Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
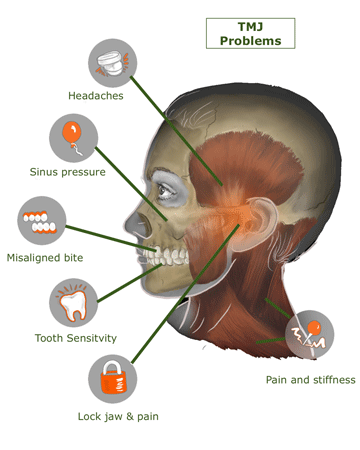
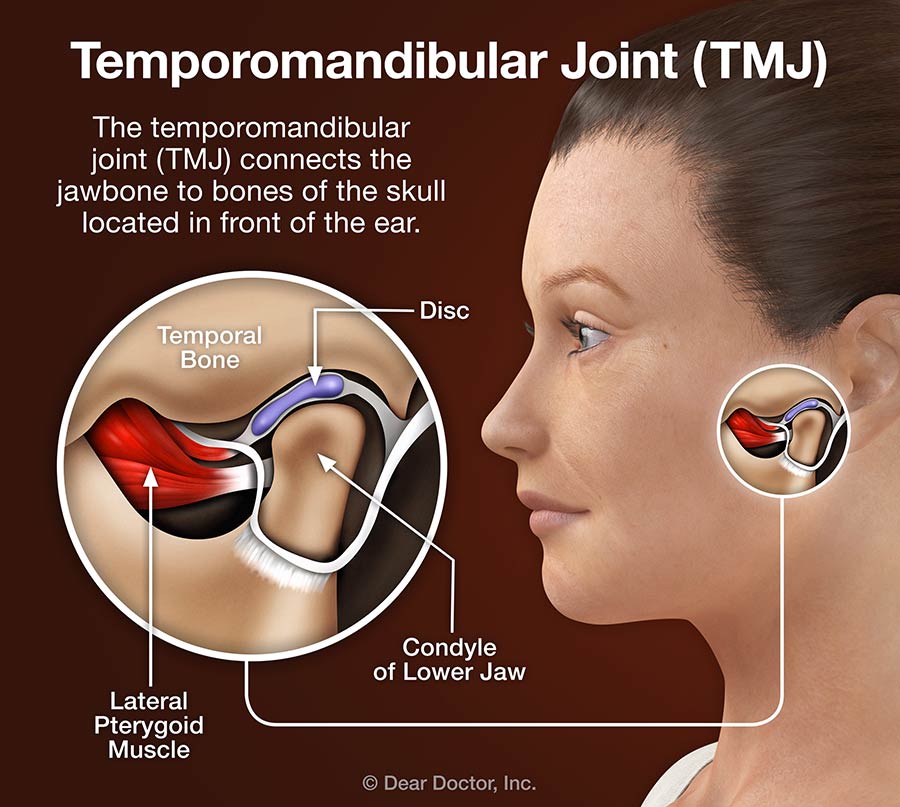
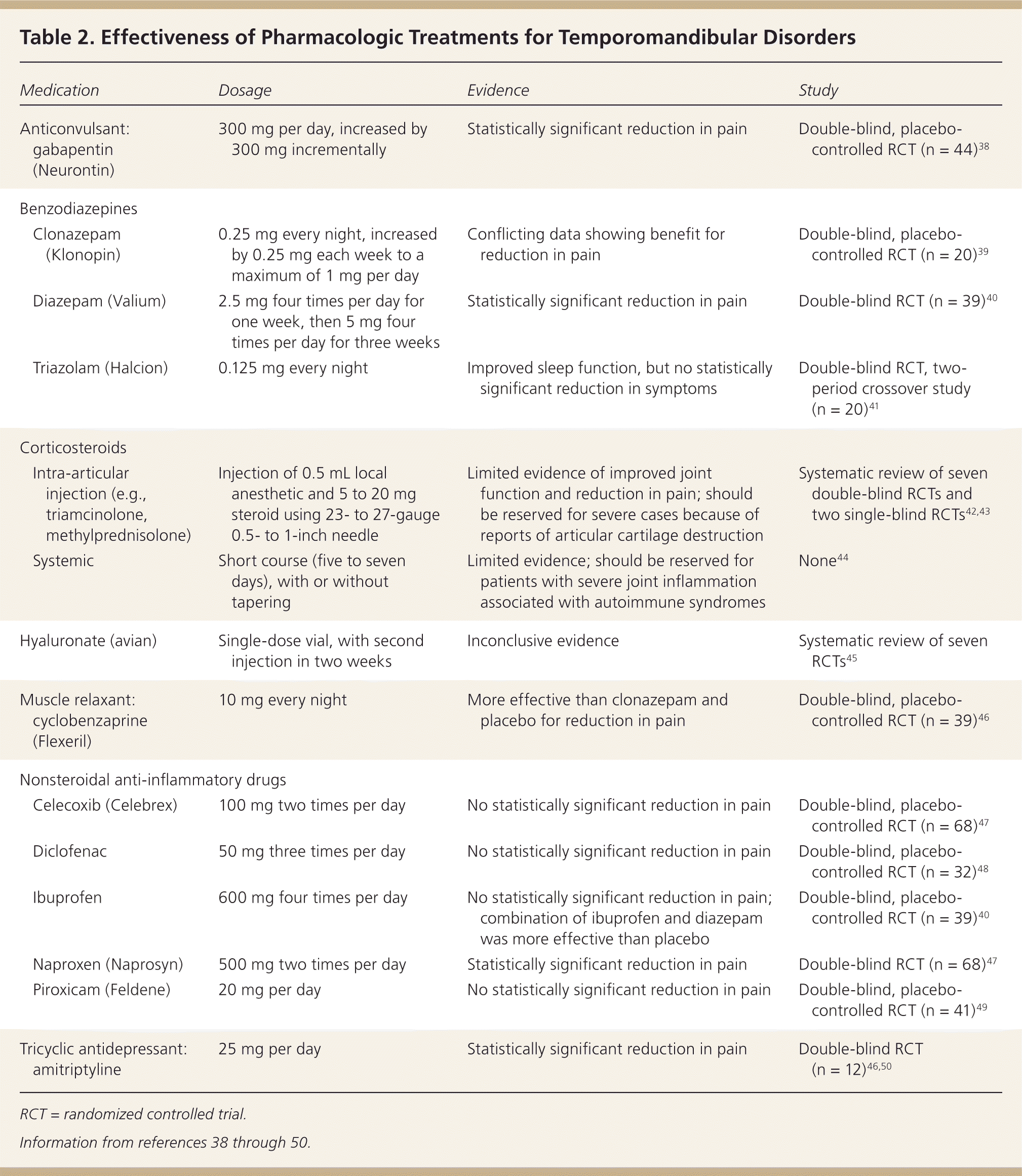
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) pain, or jaw pain, is pain that develops as a consequence of a disorder of the joint that connects the jaw to the temporal bones on the sides of the skull. TMJ disorders can affect the joint itself, as well as the muscles and ligaments in the face that control it, leading to an impaired function of the TMJ joint. In a double-blind, 12-week randomized controlled clinical trial, investigators demonstrated that gabapentin showed significant pain decrease on a VAS pain score versus placebo for myogenous TMD. After the initial dose of 300 mg/d, patients’ dose was increased by 300 mg every 3 days until pain was controlled with no adverse effects, with a Who Can Treat TMJ Pain? How is Jaw Pain Treated? Opiates Other Types of Treatment and TMJ Pain Management Why Pain Management is Important for TMJ Disorder Patients Medical care is a partnership between you and your medical professional, and you must be very vocal. Pain management is no different. Treatment with no options is simply not Anticonvulsants commonly used to treat neuropathic (nerve) pain have been found to be effective in the treatment of certain chronic pain disorders such as fibromyalgia, diabetic neuropathy or postherpetic neuralgia. Examples: gabapentin (Neurontin), pregabalin (Lyrica). There are a number of other anticonvulsants that have also shown varying Gabapentin has been reported to reduce spontaneous TMD myogenous pain and tender trigger sites at the temporalis and masseter compared to placebo (10,16). In this randomized controlled trial, the initial dose of gabapentin was 300 mg. Gabapentin: A Detailed Review of Effectiveness, Side Effects, and Comparisons for Treating temporomandibular joint disorders (TMD). When this area becomes painful, stops functioning correctly, or starts making unusual noises, you may be experiencing temporomandibular joint dysfunction, formally known as temporomandibular joint Nerve pain medications: Medications such as amitriptyline and gabapentin are used to treat many types of nerve pain, including nerve damage caused by TMJ disorders. Antidepressants: Temporomandibular disorders affect between 5% and 12% of the population and present with symptoms such as headache, bruxism, pain at the temporomandibular joint, jaw popping or clicking, neck pain Gabapentin can be used as an effective option for the treatment of pain-related TMD disorders as central sensitization plays an important role in the development and progression of TMD disorders.[22 23] Gabapentin is a novel anticonvulsant that works on the CNS and has shown promise in a variety of chronic pain disorders, including TMD. Many Biobehavioral model of pain perception and motor behavior. A fundamental aspect of our model is the fact that musculoskeletal pain produces changes in motor behavior. 181 It has also been observed that pain-related movement disorders are an important cause that influences the impairment of functional capacity and the patient’s quality of life, 182 including the possible interaction that i found that i really needed to do other interventions to treat the root cause of the tmj nerve compression pain (radiofrequency ablation, changes in my posture & a lot of lifestyle changes.. see my post!) to release the actual compression gabapentin will just temporarily relieve a symptom it wont treat the root cause If you know or suspect you have a TMJ disorder, find out how Dr. Katherine S. Phillips can help you find relief. She holds a Master of Science in Orofacial Pain, is board certified in dental sleep medicine, and has dedicated her practice to the treatment of TMD (temporomandibular joint disorders) and sleep breathing disorders (obstructive sleep apnea and snoring) for the last 11 years. It sounds as if, with the last surgery being a total failure, that you should be on some type of narcotic pain med, such as oxycodone, when the pain gets out of control. Just my opinion, and you probably don't want to take narcotics, but they may be your best chance for pain relief. Anticonvulsants are sometimes prescribed to treat pain from TMJ disorders. Neurontin (gabapentin) and Lyrica (pregabalin) are examples of anticonvulsant drugs that may help relieve TMJ pain. Muscle relaxants. Muscle relaxants are a class of drugs that treat muscle spasms. Healthcare providers may prescribe a muscle relaxant for TMJ problems I tried gabapentin like a month ago for back pain caused by the TMD, and within a couple of days I had a pretty bad cold. I read about the side effects, and lo and behold: it says a very common side effect is to lower the immune defense against viruses. Gabapentin and pregabalin have been used for the treatment of TMD. Both are synthetic compounds structurally related to GABA, the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS. My doctor prescribed me some gabapentin to help with the TMJ pain. I haven't started it yet because I'm afraid of side effects. I read in some cases it can affect your mood and cause further depression. Does anyone have experience with this drug? Is it helpful? Any bad side effects? Thanks! Gabapentin has been shown to reduce TMD pain, 17 but there is limited evidence that pregabalin does. Drawbacks: Gabapentin and pregabalin are associated with some adverse effects (dizziness, blurred vision, drowsiness, etc.) but otherwise are generally considered safe. My pain doctor prescribed me 300mg gabapentin every night and will titrate up. I'm on day 4, and maybe this is placebo effect, but my pain is significantly better I notice I have more mobility (I can open my mouth a bit more), I have less headaches and less sharp pain in my TMJ/jaw/cheek areas.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |