with other published studies in infants. The improvement in outcomes with few adverse events suggests a beneficial role for gabapentin. Keywords: gabapentin; infants; irritability; neonates; pain; visceral hyperalgesia. In patients with a severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min), the average half-life was 52 hours with a rate of renal clearance of 10 mL/min. Gabapentin doses should be adjusted in patients with renal impairment; no adjustment is necessary for patients with hepatic impairment. A study of gabapentin single-dose pharmacokinetics and safety in healthy children found that children under five require approximately 30% higher daily doses of gabapentin, presumably due to age-related changes in pediatric renal function . %PDF-1.7 %âãÏÓ 112 0 obj > endobj xref 112 123 0000000016 00000 n 0000003281 00000 n 0000003486 00000 n 0000003527 00000 n 0000003562 00000 n 0000004020 00000 n 0000004126 00000 n 0000004241 00000 n 0000004349 00000 n 0000004463 00000 n 0000004571 00000 n 0000004686 00000 n 0000004791 00000 n 0000004906 00000 n 0000005013 00000 n 0000005128 00000 n 0000005235 00000 n 0000005350 00000 n A study of gabapentin single-dose pharmacokinetics and safety in healthy children found that children aged under 5 years require approximately 30% higher daily doses of gabapentin, presumably due to age-related changes in pediatric renal function. 10 Six of the 8 preterm infants were started on a dose of 5 mg/kg every 12 hours. 4 Assuming Treatment Timing and Duration. The median age at first administration of gabapentin was 66 postnatal days (25th-75th%: 37–125; Table 3).Those born ≥37 weeks GA had the earliest median age at first dose (47 days; 25th-75%: 30–78) and those ≤28 weeks had the latest (158 days, 25th-75th: 120–242; 32–74 days after 40 weeks’ post-term corrected age) (). Gabapentin therapy appears to be an effective option for neonates and infants with refractory pain and agitation. Gabapentin was well tolerated and associated with decreases in pain scores. It's use resulted in decreased requirements for analgesic and sedative medications. Gabapentin is well tolerated in neonates and infants. Gabapentin decreases pain scores and the need for other neurosedative medications in neonates and infants. This article is commented on by Vollmer on page 272 of this issue. The average gabapentin starting dose was 10.2 mg/kg/day, with maximum doses up to 25.5 mg/kg/day. The median N-PASS score at gabapentin therapy initiation was 3.1 and after gabapentin initiation the last N-PASS score documented was 0 in all but 5 patients. Gabapentin use reduced the need for analgesic or sedative medications.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |