Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
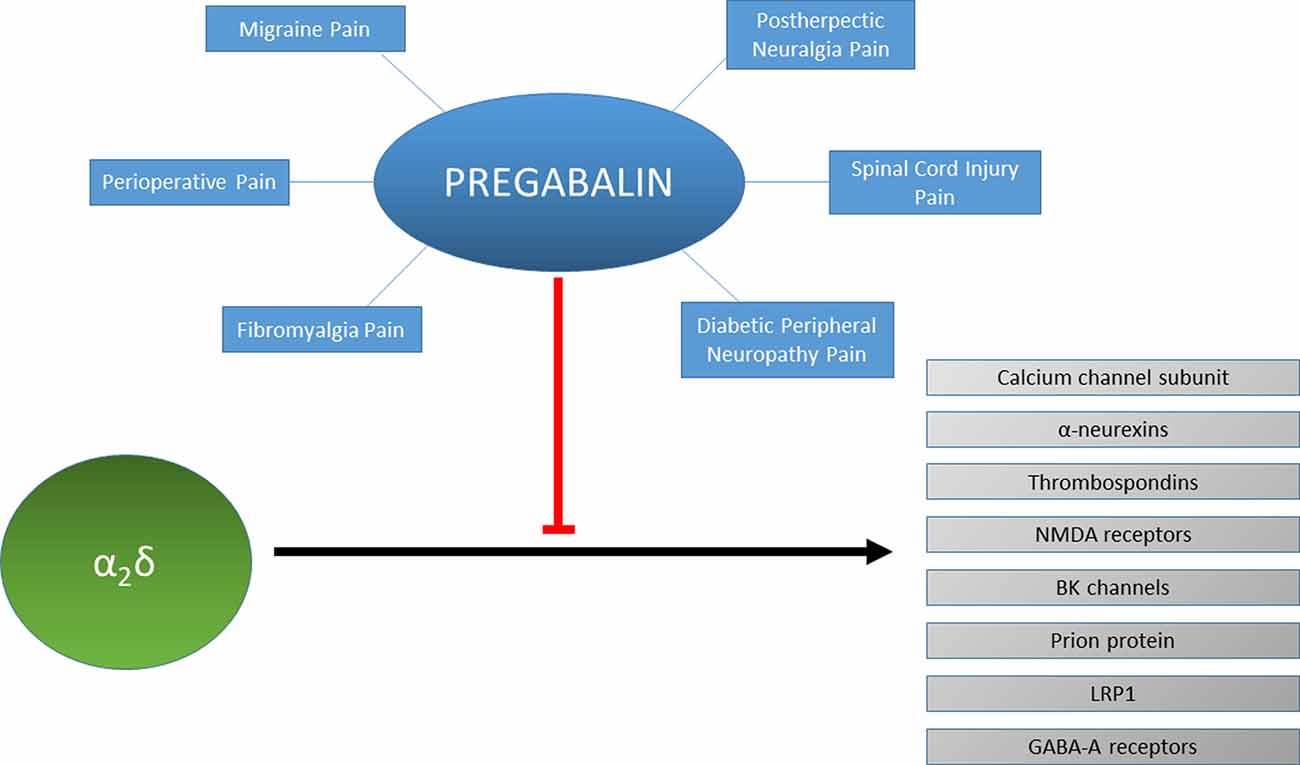 |
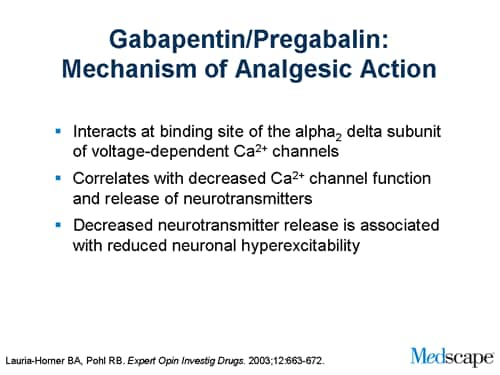
The mechanism of action of gabapentin and pregabalin has been the subject of many studies in recent years and, at present, is still not clear. the analgesic mechanism of action of the TCAs and Gabapentin and pregabalin are structurally related compounds with recognized efficacy in the treatment of both epilepsy and neuropathic pain. The pharmacological mechanisms by which these agents exert their clinical effects have, until recently, remained unclear. Mechanisms of action Gabapentin and pregabalin do not bind to GABA receptors despite their structural similarity but have a high affinity for the α2δ-1 subunit of voltage-gated cal-cium channels (VGCCs).19 VGCCs are composed of multiple subunits: 1, β, γ and α α2δ. The α 1 subunit allows entry of calcium and the extracellular α 2δ is Gabapentin and pregabalin are structurally similar to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), although they do not bind to GABA receptors. They bind to the α-2-delta subunit of voltage-dependent calcium channels (aka alpha-2-delta calcium channel ligands). Here we review the current understanding of the pathophysiological role of the α 2 δ‐1 subunit, the mechanisms of analgesic action of gabapentinoid drugs and implications for efficacy in the clinic. Despite widespread use, the number needed to treat for gabapentin and pregabalin averages from 3 to 8 across neuropathies. To recap: Pregabalin and gabapentin exhibit identical primary mechanisms of action as inhibitors of α2δ-subunit-containing voltage-dependent calcium channels. Pregabalin is more potent than gabapentin (by approximately 6-fold) in its magnitude of voltage-dependent calcium channel inhibition. The analgesic effects of pregabalin and gabapentin are facilitated by their modes of action, which involve binding to the α2δ subunit of voltage-activated calcium channels. Additionally, gabapentinoids have been shown to reduce analgesic tolerance and opioid-induced hyperalgesia ( 52 ). Mechanism of action of gabapentinoids Site of action The actions of gabapentinoids are mainly at an intracellular site and require active uptake.21 They were originallydesigned as g aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogues but do not have any effects on GABA receptors. Gabapentin binds to a 2d receptors with greater affinity to the a 2d-1 subtype.22 Although the exact mechanism of action is somewhat unclear, the drugs’ efficacy in neuropathic pain is linked to their ability to bind to voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system (CNS), specifically to the alpha-2-delta protein. The mechanism of action of onabotulinumtoxin A is to inhibit excitatory Preferential action of gabapentin and pregabalin at P/Q-type voltage Recently, it has been approved for treatment of anxiety disorders in Europe. Pregabalin is structurally related to the antiepileptic drug gabapentin and the site of action of both drugs is similar, the alpha 2 –delta (α 2 –δ) protein, an auxiliary subunit of voltage-gated calcium This document summarizes information about the anti-seizure medications gabapentin and pregabalin. It discusses gabapentin's mechanism of action, approved uses, dosing, pharmacokinetics, interactions, adverse effects and overdose treatment. Pregabalin and gabapentin share a similar mechanism of action, inhibiting calcium influx and subsequent release of excitatory neurotransmitters; however, the compounds differ in their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic characteristics. The interaction of gabapentin and pregabalin with conventional antiepileptic and analgesic drug targets is likely to be modest, at best, and has been largely dismissed in favour of a selective inhibitory effect on voltage-gated calcium channels containing the α 2 δ-1 subunit. This mechanism is consistently observed in both rodent- and human First, gabapentin is primarily absorbed in the small intestine, while pregabalin is absorbed at multiple sites, the small intestine and the ascending portion of the colon. 6 Second, gabapentin’s absorption is saturable; meaning that as gabapentin doses increase, the rate of absorption and resulting bioavailability decreases. Gabapentin and pregabalin are structurally related compounds with recognized efficacy in the treatment of both epilepsy and neuropathic pain. The pharmacological mechanisms by which these agents exert their clinical effects have, until recently, remained unclear. Gabapentin and pregabalin are structurally related compounds with recognized efficacy in the treatment of both epilepsy and neuropathic pain. The pharmacological mechanisms by which these agents Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic agent but now it is also recommended as first line agent in neuropathic pain, particularly in diabetic neuropathy and post herpetic neuralgia. α2δ-1, an auxillary subunit of voltage gated calcium channels, has been documented as its main target and its specific binding to this subunit is described to produce different actions responsible for pain attenuation Gabapentin and pregabalin are structurally related compounds with recognized efficacy in the treatment of both epilepsy and neuropathic pain. The pharmacological mechanisms by which these agents exert their clinical effects have, until recently, remained unclear. Mechanisms of action. Gabapentin and pregabalin do not bind to GABA receptors despite their structural similarity but have a high affinity for the α2δ-1 subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs). 19 VGCCs are composed of multiple subunits: α 1, β, γ and α 2 δ.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |