Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
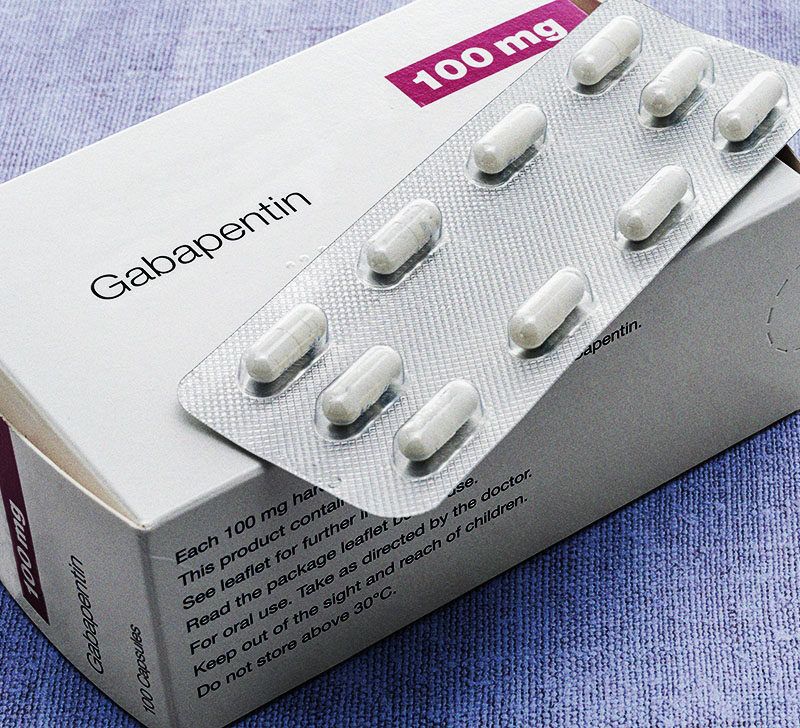
Side Effects Common side effects of gabapentin. Gabapentin can cause several common side effects, including dizziness, drowsiness, and fatigue. Other commonly reported side effects include headache, nausea, and blurred vision. These side effects are usually mild and tend to improve over time as the body adjusts to the medication. These side effects are usually mild and go away after a few days or weeks. However‚ if you experience any side effects that are severe or that do not go away‚ talk to your doctor. Gabapentin can also cause serious side effects‚ such as⁚ Stevens-Johnson syndrome (a rare but serious skin condition) Research suggests that gabapentin may increase slow-wave sleep, also known as deep sleep, which is crucial for physical recovery and memory consolidation. This effect could be particularly beneficial for individuals who struggle to achieve restorative sleep due to pain or anxiety. Find patient medical information for Gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin) on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings, and user ratings Side effects: Even if gabapentin works well for the treatment of your sleep disorder, it may induce unwanted side effects. Common side effects reported among gabapentin users include: dizziness, somnolence, gait disturbance, and peripheral edema – respectively. Gabapentin is a medication commonly used to treat seizures, nerve pain, and other conditions. While it can be an effective treatment option for many patients, it's important to be aware of the potential side effects, including insomnia. What is Insomnia? Insomnia is a sleep disorder that can make it difficult to fall asleep, stay asleep, or both. Some research suggests that gabapentin might alter the distribution of sleep stages throughout the night, potentially affecting the duration and quality of REM sleep. Research findings on gabapentin’s effects on REM sleep have yielded mixed results, highlighting the complexity of sleep pharmacology. Gabapentin side effects are usually mild, and they may be less common with gabapentin ER forms. Examples of mild side effects that can happen include: Vertigo (dizziness) Feeling fatigued or sleepy. Fluid retention. Trouble balancing or controlling movement. Diarrhea or constipation. Nausea and vomiting. Brain fog. Headache. Weight gain. Dry mouth Both gabapentin and many sleep aids act on the central nervous system (CNS), and combining CNS depressants can lead to enhanced sedation and potentially dangerous side effects. Known drug interactions between gabapentin and sleep aids are relatively few, but the cumulative effects of multiple CNS depressants can be significant. Note: In general, seniors or children, people with certain medical conditions (such as liver or kidney problems, heart disease, diabetes, seizures) or people who take other medications are more at risk of developing a wider range of side effects. View complete list of side effects. 4. Bottom Line. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain Dizziness and drowsiness are gabapentin’s most common side effects. Serious side effects include dependence, misuse, and trouble breathing. If you’re over the age of 65, take other medications that cause drowsiness, or drink alcohol, gabapentin may not be the best option for you. Dangerous side effects could occur. Gabapentin side effects. Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction to gabapentin: hives, difficult breathing, swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat. Seek medical treatment if you have a serious drug reaction that can affect many parts of your body. One of the most common side effects of gabapentin is drowsiness. In people taking gabapentin for its approved conditions (certain epileptic seizures and postherpetic neuralgia), 19% of patients older than 12 years of age with epilepsy and 21% of patients with postherpetic neuralgia reported drowsiness as a side effect. It took almost 2 weeks after that before those mining explosions stopped. For me, I have to stay on gabapentin at this high dose and accept side effects. If you can do without gabapentin and you don't like side effects, do that. I do sleep better these last 5 years since I started gabapentin. The comparison of Gabapentin vs Doxepin for Sleep: Comparing Effectiveness and Side Effects is one such consideration, as doxepin may offer sleep-promoting benefits with a different side effect profile. However, any medication changes should be made under close medical supervision and with careful consideration of the patient’s overall health Common side effects when using gabapentin as a sleep aid can include dizziness, drowsiness, and fatigue. These effects may be more pronounced in the beginning of treatment and often subside as the body adjusts to the medication. Some side effects of gabapentin may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. However, misusing gabapentin can lead to more severe sleep-related side effects. Plus, those taking gabapentin for reasons other than insomnia may find the drowsiness uncomfortable. If you or someone you love is taking gabapentin without a prescription or struggling with substance use, Zinnia Health can offer the guidance you need.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |