Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 | |
 |  |
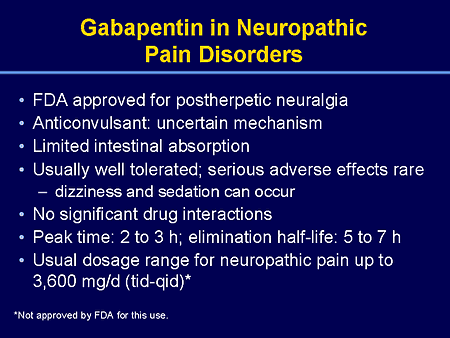 |  |
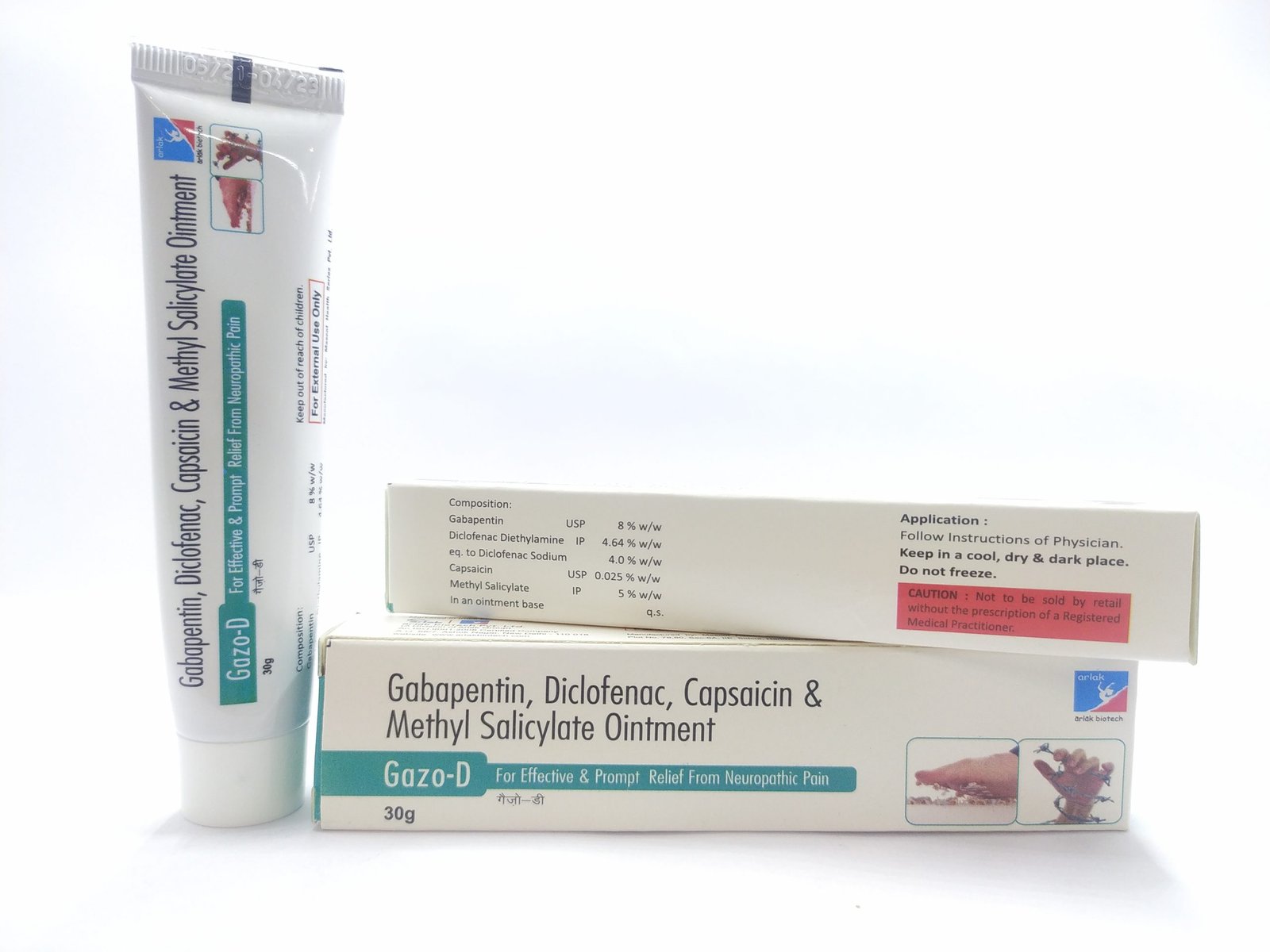
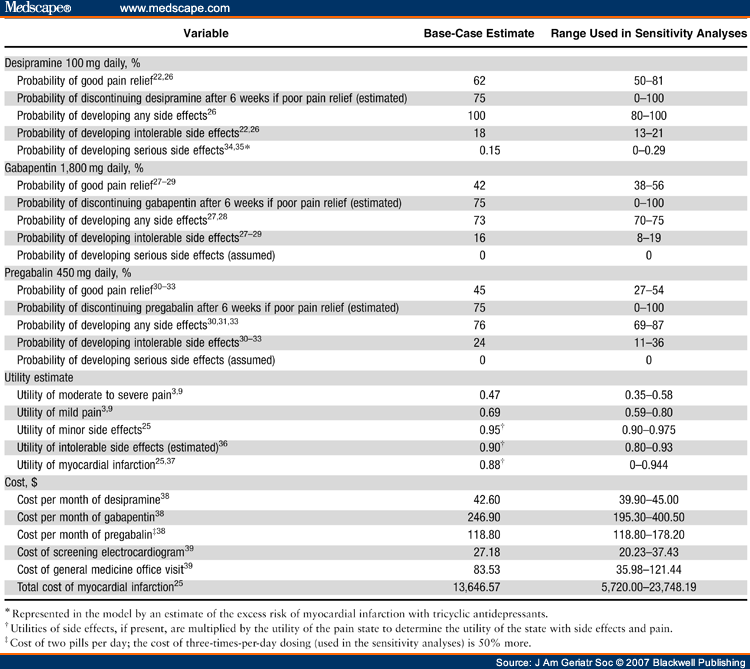
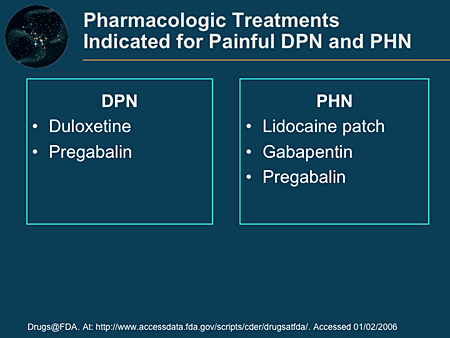
Abstract. Topical delivery of gabapentin is desirable to treat peripheral neuropathic pain conditions whilst avoiding systemic side effects. To date, reports of topical gabapentin delivery in vitro have been variable and dependent on the skin model employed, primarily involving rodent and porcine models. Background: Systemic gabapentin is a mainstay treatment for neuropathic pain though there are side-effects. Localized therapy may curtail such side-effects so a topical gabapentin dermal application was examined in the chronic constriction injury (CCI) model of neuropathic pain. Gabapentin/Ketoprofen/Lidocaine HCl Topical Cream is a compounded medication used to relieve pain. It combines the effects of Gabapentin, Ketoprofen, and Lidocaine HCl for localized treatment. Gabapentin helps reduce nerve pain, Ketoprofen is an anti-inflammatory drug, and Lidocaine HCl is a local anesthetic that numbs the treated area. Treatment for nerve pain generally requires a prescription, but these four OTC medications are also available. Lidocaine, along with other topical creams, can help treat nerve pain near the Topical gabapentin 10% gel also significantly allayed hyperalgesia and allodynia in a rat chronic sciatic nerve constriction injury neuropathic pain model . These studies involving animals provide evidence of the potential of topical gabapentin use in the treatment of neuropathic pain, although it must be emphasized that the models do not The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of Lipoderm Cream, VersaBase Gel, and Emollient Cream on the release and permeation of gabapentin formulated for neuropathic pain. Gabapentin of different strengths (1%, 5%, and 10%) was compounded with the bases, diffusion of the drug from t A Cochrane review of combination therapy for neuropathic pain demonstrated that gabapentin and opioids provide better pain relief than gabapentin or opioids alone, but this was associated with increased levels of adverse events. The calculated NNT was 9.5 (5.0–86), and the NNH was 10 (6.5–25). Keywords: neuropathic pain, tramadol, capsaicin, cubosomes, niosomes, pregabalin, gabapentin. 1. Introduction. Neuropathic pain (NeP) is caused by damage or dysfunction of the nervous system, which can result in abnormal sensory processing and pain signals being sent to the brain . We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. For neuropathic pain, topical gabapentin may be used in combination with other compounds or as a standalone product. 3,4 In terms of physicochemical characteristics, gabapentin is water soluble and has a molecular weight and log P of 171.34 g/mol and −1.10, 5 respectively . Focal points • Some patients cannot tolerate oral gabapentin for neuropathic pain due to significant central side effects • Topical gabapentin, an NHS Pharmaceutical unlicensed 'special', has been used as a treatment alternative • Significant reduction in pain scores after treatment were demonstrated (n = 23) with no reported side effects • Topical gabapentin is an alternative What is localized neuropathic pain? A first proposal to characterize and define a widely used term. Pain Manage. 2012;2:71-7. Sawynok J. Topical analgesics for neuropathic pain: preclinical exploration, clinical validation, future development. Eur J Pain. 2014:18:465-81. Zur E. Topical treatment of neuropathic pain using compounded medications. 2003 40 Peripheral neuropathic pain 1 wk Statistically reduced pain Capsaicin 0.075% Mason et al, 20 2004 656 Chronic musculoskeletal pain 4 wk 50% reduction in pain Chronic neuropathic pain 8 wk 8% Maihofner and Heskamp, 21 2014 1044 Peripheral neuropathic pain 12 wk 25% reduction in pain 0.075% Casanueva et al, 22 Results: For the primary outcome, no differences were found in the mean reduction in average pain scores between the treatment and control groups for patients with neuropathic pain (-0.1 points [95% CI, -0.8 to 0.5 points]), nociceptive pain (-0.3 points [CI, -0.9 to 0.2 points]), or mixed pain (-0.3 points [CI, -0.9 to 0.2 points]), or for all The paper stresses a pivotal clinical point: In the localized neuropathic pain, the pain should be perceived by the patient as superficial. [PMC free article] 5. •• Finnerup NB, Attal N, Haroutounian S, McNicol E, Baron R, Dworkin RH, et al. Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gabapentin 10% Topical Gel is a specialized medication designed for direct application to the skin. The active ingredient, gabapentin, is more commonly known for its use in oral form to manage neuropathic pain and as an adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial seizures. These recommendations were finalized in 2019 and published in April 2020. Following the GRADE system, the recommendations suggest first-line treatment options including serotonin-noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (duloxetine and venlafaxine), gabapentin, tricyclic antidepressants, and specific use of topical lidocaine and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for peripheral neuropathic pain. Gabapentin 1%, 5%, 10% Cream or Gel. Gabapentin topical creams and gels have been shown to be effective for treating chronic neuropathic pain. Neuropathic pain is pain coming from damaged nerves. It differs from pain messages carried along healthy nerves from damaged tissue that can come from a burn or a cut. Gabapentin 6% Topical Gel is a semisolid formulation designed for targeted treatment of various conditions such as neuropathic pain, postherpetic neuralgia, and diabetic neuropathy. This medication works by inhibiting the release of specific neurotransmitters in the brain, thereby reducing pain and inflammation. An anti-NeP topical cream with ketamine 10%, gabapentin 10%, imipramine 3%, and bupivacaine 5% was shown to resolve NeP symptoms for several hours; it was also successful in reducing flare-ups in a patient with cervicalgia and TGN, refractory to several treatments. 10 Ketamine and gabapentin are more effective together as they mitigate
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |