Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
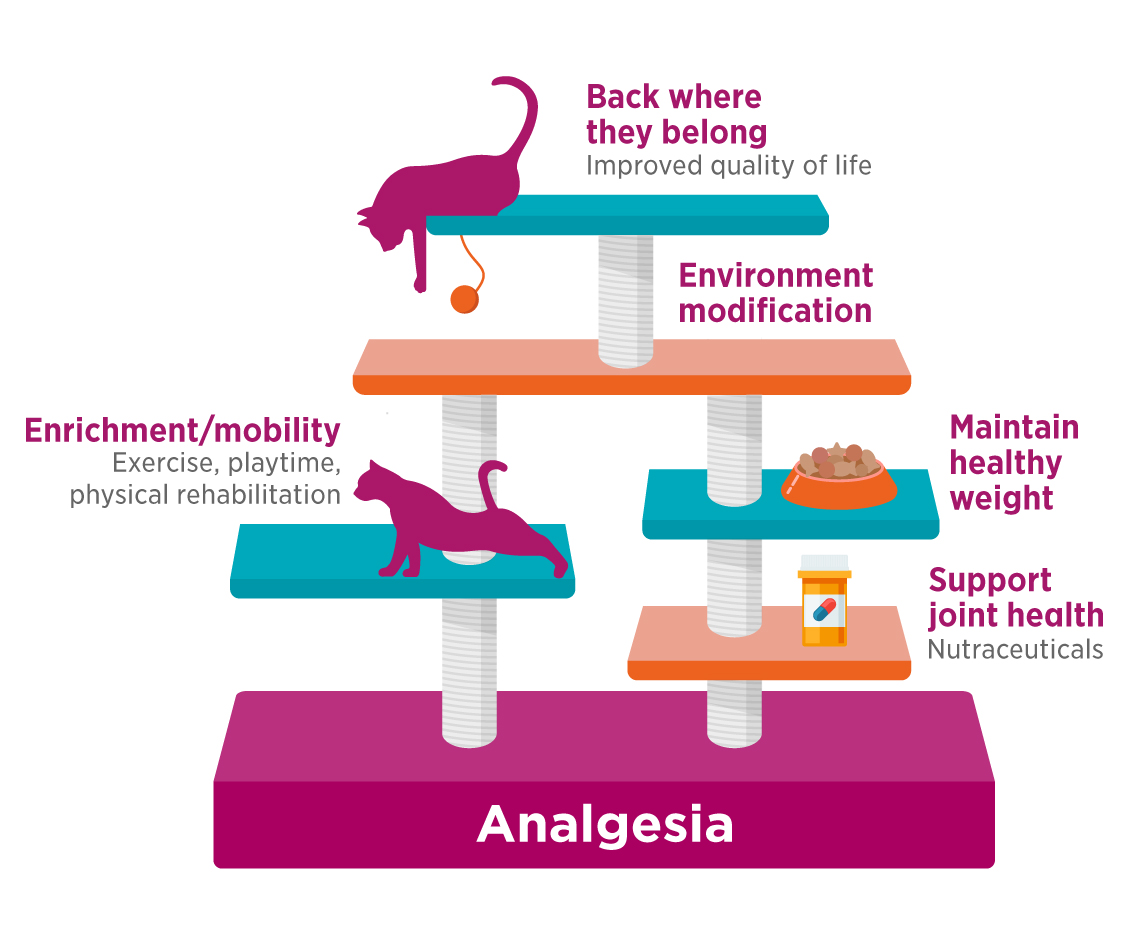
In cats, it showed efficacy in post-ovariohysterectomy-related pain and in anxiety management. In horses, gabapentin has been administered as an analgesic for chronic pain management. Gabapentin Onset of Action: How Long Does It Take to Take Effect? Pharmacokinetics of Gabapentin. Gabapentin, a medication commonly used to treat neuropathic pain and seizures, has a unique pharmacokinetic profile. After oral administration, gabapentin is absorbed slowly, with maximum plasma concentrations typically reached within 3 to 4 hours Objectives: To evaluate the pharmacokinetics of clinically relevant dosing regimens of gabapentin in cats. Animals: Eight research-purpose mixed-breed cats. Methods: Cats were enrolled in a serial order, non-randomized pharmacokinetic study. Gabapentin Dosage for Cats. The dosage for gabapentin may vary depending on a cat’s size, as well as whether it’s being used as a pain medication, as part of seizure management, or as a sedative before vet visits or travel. From a safety perspective, a gabapentin dosage for cats will typically not exceed 50-100mg per cat to address pain or FAQ About Gabapentin for Cats. 1. Does gabapentin make cats sleepy? 2. Is gabapentin used for pain management in cats? 3. Can gabapentin help reduce anxiety in cats? 4. How long does the sedative effect of gabapentin last in cats? 5. Can liquid gabapentin be stored at room temperature? 6. How long is liquid gabapentin stable once prepared? 7 Gabapentin in the management of restless legs syndrome (RLS) has been evaluated in small controlled trials, demonstrating benefits compared with placebo. Gabapentin enacarbil is FDA-approved for the treatment of RLS Garcia-Borreguero 2002, Saletu 2010. The . Social anxiety disorder, adjunct to antidepressants or monotherapy (alternative agent)c The question of how quickly gabapentin works for pain in cats is a common one for pet owners seeking relief for their feline companions. The short answer is that gabapentin can begin to provide pain relief within one to two hours of administration, though the full effects and duration can vary. In general, Gabapentin has a half-life of around 2-3 hours in cats, meaning that it takes this amount of time for half of the medication to be eliminated from the body. However, the effects of Gabapentin can last longer than its half-life due to the way it is metabolized in the body. Gabapentin enacarbil (brand name Horizant) is a prodrug of gabapentin that has been designed to overcome the limitations of gabapentin, such as poor absorption and a short duration of action. It requires hydrolyzation in the gastrointestinal tract to become active. Gabapentin belongs to the group of medicines known as anticonvulsants. 2. Upsides In summary, Gabapentin works relatively quickly in cats when administered properly. Oral administration takes effect within one to two hours, while sublingual administration can provide relief within 15-30 minutes. Most cats will feel the impact of gabapentin for about 8 to 12 hours, with the medication’s effects being largely gone within 24 hours. However, this timeframe can be extended in cats with kidney or liver impairment , as these conditions can slow the body’s ability to process and remove the drug. The number of clinical studies into gabapentin’s efficacy in cats has been limited, but a study from 2017 published in the Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association confirmed that administering the medication to cats 90 minutes prior to a vet visit significantly reduces signs of stress-related behaviors during transportation and Gabapentin has several features that make it attractive for use as an analgesic in cats. Gabapentin is not a controlled substance and is widely available as an oral formulation. Gabapentin is the most commonly prescribed medication for the treatment of chronic musculoskeletal pain in cats. Despite this common and chronic usage, clinically relevant pharmacokinetic data is lacking. To evaluate the pharmacokinetics of clinically relevant dosing regimens of gabapentin in cats. Eight research‐purpose mixed‐breed cats. Gabapentin is a commonly prescribed medication for cats, used primarily for managing pain, anxiety, and seizures. But how long does it take for this medication to actually start working? The short answer is that gabapentin typically begins to take effect within one to two hours after administration. Cats: 50–100 mg/cat. Class. Serotonin 2A antagonist/reuptake inhibitor (SARI) MOA. Some selective inhibition of 5HT reuptake, antagonizes 5HT2A receptors, releasing 5HT1A. Onset of action. 60–120 minutes. Duration of action. About 8 hours. Contraindications. Use caution in patients with severe systemic disease. Drug interactions Gabapentin (brand names: Neurontin®, Aclonium®, Equipax®, Gantin®, Gabarone®, Gralise®, Neurostil®, Progresse®) is an anti-seizure and pain medication that is used with other medications to treat seizures and chronic pain, primarily nerve pain, in dogs and cats. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug, which presents an established clinical efficacy in human patients for the management of refractory partial seizures, secondarily generalized tonic-clonic seizures, and for the control of chronic neuropathic pain. Gabapentin was synthesized as a structural analog While the duration of action of gabapentin can vary, it typically lasts around 8 to 12 hours in a cat. By working closely with your veterinarian and monitoring your cat for any signs of distress or side effects, you can help ensure that gabapentin is safe and effective for your furry friend. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug, which presents an established clinical efficacy in human patients for the management of refractory partial seizures, secondarily generalized tonic-clonic seizures, and for the control of chronic neuropathic pain. Gabapentin was synthesized as a structural analogue of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA, with GABA-mimetic effects, able to cross the blood
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |