Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 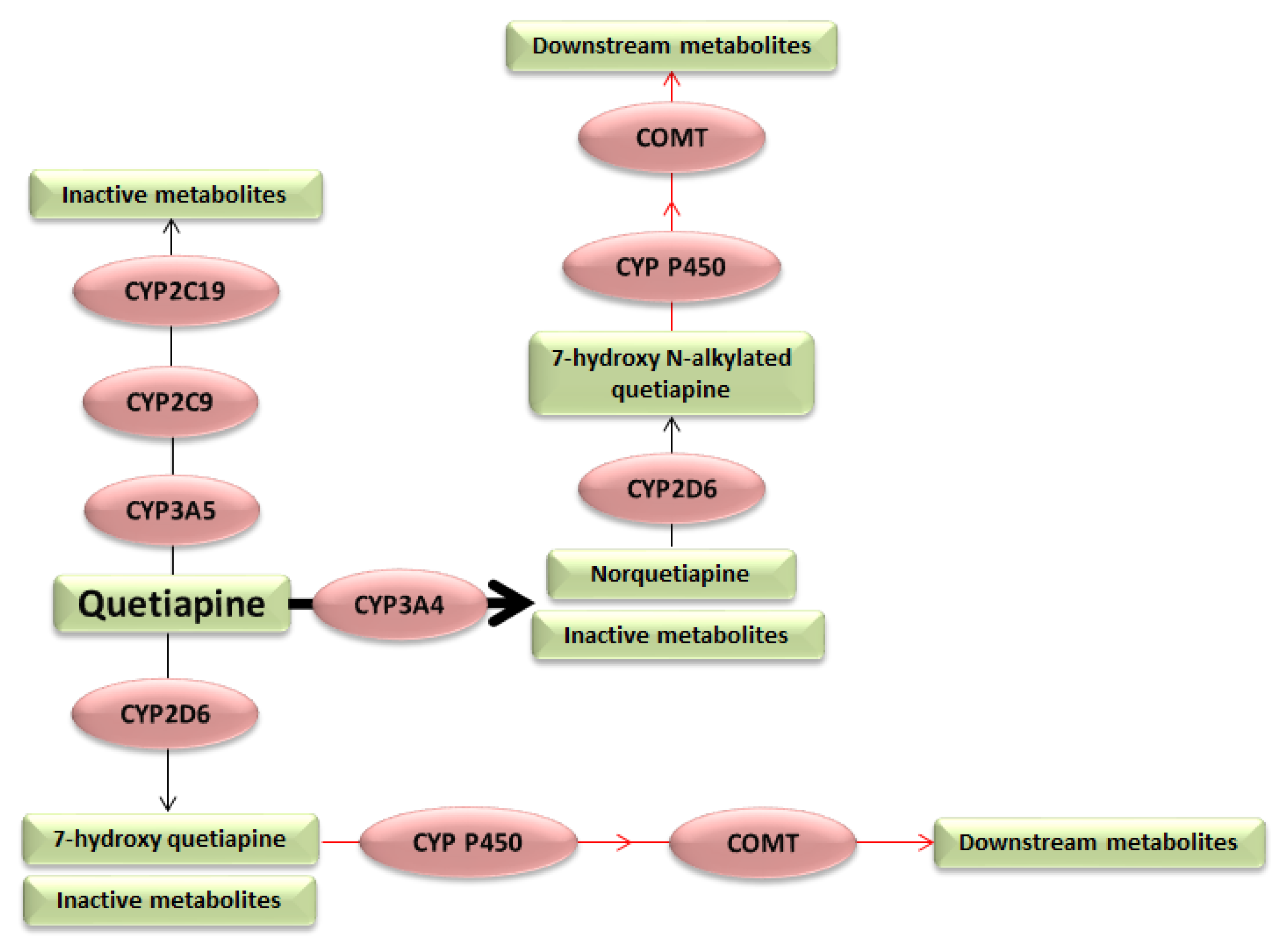 |
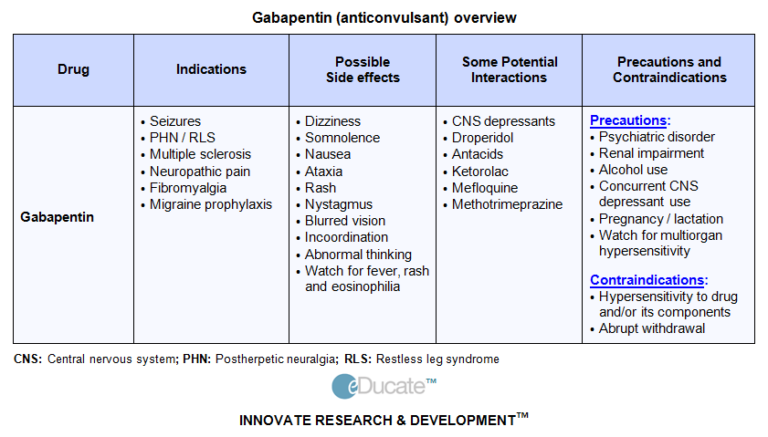
Find patient medical information for Quetiapine (Seroquel) on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings, and user ratings Drug interactions are reported among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin) and Quetiapine fumarate (quetiapine fumarate). Common drug interactions include immunodeficiency among females and drug ineffective among males. Using gabapentin together with QUEtiapine may increase side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, confusion, and difficulty concentrating. Some people, especially the elderly, may also experience impairment in thinking, judgment, and motor coordination. Quetiapine belongs to class of medications called atypical antipsychotics. It works by changing the activity of certain natural substances in the brain. Quetiapine side effects. Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction to quetiapine: hives, difficult breathing, swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat. Both Quetiapine and Gabapentin have effects on the CNS and can cause sedation, which might affect the ability to perform skilled tasks (see 'Drugs and Driving' in Guidance on Prescribing). In some cases, use of two or more drugs that have effects on the CNS might also increase the risk of CNS depressant effects (which could range from sedation Quetiapine extended-release tablets are also used along with other medications to treat depression. Quetiapine tablets may be used as part of a treatment program to treat bipolar disorder and schizophrenia in children and teenagers. Quetiapine is in a class of medications called atypical antipsychotics. Drug Interactions: A total of 270 drugs are known to interact with Gabapentin: 28 major drug interactions (148 brand and generic names) 232 moderate drug interactions (1026 brand and generic names) 10 minor drug interactions (52 brand and generic names) A total of 743 drugs are known to interact with Seroquel: Using gabapentin together with QUEtiapine may increase side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, confusion, and difficulty concentrating. Some people, especially the elderly, may also experience impairment in thinking, judgment, and motor coordination. The study uses data from the FDA. It is based on gabapentin and quetiapine fumarate (the active ingredients of Gabapentin and Seroquel, respectively), and Gabapentin and Seroquel (the brand names). Other drugs that have the same active ingredients (e.g. generic drugs) are not considered. Many medications, supplements, and beverages interact with quetiapine. Examples include carbamazepine (Tegretol), St. John’s wort, and alcohol. Other medications that can cause quetiapine interactions include Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir / ritonavir), rifampin (Rifadin), and metoclopramide (Reglan). Quetiapine is principally metabolized by CYP3A4 to active and inactive metabolites. Gabapentin is eliminated unchanged by the kidney for 100%. This combination of drugs may have possible synergistic effects. Applies to: gabapentin and Seroquel (quetiapine) Using gabapentin together with QUEtiapine may increase side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, confusion, and difficulty concentrating. Some people, especially the elderly, may also experience impairment in thinking, judgment, and motor coordination. Toxicity may exist for patients taking large amounts of gabapentin and/or quetiapine. Clinicians should exercise vigilance when using either to treat patients who use alcohol or illicit drugs, particularly if gabapentin and quetiapine are prescribed concomitantly. Quetiapine is not clearly more acceptable than typical antipsychotic drugs. These findings are based on data of moderate quality. RR 0.91 (0.81 to 1.01) Moderate: Adverse effects Extrapyramidal effects: Quetiapine may reduce the chance of experiencing these movement disorders. This finding is based on data of moderate quality. RR 0.17 (0.09 to Review detailed drug interaction details between Gabapentin and Quetiapine, including severity, interaction details, how to manage the interaction, and more. 743 medications are known to interact with quetiapine. Includes amlodipine, gabapentin, lisinopril. Medicines that interact with quetiapine may either decrease its effect, affect how long it works, increase side effects, or have less of an effect when taken with quetiapine. An interaction between two medications does not always mean that you must stop taking one of the medications; however, sometimes it does. Speak to your doctor about how The following applies to the ingredients: Gabapentin and Quetiapine (found in Seroquel) MONITOR: Central nervous system- and/or respiratory-depressant effects may be additively or synergistically increased in patients taking multiple drugs that cause these effects, especially in elderly or debilitated patients. Quetiapine is a prescription drug. It comes in the form of a tablet you take by mouth. There are two versions of the tablet. The immediate-release version is released into the bloodstream right away. When a medication works right, it boosts your health or helps you feel better. But a drug can bring on problems if it doesn't mix well with something else you put into your body, like another
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |