Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
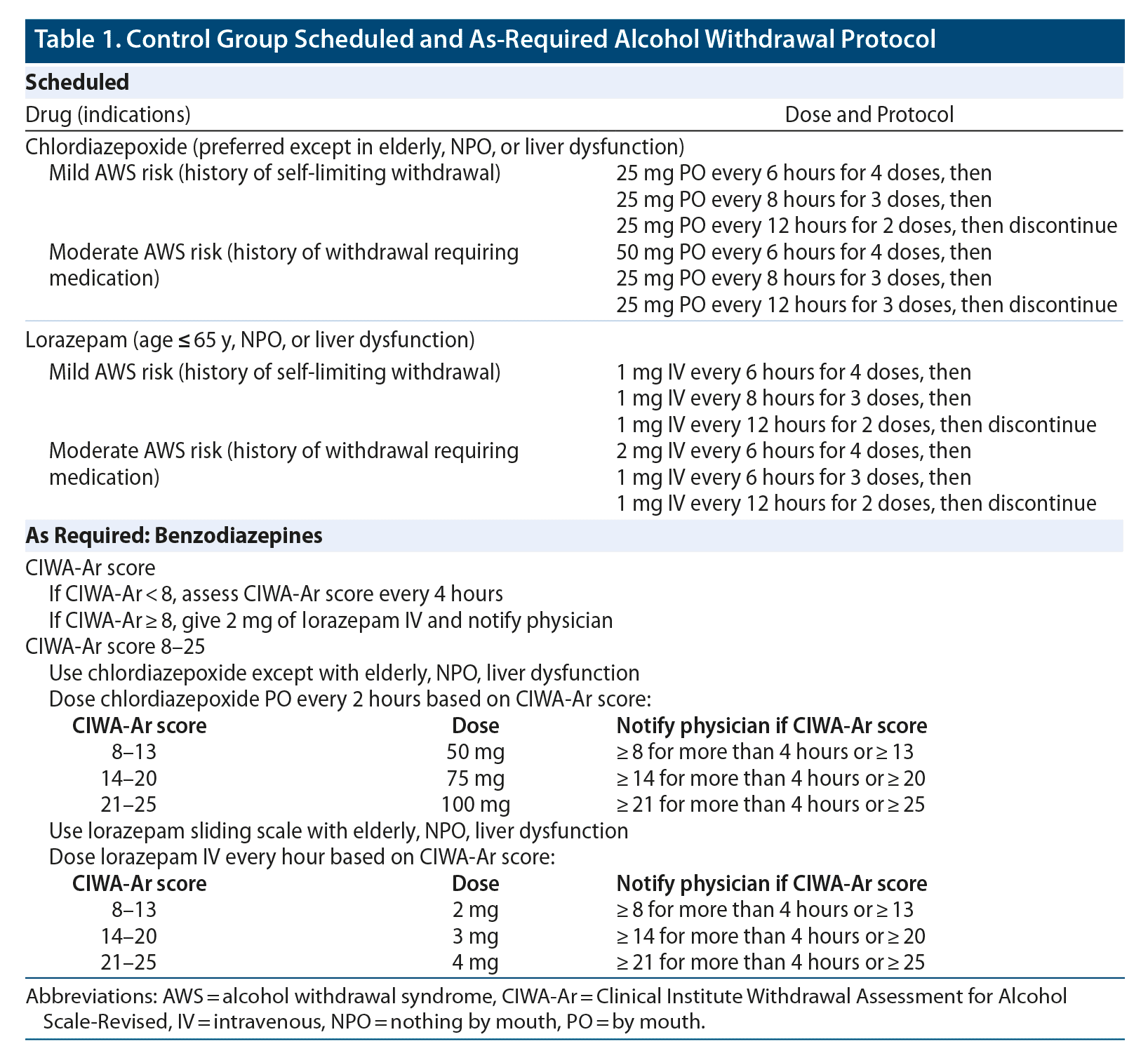
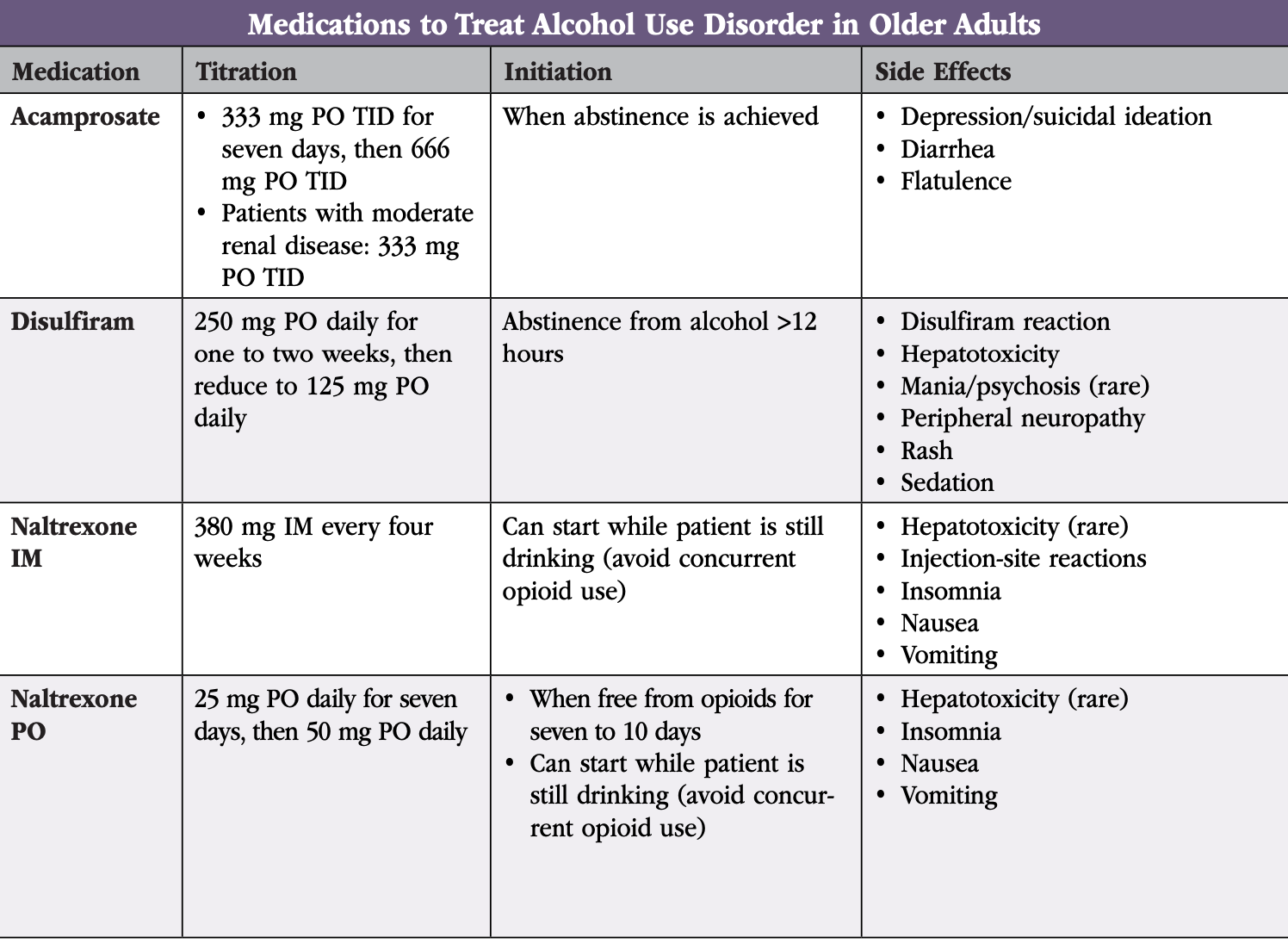
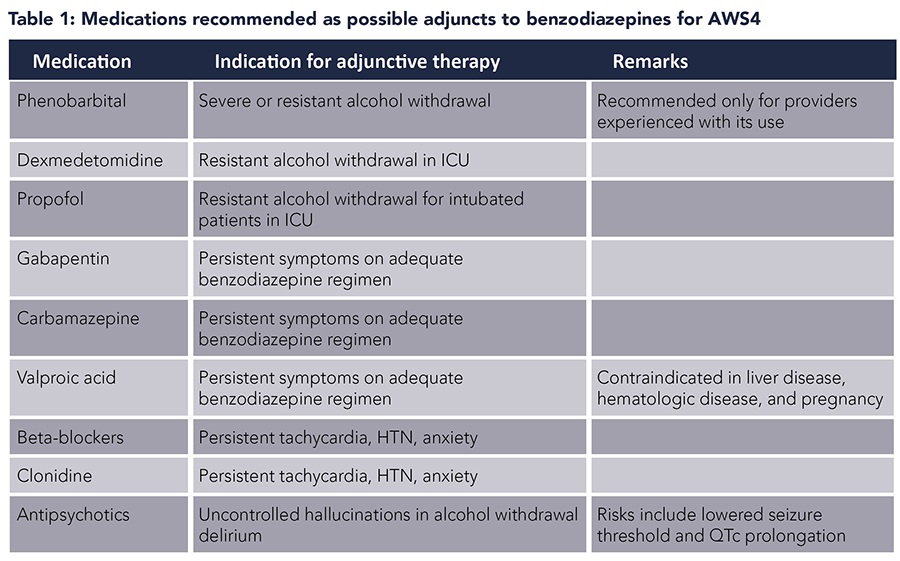
Objective: Gabapentin (GBP) and pregabalin (PGB) have been used to treat alcohol use disorder (AUD) and alcohol withdrawal, but with inconsistent results. In this meta-analysis, we explored the effects of GBP/PGB treatment on AUD and their effects on withdrawal, craving, depression, and sleep disturbance in AUD patients. People with a history of drug or alcohol abuse⁚ Gabapentin may be habit-forming in people with a history of drug or alcohol abuse. Pregnant women⁚ Gabapentin should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. CONTENTS Rapid Reference Preamble & disclaimer Diagnosis Alcohol withdrawal vs. hepatic encephalopathy Therapeutic target (CIWA vs RASS) Treatment: Phenobarbital monotherapy Phenobarbital pharmacology Advantages of phenobarbital over benzodiazepines Contraindications to phenobarbital ️ Phenobarbital guideline Checking phenobarbital levels? ️ Pitfalls of phenobarbital Alternative agents Excessive alcohol use is a leading cause of preventable death in the United States, contributing to an estimated 1 in 5 deaths among adults 20 to 49 years of age between 2015 and 2019. 1 Alcohol Anton RF, Latham P, Voronin K, et al. Efficacy of Gabapentin for the Treatment of Alcohol Use Disorder in Patients With Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern Med 2020; 180:728. Kranzler HR, Feinn R, Morris P, Hartwell EE. A meta-analysis of the efficacy of gabapentin for treating alcohol use disorder. Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29, 30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32, 33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or naltrex Nevertheless, from a mechanistic point of view, there is rationale to support the use of gabapentin during acute alcohol withdrawal. Gabapentin has been found to potentiate CNS GABA in humans (Petroff et al., 1996), inhibit glutamate synthesis, modulate calcium current, inhibit sodium channels, and reduce norepinephrine and dopamine release Is gabapentin an effective treatment for alcohol use disorder (AUD)? Gabapentin treatment avoided more heavy drinking days (> 5 standard drinks/day) than placebo (27% vs 9%). Gabapentin can be a second-line, off-label option to treat AUD. However, there is mixed evidence and concerns about abuse-misuse, and drug-related harms. Gabapentin was well tolerated and effectively diminished the symptoms of alcohol withdrawal in our population especially at the higher target dose (1200 mg) used in this study. Gabapentin reduced the probability of drinking during alcohol withdrawal and in the immediate postwithdrawal week compared Find out what you need to know about gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal and discover the pros, cons, risks, and benefits, and how it may affect health. Further evidence supporting the use of pregabalin for the treatment of withdrawal symptoms comes from randomized controlled studies of gabapentin, another α2δ subunit ligand. These studies have shown the potential of gabapentin for the treatment of opioid [57, 58], alcohol [59, 60], and cannabis dependence . Abstract Background. Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant medication, has been proposed as a treatment for alcohol use disorder (AUD). A multisite study tested gabapentin enacarbil extended-release (GE-XR; 600 mg/twice a day), a prodrug formulation, combined with a computerized behavioral intervention, for AUD. In a 12-week RCT involving recently abstinent alcohol dependent outpatients (n=150), gabapentin was found to increase abstinence rates without serious adverse side effects . Gabapentin in combination with naltrexone was found to exhibit additive effects compared to naltrexone alone [ 51 ]. Conducted by scientists supported by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA), part of the National Institutes of Health, the study found that alcohol dependent patients using gabapentin were more likely to stop drinking or refrain from heavy drinking than those taking placebo. Gabapentin can help with alcohol withdrawal by counteracting the physiological effects of the syndrome. Evidence indicates that symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome stem from reduced Evidence from single-site studies lend support to the safety and efficacy of gabapentin as a novel treatment for alcohol use disorder, with unique benefits for alcohol-related insomnia and negative affect, relative to available treatments. GABAPENTIN IN MANAGEMENT OF ALCOHOL WITHDRAWAL SYNDROME . Abstract. Alcohol abuse, complicated by a dependency relationship, is the third leading modifiable cause of death in the United States. In patients with chronic alcohol use disorder who experience a sudden cessation or Gabapentin is a prescription medication used to treat epilepsy, nerve pain, shingles, restless leg syndrome, and alcohol use disorder. However, it can be dangerous to drink alcohol while taking gabapentin. Both substances are depressants that slow down the body and brain.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |