Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
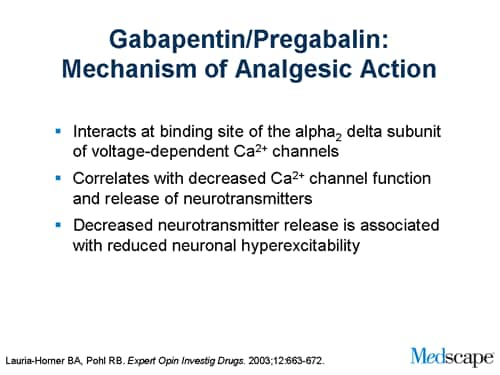
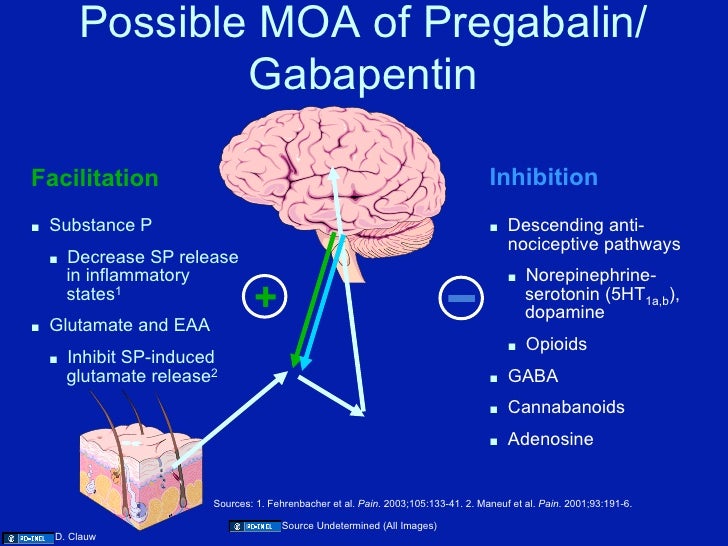
Among gabapentinoid drugs, gabapentin and pregabalin have been shown to be equally in reducing pain intensity, improving sleep quality and depression in patients with painful peripheral neuropathy (Biyik 2012). However, Saldana and co-workers have demonstrated the efficacy of pregabalin in gabapentin refractory patients (Saldaña et al. 2012). Pregabalin and gabapentin differ somewhat in terms of their dose-response curves. One study analyzed data from phase 2 trials of gabapentin and pregabalin and created a pharmacodynamic model. 3 The authors found that in patients with postherpetic neuralgia, mean pain scores decreased as the dose of both gabapentin and pregabalin increased. It discusses gabapentin's mechanism of action, approved uses, dosing, pharmacokinetics, interactions, adverse effects and overdose treatment. It then summarizes a clinical study comparing the dose-response relationship of pregabalin and gabapentin in patients with partial seizures, finding that pregabalin was more potent and effective at Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Gabapentin and pregabalin are analogs of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and share a similar mechanism of action, although they differ in some aspects. Both drugs bind to the α2δ subunit of calcium channels in neurons, but pregabalin exhibits greater affinity and potency in its binding (5, 6). The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are key front‐line therapies for various neuropathies of peripheral and central origin. Originally designed as analogs of GABA, the gabapentinoids bind to the α 2 δ‐1 and α 2 δ‐2 auxiliary subunits Gabapentinoids, including gabapentin and pregabalin, are extensively used for treatment of neuropathic pain, restless legs syndrome, and focal seizures. Their efficacy in these disorders is primarily attributed to their effects in inhibiting the functions of the α2δ subunit of presynaptic VGCCs, thereby reducing neurotransmitter release. A head-to-head trial between pregabalin (Lyrica) vs gabapentin (Neurontin) in patients with chronic sciatica found that gabapentin was superior to pregabalin in reducing leg pain with fewer side effects. Gabapentin and pregabalin are structurally related compounds with recognized efficacy in the treatment of both epilepsy and neuropathic pain. The pharmacological mechanisms by which these agents exert their clinical effects have, until recently, remained unclear. Pregabalin is administered BID or TID, gabapentin TID. Pregabalin is approximately 2.5 times more potent than gabapentin based on plasma concentrations. Distinct pharmacokinetic advantages exist for the second generation alpha-2-delta ligand, pregabalin. Pregabalin and gabapentin both show dose-response relationships in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia and partial seizures. For neuropathic pain, a pregabalin dosage of 450 mg/day appears to reduce pain comparably to the predicted maximum effect of gabapentin. Pregabalin and gabapentin both show dose-response relationships in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia and partial seizures. For neuropathic pain, a pregabalin dosage of 450 mg/day appears to reduce pain comparably to the predicted maximum effect of gabapentin. Both gabapentin and pregabalin are also effective treatments, with pregabalin recommended at a dose of 300 mg to 600 mg daily resulting in a significant reduction in pain scores (Juhn et al., 2015). Pregabalin suppresses the activity of excitatory primary afferent fibers that carry nociceptive information to the spinal dorsal horn (Biggs et al What are pregabalin and gabapentin? Pregabalin and gabapentin, collectively gabapentinoids, are primarily anticonvulsant drugs. Over the past decade, they have been increasingly prescribed for pain. 1 They are recommended for neuropathic pain in adults 2 3 (table 1), but are commonly used off-label for other pain disorders such as low back pain, sciatica, and migraine. 9 10 Pregabalin was one through system L-neutral amino acid transporters, pregabalin is rapidly and completely absorbed with peak plasma con-centrations within 1 h as opposed to 3 h with gabapentin.27 Unlike gabapentin, absorption of pregabalin is not saturable, with a linear pharmacokinetic profile and less variable bioavailability.27 Although peak plasma Gabapentin and pregabalin are narrow-spectrum antiepileptic drugs primarily employed in the management of refractory focal seizures, or seizures poorly controlled by other drugs. Gabapentin and pregabalin block voltage gated Ca2+ channels , thereby inhibiting calcium currents and subsequently reducing neurotransmitter release . Converting to Pregabalin. Conversion from gabapentin to pregabalin or vice versa seems like a daunting task. However, there are a few studies examining such conversions. It is important to note that the studies specifically examined the conversion of gabapentin to pregabalin and the bi-directionality of this conversion was not investigated. The interaction of gabapentin and pregabalin with conventional antiepileptic and analgesic drug targets is likely to be modest, at best, and has been largely dismissed in favour of a selective inhibitory effect on voltage-gated calcium channels containing the α 2 δ-1 subunit. This mechanism is consistently observed in both rodent- and human Like gabapentin, the precise mechanism of action of pregabalin is unknown. 4 However, gabapentin differs from pregabalin because of the reduced binding affinity to voltage-gated calcium channels. 6 Pregabalin is six-times more potent than gabapentin in binding affinity to the alpha 2 -delta voltage-gated calcium channel. 9 The manufacturer The substitution of gabapentin with pregabalin in gabapentin responders resulted in improved pain relief and fewer adverse events. 35 However, gabapentin non-responders who had adverse effects with gabapentin also experienced adverse effects with pregabalin. 35. Central nervous system effects
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |