Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
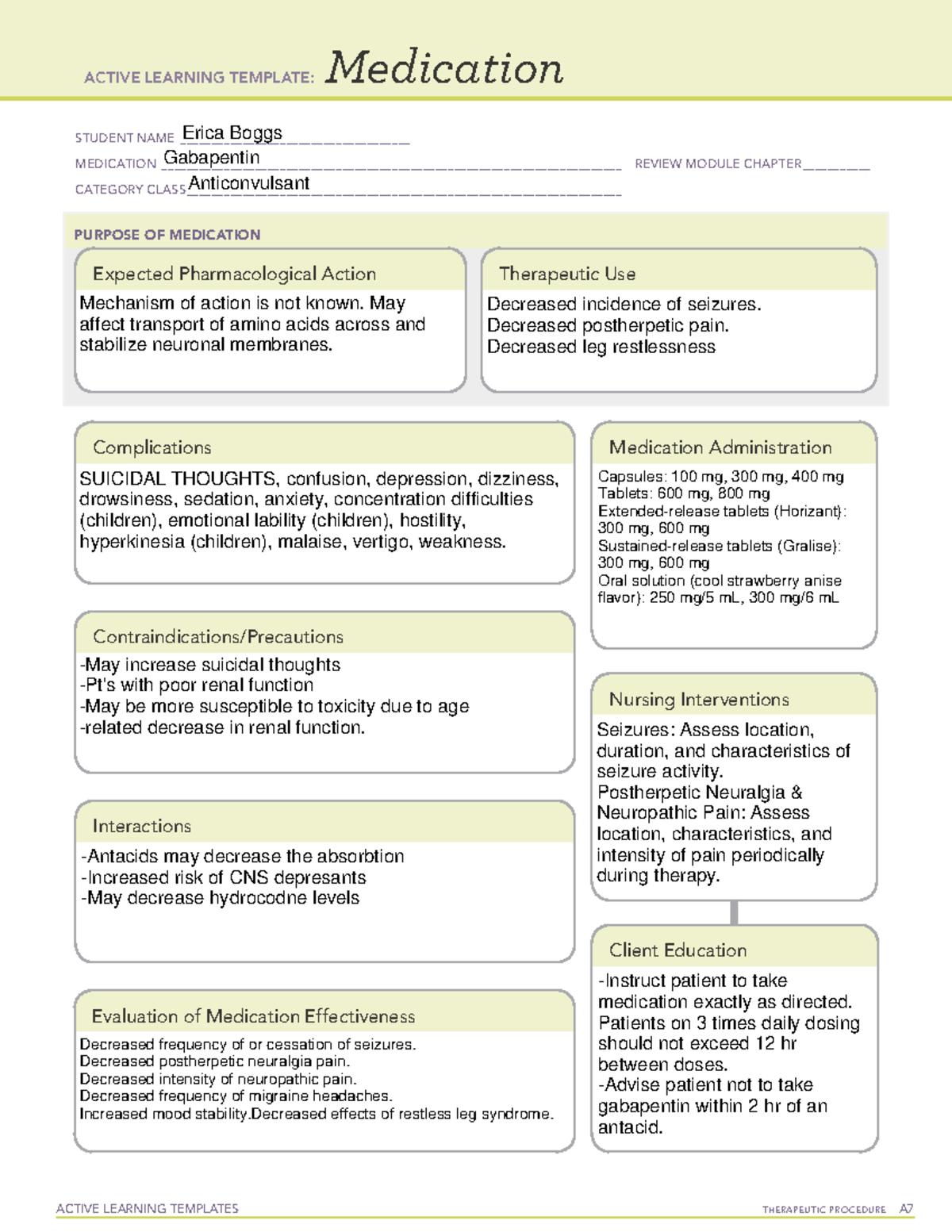
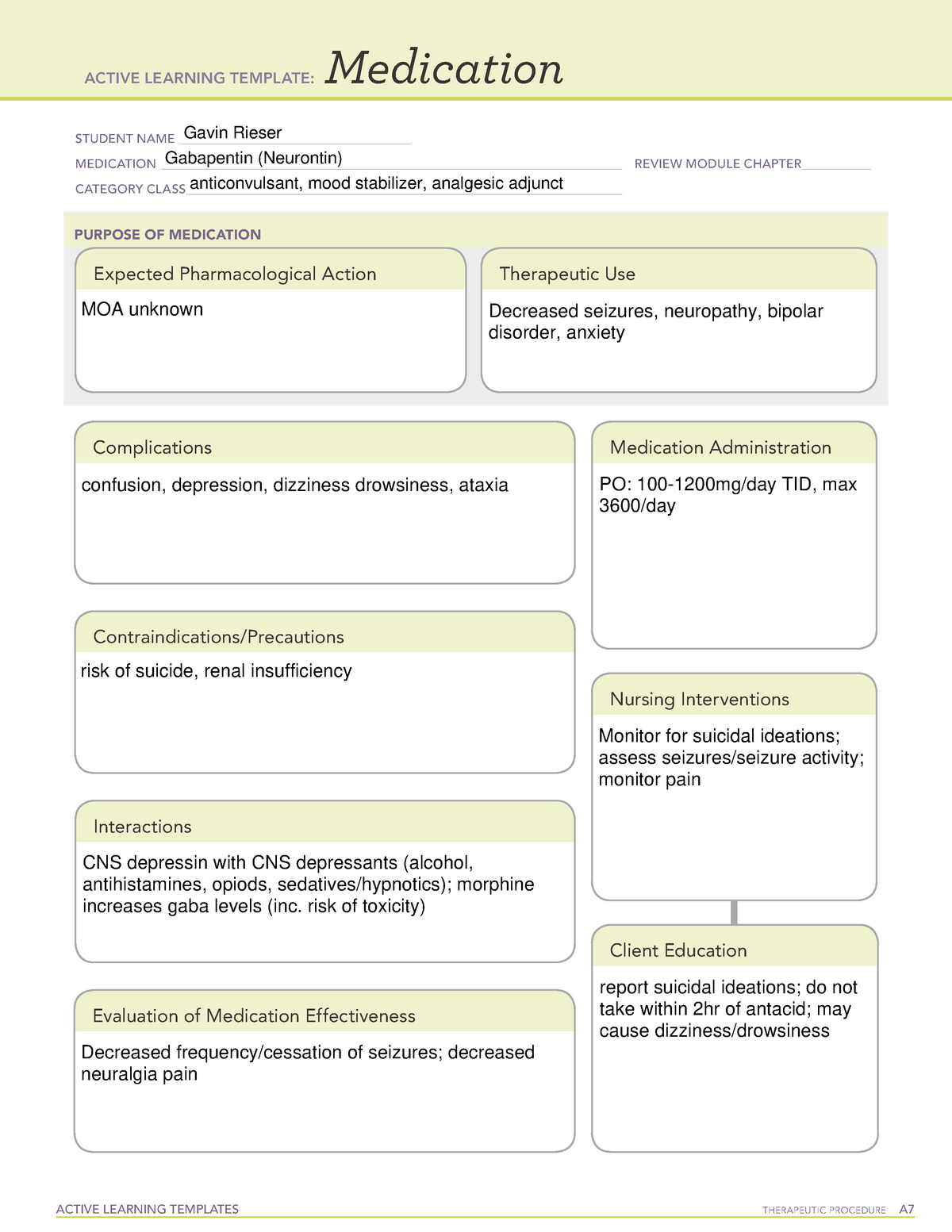
Gabapentin administration requires meticulous nursing care. Nurses ensure proper medication administration, closely monitor side effects such as drowsiness and dizziness, and assess for drug interactions. Patient education is crucial to promote adherence and minimize adverse effects. Nursing Considerations for Gabapentin. When administering or caring for patients taking gabapentin, nurses should consider several important factors. Nursing Assessment. 1. Assess the patient’s medical history, including any known allergies, previous adverse reactions to gabapentin or similar medications, and relevant medical conditions. Gabapentin This information from Lexicomp explains what you need to know about this medication, including what it’s used for, how to take it, its side effects, and when to call your healthcare provider. Brand Names: US Gabarone; Gralise; Neurontin Brand Names: Canada AG-Gabapentin; APO-Gabapentin; Auro-Gabapentin; BIO-Gabapentin [DSC]; Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used in the prevention of partial seizures. It is frequently used for neuropathic pain including diabetic neuropathy, radiculopathy, shingles, and trigeminal neuralgia. Antiseizure agents (also known as antiepileptic drugs or as anticonvulsants) are drugs used to manage epilepsy, the most prevalent neurological disorder. Antiseizure agents of choice depends on the type of epilepsy, age of the patient, patient tolerance, and specific patient characteristics. Table of Common Drugs and Generic Names Here is a table of commonly encountered antiseizure agents "Mosby's 2021 Nursing Drug Reference (34e)" Mosby (2021) "Pharmacology: A Patient-Centered Nursing Process Approach (8e)" Elsevier Health Sciences (2014) "Focus on Nursing Pharmacology" LWW (2019) "Saunders Comprehensive Review for the NCLEX-RN Examination (8e)" Saunders (2020) "Lehne's Pharmacology for Nursing Care" Elsevier Health Sciences (2014) Gabapentin may cause suicidal thoughts, ataxia, or lack of muscle control and depression with these things in mind, monitor your patient for changes and behavior and depression while on Gabapentin, make sure you assess seizure activity and pain level in your patient, teach your patient to take this medication exactly as it's directed and to Lehne’s Pharmacology for Nursing Care (11th Edition) The Eleventh Edition of Lehne’s Pharmacology for Nursing Care provides a thorough understanding of key drugs and their implications for nursing care. This text, written by renowned nursing educators, helps you comprehend and apply pharmacology principles. Generic Name: gabapentin. Brand Name: Apo-Gabapentin (CAN), Gen-Gabapentin (CAN), Neurontin. Classification: Antiepileptic. Pregnancy Category C. Dosage & Route. Available forms : Capsules—100, 300, 400 mg; tablets—100, 300, 400, 600, 800 mg; oral solution—250 mg/5 mL. ADULTS. Epilepsy: Starting dose is 300 mg PO tid, then titrated up as Point of Care - Clinical decision support for Gabapentin. Treatment and management. Indications, Mechanism of Action, Administration, Adverse Effects, Contraindications, Monitoring, Toxicity, Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes Gabapentin may cause suicidal thoughts, ataxia, or lack of muscle control and depression with these things in mind, monitor your patient for changes and behavior and depression while on Gabapentin, make sure you assess seizure activity and pain level in your patient, teach your patient to take this medication exactly as it's directed and to Understanding gabapentin's indications, mechanisms, and potential complications helps nurses provide comprehensive care and improve patient outcomes. Nursing Considerations Therapeutic Effects Side/Adverse Effects; Anticonvulsant: gabapentin: Administer first dose at bedtime to decrease dizziness and drowsiness Monitor for worsening depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior Taper dose; do not stop abruptly: Decreased neuropathic pain or seizures Find information on Gabapentin (Gralise, Horizant) in Davis’s Drug Guide including dosage, side effects, interactions, nursing implications, mechanism of action, half life, administration, and more. SN to educate patient concerning the use of gabapentin is to increased pain relief affects by using the CNS to decrease symptoms of pain and assist Tramadol or other prescribed pain medications, even Tylenol ER in ultimate pain relief. SN to advise patient to not allow pain level to linger for long periods of time; try taking either drug 30mins Gabapentin is one of the top 100 drugs prescribed in the US, so there’s a very good chance it will show up on NCLEX or your nursing school exams. Let’s go through the key things you need to know about this medication using the Straight A Nursing DRRUGS framework. Identify appropriate indications for use of gabapentin. Relate general characteristics of gabapentin to specific patient situations. Apply nursing process considerations for gabapentin to specific patient situations. Correctly calculate dosage for gabapentin. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication commonly prescribed for epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and various off-label uses. Understanding proper nursing considerations is crucial for safe and effective patient care. In this article, you’ll learn about Gabapentin (Neurontin) nursing implications and patient teachings. Also, its dosage, indication, contraindications, interactions, side effects, nursing assessment, and nursing interventions. Generic Name: Gabapentin. Brand Names: Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant. What are the indications of gabapentin (Neurontin)? Other recommended site resources for this nursing care plan: Nursing Care Plans (NCP): Ultimate Guide and Database MUST READ! Over 150+ nursing care plans for different diseases and conditions. Includes our easy-to-follow guide on how to create nursing care plans from scratch. Nursing Diagnosis Guide and List: All You Need to Know to Master
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |