Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
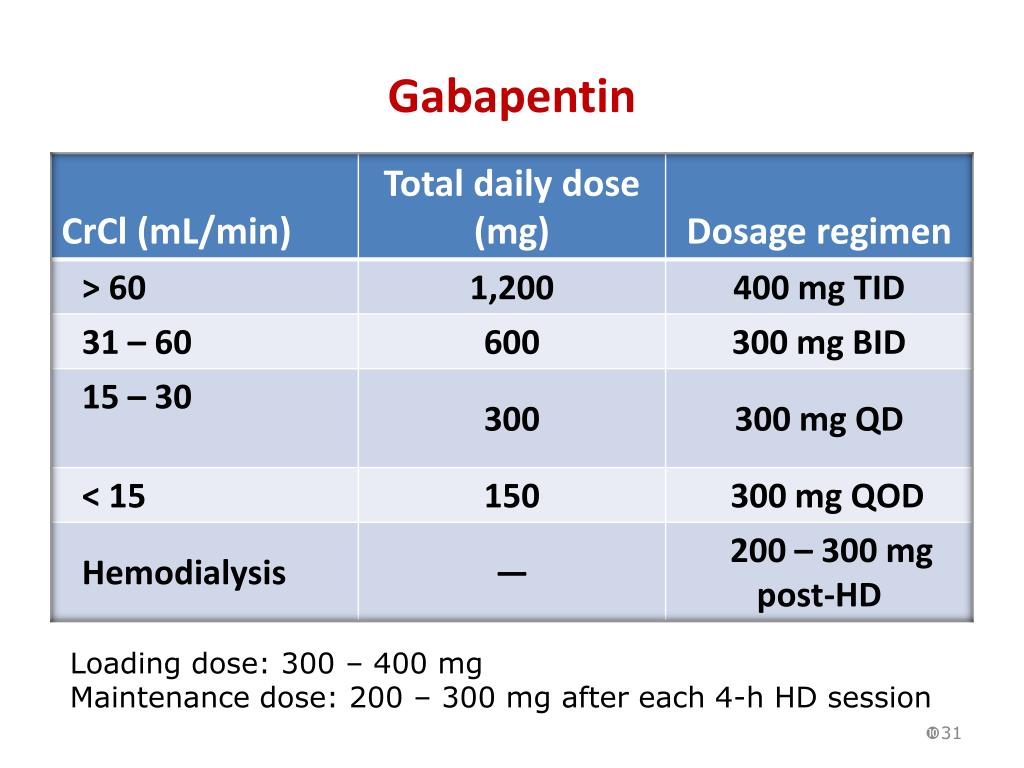
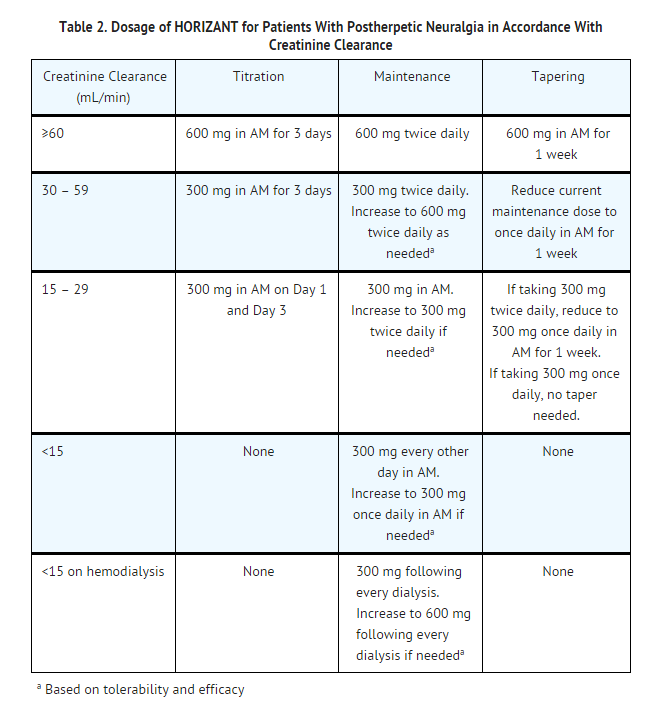
Renal clearance (CLr) and CLr adjusted for body surface area also declined with age; however, the decline in the renal clearance of gabapentin with age can largely be explained by the decline in renal function. Reduction of gabapentin dose may be required in patients who have age related compromised renal function. Medscape - Indication-specific dosing for Alavert Allergy & Sinus D, Claritin D, ChlorTripolon, Alavert D-12, Claritin D-24 Hour (pseudoephedrine, loratadine), frequency-based adverse effects, comprehensive interactions, contraindications, pregnancy & lactation schedules, and cost information. Medscape - Seizure dosing for Neurontin, Gralise (gabapentin), frequency-based adverse effects, comprehensive interactions, contraindications, pregnancy & lactation schedules, and cost In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the dose needs to be adjusted according to the GFR. For patients on dialysis, the recommended dose is 100-300mg post dialysis on dialysis days only. The initial dose should be 50 mg once or twice daily, increased every 3-7 days by 50 to 100 mg. The maximum daily dose is 400 mg in patients younger than 75 years, and 300 mg in older patients. Dosage should be further reduced in renal impairment. 5% Lidocaine Transdermal Patch gabapentin. gabapentin, fexofenadine. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of CNS depressants can result in serious, life-threatening, and fatal respiratory depression. Use lowest dose possible and monitor for respiratory depression and sedation. gabapentin enacarbil Per Lexicomp, Gabapentin’s recommended dose in patients with renal impairment is as follows: CrCl >15 to 29 mL/minute: 200 to 700 mg once daily. CrCl 15 mL/minute: 100 to 300 mg once daily. Find medical information for gabapentin on epocrates online, including its dosing, contraindications, drug interactions, and pill pictures. renal dosing Dosage adjustment of GRALISE is necessary in patients with impaired renal function. GRALISE should not be administered in patients with creatinine clearance <30 mL/min or in patients undergoing hemodialysis. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant use of fostamatinib may increase concentrations of P-gp substrates. Monitor for toxicities of the P-gp substrate drug that may require dosage reduction when given concurrently with fostamatinib. gabapentin. gabapentin, loratadine. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. The half-life of gabapentin immediate-release formulation is 5–7 hours in patients with normal renal function and is prolonged up to 52 hours in patients with CrCl<30 mL/min. 26 The half-life of pregabalin is 16.7 hours in patients with CrCl 30–59 mL/min, 25 hours in patients with CrCl 15–29 mL/min, and 48.7 hours in patients with CrCl<15 Usual initial gabapentin dose: 300mg q8h. Usual maintenance dose: 300-600mg q8h. Maximum dosage/day: 3600 mg. [15-29]: Dosage range: 200-700mg/day. [<15]: 100-300 mg/day. Use lower end of this range for CRCL <7.5 ml/min. TABLE 1. Gabapentin Dosage Based on Renal Function. TID = Three times a day; BID = Two times a day; QD = Single daily dose. a. Medscape - Seizure, fibromyalgia, neuropathic pain-specific dosing for Lyrica (pregabalin), frequency-based adverse effects, comprehensive interactions, contraindications, pregnancy & lactation schedules, and cost information. Gabapentin dosing guidelines for adult with renal impairment are summarized in Table 3. Dosing guidelines for gabapentin immediate-release are also applicable for adolescents 12 years of age and older with renal impairment. Gabapentin use in pediatric patients younger than 12 years of age with impaired renal function has not been evaluated 1-5. Pregabalin's linear pharmacokinetics and low intersubject variability allow it to be initiated at or adjusted to the target dosage more rapidly compared with gabapentin, which requires a long 3 days. The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. NEURONTIN may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or Max dosage 3600mg if patient already on gabapentin; Taper dose > 7 days to discontinue; Pediatric Dosing Partial seizures. Adjunct for partial seizures with out secondary generalization in patients> 12yo with epilepsy; also adjunctive therapy for partial seizures in patients 3-12 years <3 years: Safety and efficacy not established Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. 4. Renal Dosing Recommendations. Mild Kidney Problems (CrCl 60-90 mL/min): Dose Adjustment: 900 - 3600 mg/day TID. How Often to Take: 3 times a day. Notes: Monitor for dizziness or double vision. Moderate Kidney Problems (CrCl 30-59 mL/min): Dose Adjustment: 400-1400 mg/day BID; How Often to Take: Twice a Day; Notes: Your doctor will decide the 600 mg qDay with food at about 5:00 pm. Indicated for management of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) 600 mg PO qAM x3 days, and then increase to 600 mg PO BID. Dosing Considerations. Not
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |