Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
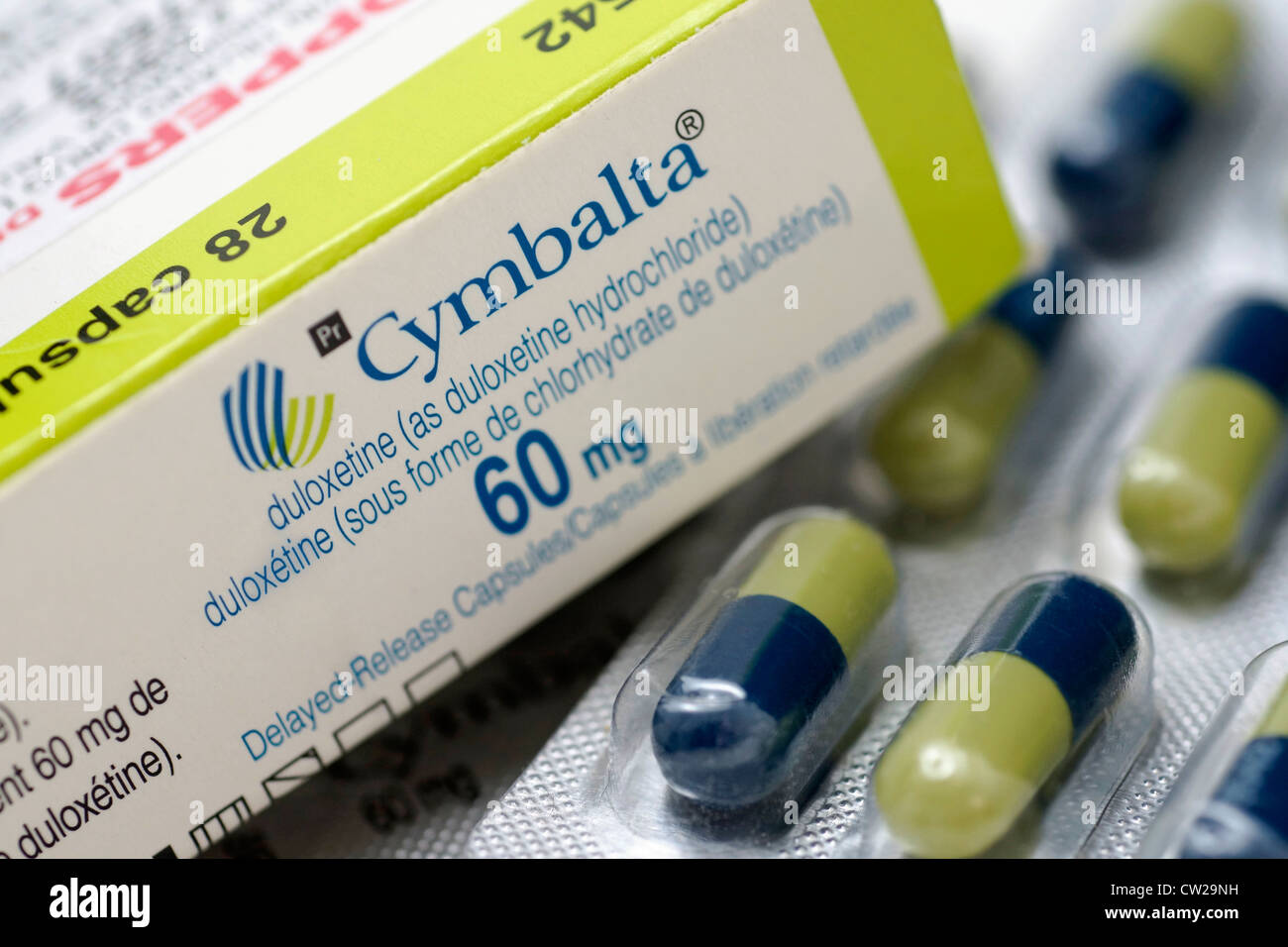
Pregabalin + Duloxetine Pregabalin + Venlafaxine: Spinal nerve ligation model in rat (von Frey test) NA: Additive anti-allodynic effect of pregabalin + duloxetine, potentially antagonistic effects with pregabalin + venlafaxine : Gabapentin + Venlafaxine: Doses titrated to achieve optimal efficacy and tolerability (dose range: CONCLUSION: Duloxetine was noninferior to pregabalin for the treatment of pain in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy who had an inadequate pain response to gabapentin. Based on the pooling of common outcomes measured in randomized, controlled trials, we conclude that duloxetine is comparably effective and tolerable in the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain to two anticonvulsants, gabapentin and pregabalin, which are pharmacologically unrelated to duloxetine. • Amitriptyline is considered by JAPC to be the most cost effective first line choice. Duloxetine is a cost effective second line choice. • Consider the potential for misuse or illicit diversion before prescribing pregabalin, gabapentin or tramadol. Patients should be told about the risk of abuse and dependence. Duloxetine, sold under the brand name Cymbalta among others, [1] is a medication used to treat major depressive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, obsessive–compulsive disorder, fibromyalgia, neuropathic pain, and central sensitization. [10] [11] It is taken by mouth. [10] Duloxetine is a serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor given careful consideration before being prescribed pregabalin and gabapentin. Treatment should be reviewed regularly. NICE Clinical guideline 173 states “Offer a choice of amitriptyline, duloxetine, gabapentin or pregabalin as initial treatment for neuropathic pain (except trigeminal neuralgia)”. Pregabalin To conduct a network meta-analysis comparing the safety and efficacy of gabapentin (GBP), pregabalin (PGB), oxcarbazepine (OXC), and duloxetine (DLX) in treating diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN). The study’s eligibility criteria includee Pregabalin/gabapentin vs. placebo: The SNRI duloxetine resulted in moderate improvements in short-term pain and small improvements in short-term function and quality of life compared with Approved or recommended drugs in this indication include duloxetine (DLX), pregabalin (PGB), gabapentin (GBP) and amitriptyline (AMT). We conducted an indirect meta-analysis to compare the efficacy and tolerability of DLX with PGB and GBP in DPNP, using placebo as a common comparator. An interaction with duloxetine could cause a serious condition called serotonin syndrome. Duloxetine is not approved for use by anyone younger than 7 years old. To make sure duloxetine is safe for you, tell your doctor if you have: heart problems, high blood pressure; liver or kidney disease; slow digestion; a seizure; bleeding problems; sexual Duloxetine, pregabalin and duloxetine plus gabapentin were generally safe and tolerable for the treatment of DPNP. Pregabalin (generic for Lyrica), a drug very similar to gabapentin, has been particularly well studied with gabapentin. One such study reported: Combining pregabalin and duloxetine for fibromyalgia improves multiple clinical outcomes vs monotherapy Pain . 2016 Jul;157(7):1532-40 Offer a choice of amitriptyline, duloxetine, gabapentin, or pregabalin. Titrate the dosage according to response and tolerability. Evaluate people carefully for a history of drug abuse before prescribing gabapentin or pregabalin and observe them for development of signs of abuse and dependence. In particular consider To compare the efficacy and safety of gabapentin (GBP), duloxetine (DLX), and pregabalin (PGB) in patients with painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPNP). Methods: A prospective, randomized, open label, 12-week study was conducted. Although both gabapentin and duloxetine can treat chronic pain, particularly neuropathic pain, they come from distinct classes, possess different mechanisms, and treat a variety of conditions beyond just nerve issues. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate therapy. Duloxetine and pregabalin show effective treatment results for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Gabapentin and pregabalin are more suitable for patients with HbA1c over 8.7. Duloxetine is recommended for patients with well-controlled HbA1c due to its effectiveness. Patients were randomized to duloxetine monotherapy (n=138), pregabalin monotherapy (n=134), or a combination of duloxetine and gabapentin (n=135). The primary objective was a noninferiority comparison between duloxetine and pregabalin on improvement in the weekly mean of the diary-based daily pain score (0- to 10-point scale) at end point. Duloxetine is used to treat depression and anxiety. It is also used for pain caused by nerve damage associated with diabetes (diabetic peripheral neuropathy). Duloxetine is also used to treat fibromyalgia (muscle pain and stiffness) and chronic (long-lasting) pain that is related to muscles and bones. Duloxetine at a daily fixed dose of 60 mg is efficacious in the relief of neuropathic pain. Pregabalin also showed a comparable outcome. Both duloxetine and pregabalin have a promising safety profile and are well-tolerated. Find patient medical information for Duloxetine (Cymbalta, Drizalma Sprinkle) on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings, and user ratings
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |