Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 | 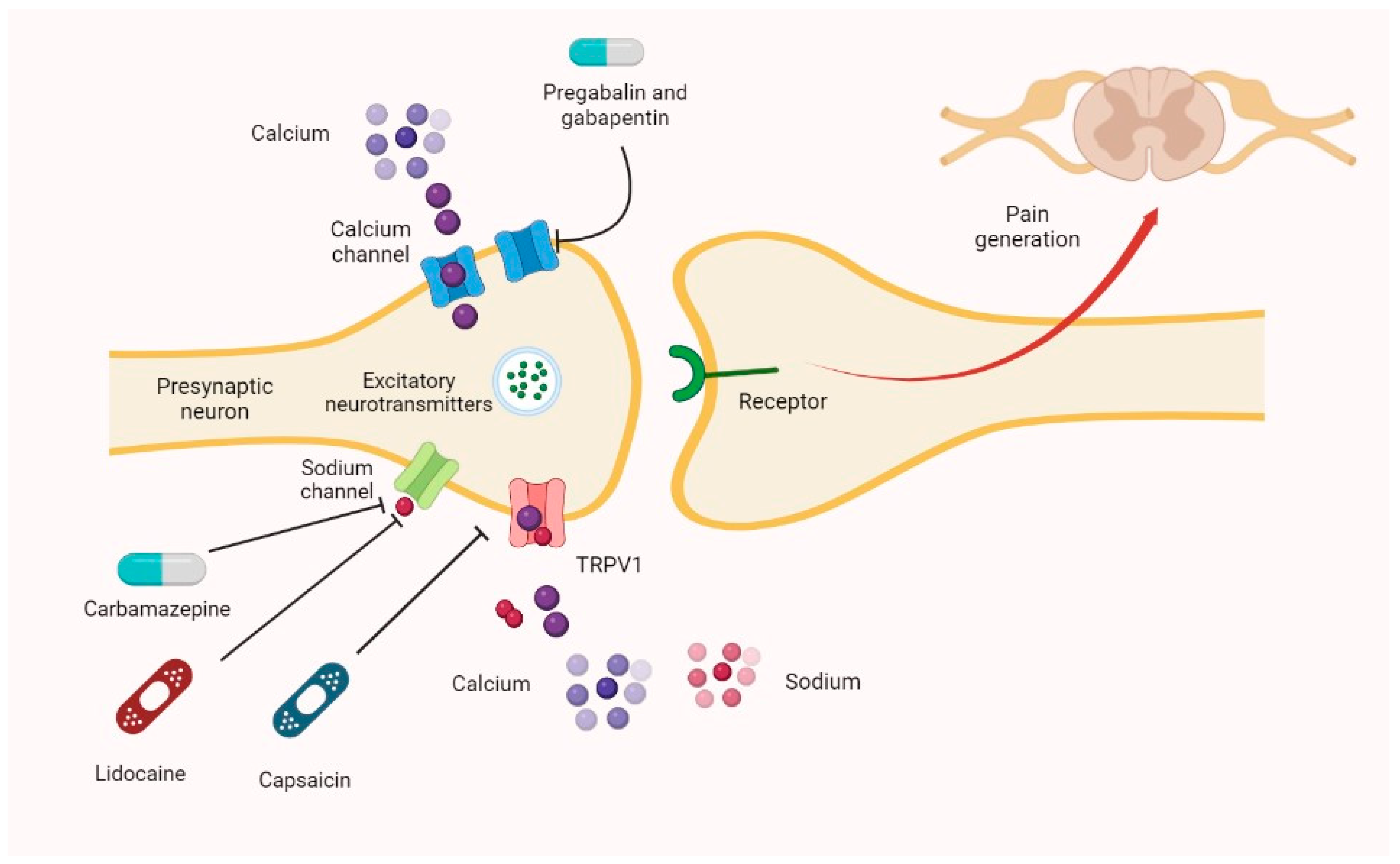 |
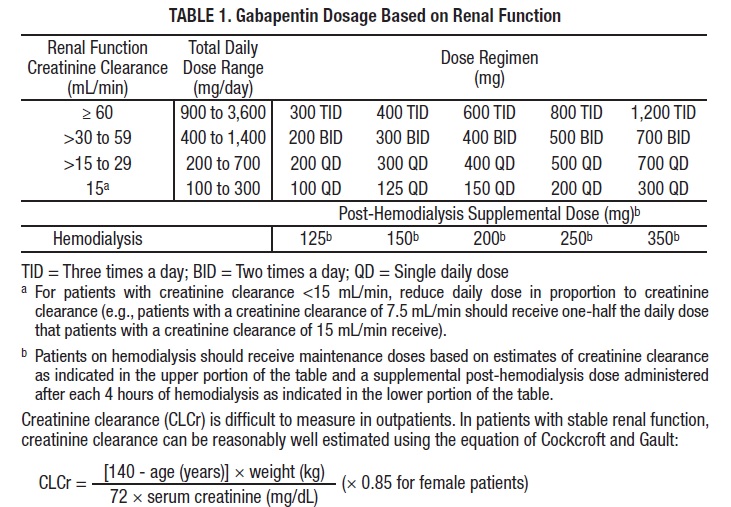
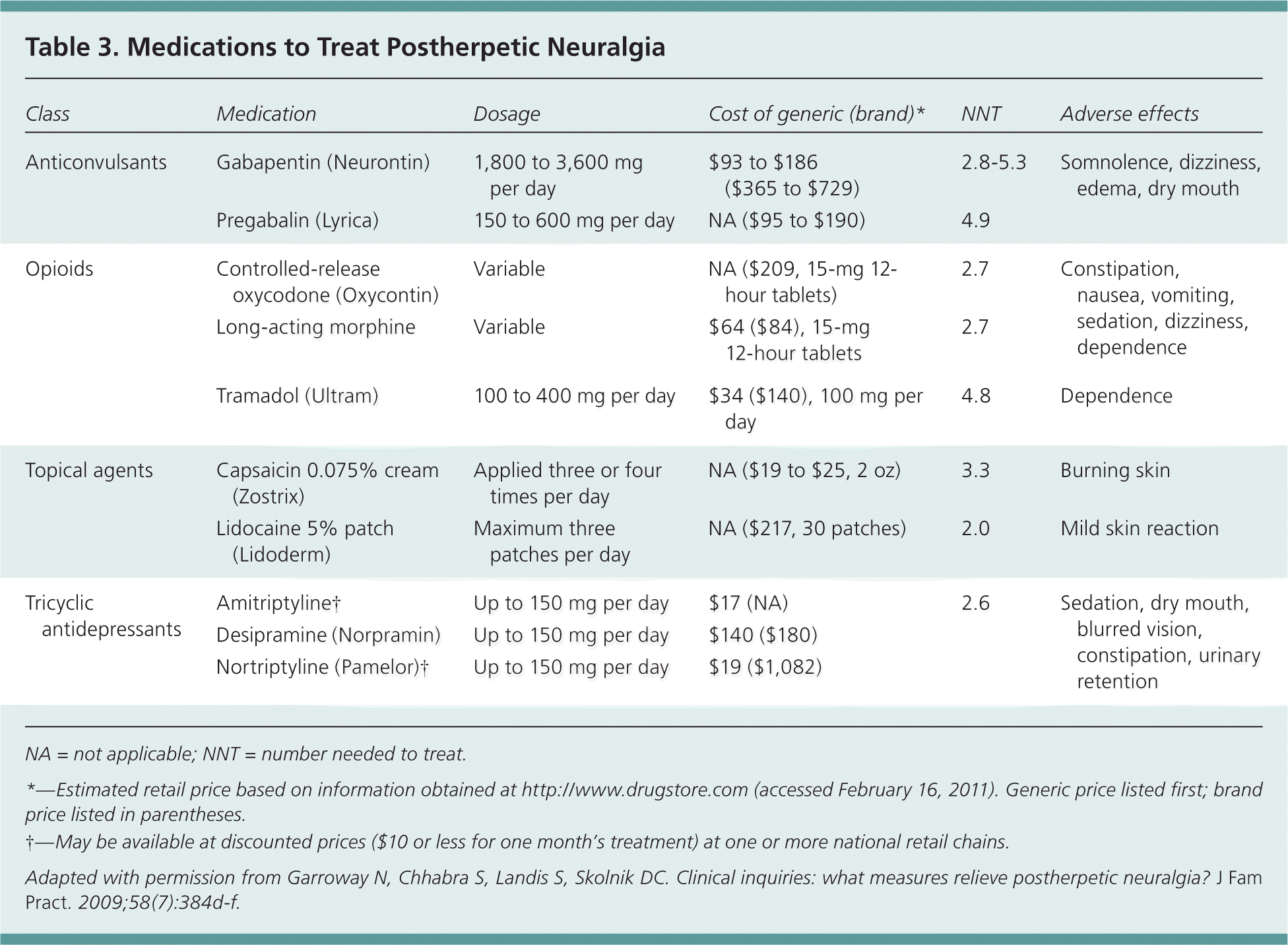
Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. The short answer is: generally, no, gabapentin does not provide immediate pain relief in the way that an opioid might. While some individuals may experience subtle effects soon after taking a dose, the significant benefits, such as pain reduction or anxiety relief, usually take time to manifest. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Had a lady picking up Gabapentin tonight who was obviously in pain. She asked what the onset of action is. I explained to her that it is usually a titration over several days to find the most effective dose for the patient. She insisted I tell her how quickly it would work. I looked in Clinical Pharmacology but could not find anything. So I The onset of action can vary based on the dosage and the condition being treated, but gabapentin is generally well tolerated and effective for both neuropathic pain and seizure management. Pregabalin and gabapentin share a similar mechanism of action, inhibiting calcium influx and subsequent release of excitatory neurotransmitters; however, the compounds differ in their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic characteristics. Gabapentin is absorbed slowly after oral administration, with m Mechanism of action. Gabapentin has no direct GABAergic action and does not block GABA uptake or metabolism. Gabapentin blocks the tonic phase of nociception induced by formalin and carrageenan, and exerts a potent inhibitory effect in neuropathic pain models of mechanical hyperalgesia and mechanical/thermal allodynia. Identify the appropriate indications for gabapentin therapy, including neuropathic pain, partial onset seizures, restless legs syndrome, and other relevant neurological and psychiatric conditions. Gabapentin's exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it is believed to work by reducing abnormal electrical activity in the brain. It is thought to bind to calcium channels, modulating their activity and reducing the release of neurotransmitters involved in seizures and nerve pain. Gabapentin is a structurally related to GABA that modulates the release of excitatory neurotransmitters. It has a variable and saturable absorption, a long half-life, and a dose-dependent clearance. The onset of action varies depending on the indication and formulation. The bioavailability of gabapentin decreases as the dosage increases, dropping from 60% at 900 mg/day to 33% at 3600 mg/day. This non-linear absorption can make its pharmacokinetics less predictable, affecting how quickly and effectively the drug works. Clinical Efficacy and Onset of Action Neuropathic Pain Onset of action may be seen as early as the second week of treatment with rapid titration, but the peak effect usually occurs about 2 weeks after a therapeutic dosage is achieved; therefore, an adequate trial may be 2 months or longer. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used for seizures or nerve pain. Learn about its different forms, how it works, common side effects, and how to take it safely. Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10] [7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. [11] 3 days. The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. NEURONTIN may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or Factors Influencing Gabapentin’s Onset of Action The time it takes for gabapentin to work in dogs is influenced by several factors, including: H3: Dog’s Individual Characteristics: Each dog’s metabolism, age, weight, and overall health can affect how quickly the medication is absorbed and processed. Gabapentin can take several weeks to reach its full effect for nerve pain, seizures, or restless legs syndrome. The dose is usually started low and increased gradually, and should not be stopped suddenly to avoid withdrawal symptoms. Although both gabapentinoids are absorbed in the small intestine, pregabalin is also absorbed in the proximal colon. Absorption of gabapentin is solely dependent on LAT that are easily saturable, resulting in dose-dependent pharmacokinetics. Onset of Action The time it takes for gabapentin to start working can vary. Many pet owners notice their dogs experience some relief within 1-2 hours of administration, but it can take longer to reach the full effect. ONSET, PEAK AND DURATION OF COMMON PAIN MEDICATIONS Medication Onset of Action (minutes)* Peak Effect (hours)* Duration of Action (hours)* Route of Admin. Comments Methadone 30 -60 1 -2 4 -6 Full analgesic effects, are not attained until 3 to 5 days after initiation of dosing. Drug is known to eliminate slowly causing high risk of overdose
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |