Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
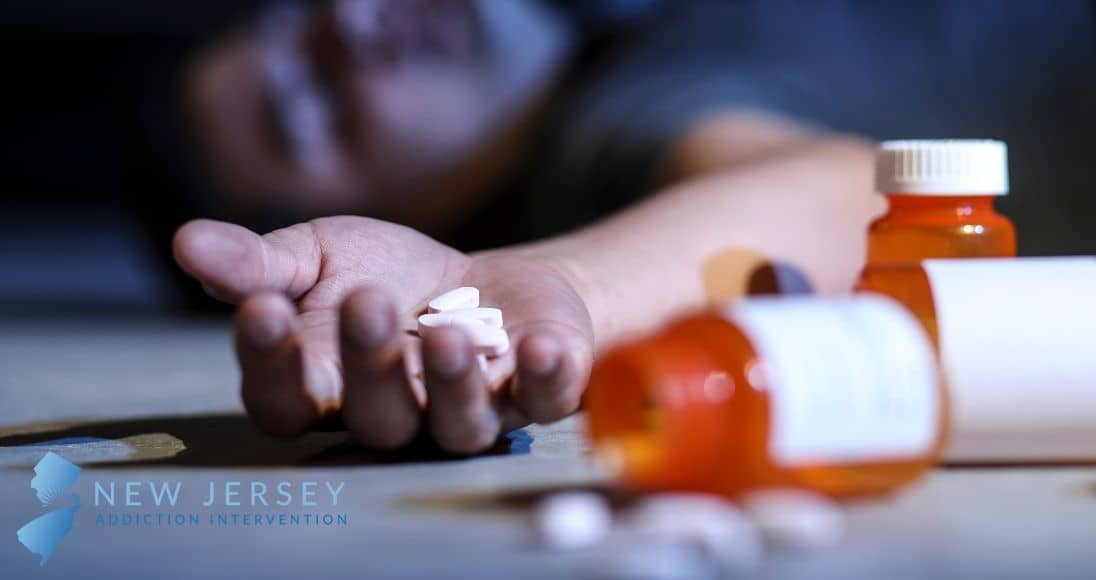
Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin overdose can be serious and may result in many symptoms, from mild drowsiness to life-threatening complications. Understanding the signs, risks, and proper management of gabapentin overdose is crucial for medical professionals and individuals using the medication. A gabapentin overdose is rare, but it is possible. The likelihood of an overdose increases when you abuse gabapentin with other drugs like opioids and alcohol. If you or someone you know is experiencing a gabapentin overdose, seek medical help immediately. Cardiovascular disease; chronic constipation; diabetes; epilepsy; history of bipolar disorder; history of psychosis; hyperthyroidism (risk of arrhythmias); increased intra-ocular pressure; patients with a significant risk of suicide; phaeochromocytoma (risk of arrhythmias); prostatic hypertrophy; pyloric stenosis; susceptibility to angle-closure glaucoma; urinary retention Overdose Symptoms of poisoning by selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors include nausea, vomiting, agitation, tremor, nystagmus, drowsiness, and sinus tachycardia; convulsions may occur. Rarely, severe poisoning results in the serotonin syndrome, with marked neuropsychiatric effects, neuromuscular hyperactivity, and autonomic instability What are the symptoms of a gabapentin overdose? Common symptoms of gabapentin overdose are drowsiness, fast heartbeat, dizziness, low blood pressure, nausea, vomiting, and impaired coordination. In severe cases, lethargy, coma, and death may occur. What happens if I overdose? Seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222. An overdose can be fatal. Overdose symptoms may include slow breathing, double vision, tremor, slurred speech, drowsiness, change in your mental state, dizziness, tiredness, or diarrhea. What should I avoid while taking gabapentin? When you stop taking gabapentin, you'll need to reduce your dose gradually to avoid withdrawal symptoms. Do not stop taking gabapentin without talking to your doctor. Talk to your doctor if you're concerned about becoming physically dependent on gabapentin. Other side effects. These are not all the side effects of gabapentin. Co-prescribing of opioids and gabapentinoids should be avoided if possible, due to the increased risk of respiratory depression, accidental overdose, and death. Gabapentinoids are commonly ingested in self-harm attempts and often misused for their sedative and euphoric properties. These medications can cause lethargy or agitation in overdose, increase risk of death combined with opioids, and manifest a withdrawal syndrome. Gabapentin enacarbil available under the trade name Horizant is the only gabapentin product approved for treatment of Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS). A daily dose of 1200 mg provided no additional benefit compared with the 600 mg dose, but caused an increase in adverse reactions. Adult Initially 25 mg once daily for 14 days, then 50 mg daily in 1–2 divided doses for further 14 days, then 100 mg daily in 1–2 divided doses for further 7 days; maintenance 200 mg daily in 1–2 divided doses, patients stabilised on lamotrigine for bipolar disorder may require dose adjustments if other drugs are added to or withdrawn from their treatment regimens—consult product View pregabalin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. View duloxetine information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, important safety information and drug action. When there is uncertainty about whether the presentation was due to therapeutic excess, the patient should be managed as a staggered overdose. A staggered overdose involves ingestion of a potentially toxic dose of paracetamol over more than 1 hour, with the possible intention of causing self-harm. All patients who have taken a staggered A lower starting dose may be necessary to prevent overdose and accumulation of the drug in the body. Monitoring of kidney function is recommended. Gabapentin use in pediatric patients. Gabapentin is approved for use in children 3 years of age and older for certain indications٫ such as partial seizures. Gabapentin may exacerbate seizures in patients with absence or myoclonic seizures (including juvenile myoclonic epilepsy), tonic or atonic seizures, Dravet syndrome, Lennox-Gastaut syndrome, and myoclonic-atonic seizures. Anaesthesia with postoperative indwelling epidural catheter (risk of paralysis—monitor neurological signs and wait 20–30 hours after apixaban dose before removing catheter and do not give next dose until at least 5 hours after catheter removal); elderly; low body-weight; risk of bleeding Anyone who shows signs of an overdose or allergic reaction to gabapentin should contact emergency medical services immediately. Left untreated, these symptoms can turn fatal. Signs and Symptoms of Gabapentin Overdose. A gabapentin overdose can be dangerous or even deadly. Some factors can increase the risk of a fatal overdose, such as taking several substances at once. Gabapentin overdose symptoms can include: Drowsiness; Movement difficulties; Dizziness; Nausea or vomiting; Rapid heartbeat; Low blood pressure
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |