Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
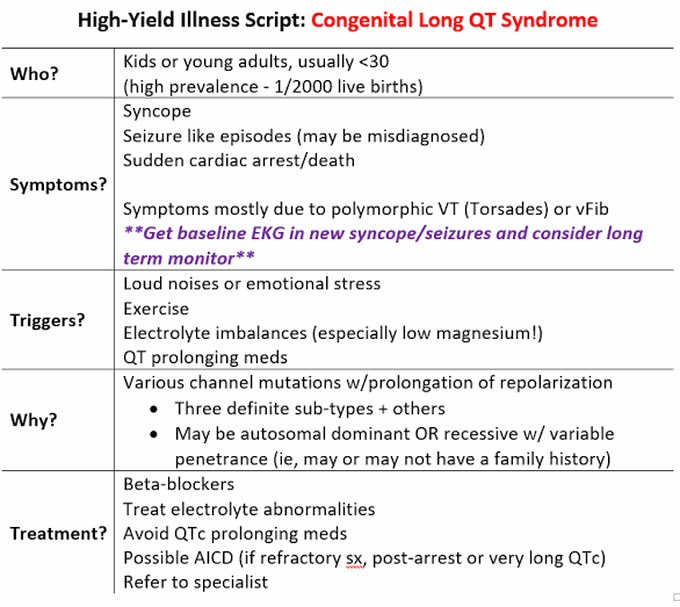
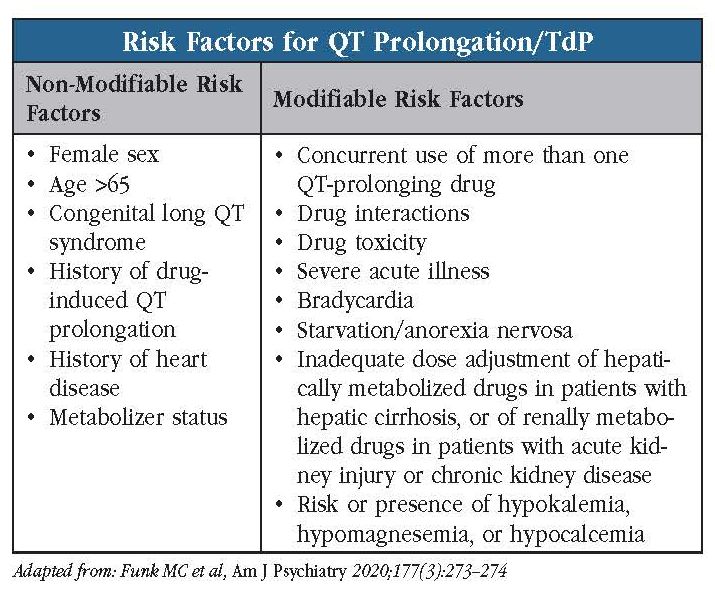
In people with Brugada Syndrome the number and range of drugs that may make the condition worse is unknown and caution must be used. Antiarrhythmics, beta-blockers and some antidepressants are known to interact badly with it. Drugs which people with Long QT Syndrome should avoid; Long QT syndrome is a cardiac repolarization disorder, and is associated with an increased risk of torsades de pointes (TdP), a life-threatening type of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, and sudden cardiac death [1]. Acquired and congenital forms can be distinguished. In general, manufacturers advise that the use of two or more drugs that are associated with QT prolongation should be avoided. Increasing age, female sex, cardiac disease and some metabolic disorders (notably hypokalaemia) predispose to QT prolongation. Prescribers should also use caution when prescribing concurrent drugs that reduce serum Acquired long QT syndrome. This type of LQTS is caused by another health condition or medicine. It usually can be reversed when the specific cause is found and treated. Causes of congenital long QT syndrome. Many genes and gene changes have been linked to long QT syndrome (LQTS). There are two types of congenital long QT syndrome: Romano-Ward QT interval varies dependent on the length of the cardiac cycle and is usually corrected (QTc) for heart rate, several formulas can be used for this, most commonly Bazett’s formula is used (QTc=QT/√RR; QT interval in seconds, RR cardiac cycle in seconds), other correction formulae such as Frederica, Hodges or Framingham may be used. Congenital long QT syndrome (LQTS) comprises a group of arrhythmia disorders, arising from cardiac channelopathies in both sodium and potassium channels. Long QT syndrome affects about 1 in 2500 individuals and is associated with syncope and sudden cardiac death. In LQTS, mutations are seen in KCNQ1, KCNH2 (hERG) and SCN5A ion channels. Many drug therapies are associated with prolongation of the QT interval. This may increase the risk of Torsades de Pointes (TdP), a potentially life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia. As the QT interval varies with a change in heart rate, various formulae can adjust for this, producing a 'corrected QT' Drugs associated with QT Prolongation, QTc prolongation including Antipsychotics, antiarrhythmics, antidepressants, and antihistamines Long QT syndrome is a cardiac repolarization disorder and is associated with an increased risk of torsades de pointes. The acquired form is most often attributable to administration of specific A comprehensive list of conditions and drugs that may prolong the QT interval, and cause torsade de pointes (TdP) and long QT syndrome (LQTS) is presented below. With regards to drugs, the risk of QT prolongation and TdP varies markedly across the list but tends to be rather similar within a drug class. Similarly, other substances in the butyrophenone group, e.g., domperidone and droperidol, have also been shown to have an increased risk of long QT syndrome [59, 60]. There is also an increased risk of QT prolongation in patients with pre-existing cardiac disease who are treated with metoclopramide [61, 62]. Langt QT syndrom (LQTs) defineres ud fra typiske ekg-forandringer med forlænget QT-interval, sygehistorie og familieanamnese (se diagnostiske kriterier senere)1, 2, 3; QT-tid beregnes fra start på Q-tak til slut på T-tak; QT-tid korrigeres for hjertefrekvens, sædvanligvis ved Bazetts formel QTc = QT / RR 0,5. QTc kalkulator 4 Long QT syndrome (LQTS) is a cardiac conduction disorder characterized by prolongation and increased dispersion of ventricular repolarization, manifested by lengthening of the QT interval on the surface electrocardiography (ECG). Subclinical long-QT syndrome 18,19 Ion-channel polymorphisms 20-22 Severe hypomagnesemia. n engl j med 350;10 www.nejm.org march 4, 2004 The new england journal of medicine 1016 Several drugs have been withdrawn from the U.S. market or have received black box warnings due to their potential to cause QT interval prolongation that leads to fatal ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. 1,2 Predicting the risks involved with most of these drugs is difficult, since they are often structurally and pharmacologically Long qt syndrome is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, also take Aspirin, and have High blood pressure. The phase IV clinical study analyzes which people have Long qt syndrome when taking Gabapentin, including time on the drug, (if applicable) gender, age, co The length of the QT interval represents the time required for ventricular depolarization and repolarization. Prolongation of ventricular repolarization can result in fatal ventricular arrhythmias [3]. Faster heart rates can shorten the QT interval [4], so it is often adjusted for rate and reported as the heart rate corrected (QTc) interval. Long QT syndrome (LQTS) is a disorder of myocardial repolarization characterized by a prolonged QT interval on the electrocardiogram (ECG) (waveform 1). Prolongation of the QT interval can be associated with life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia. Although rare cases of inherited long QT syndrome may underlie this, QT prolongation is more commonly associated with particular drug therapies in the presence of modifiable and/or non-modifiable risk factors. Long QT syndrome is a cardiac repolarization disorder, and is associated with an increased risk of torsades de pointes (TdP), a life-threatening type of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, and sudden cardiac death . Acquired and congenital forms can be distinguished.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |