Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
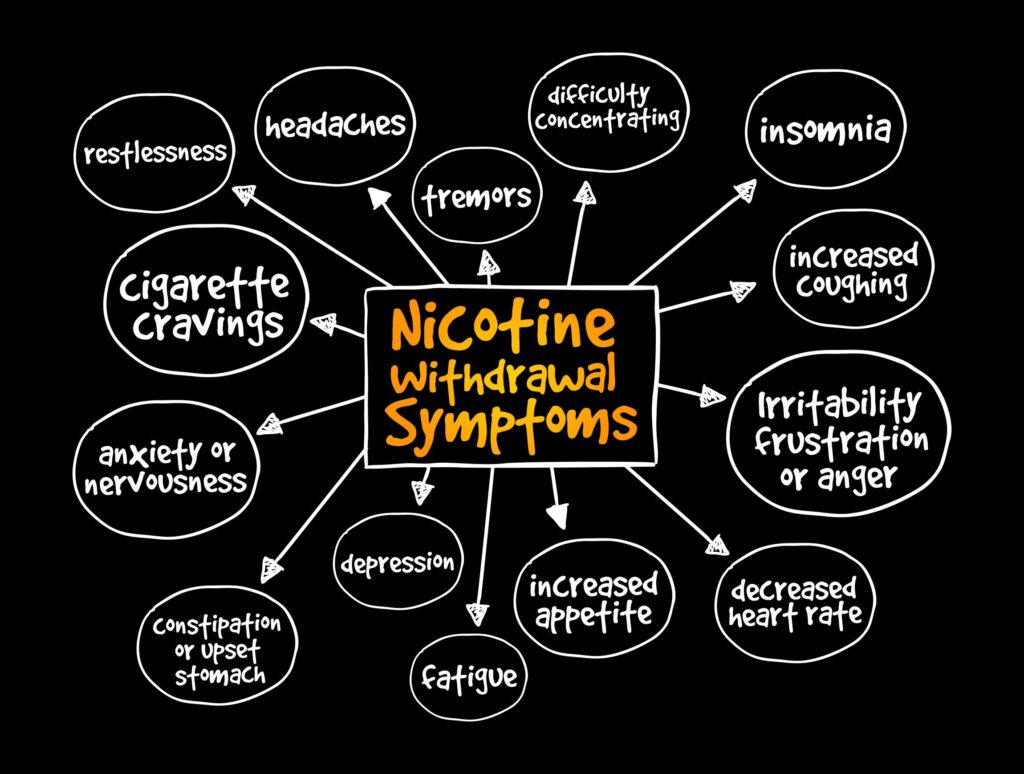 |  |
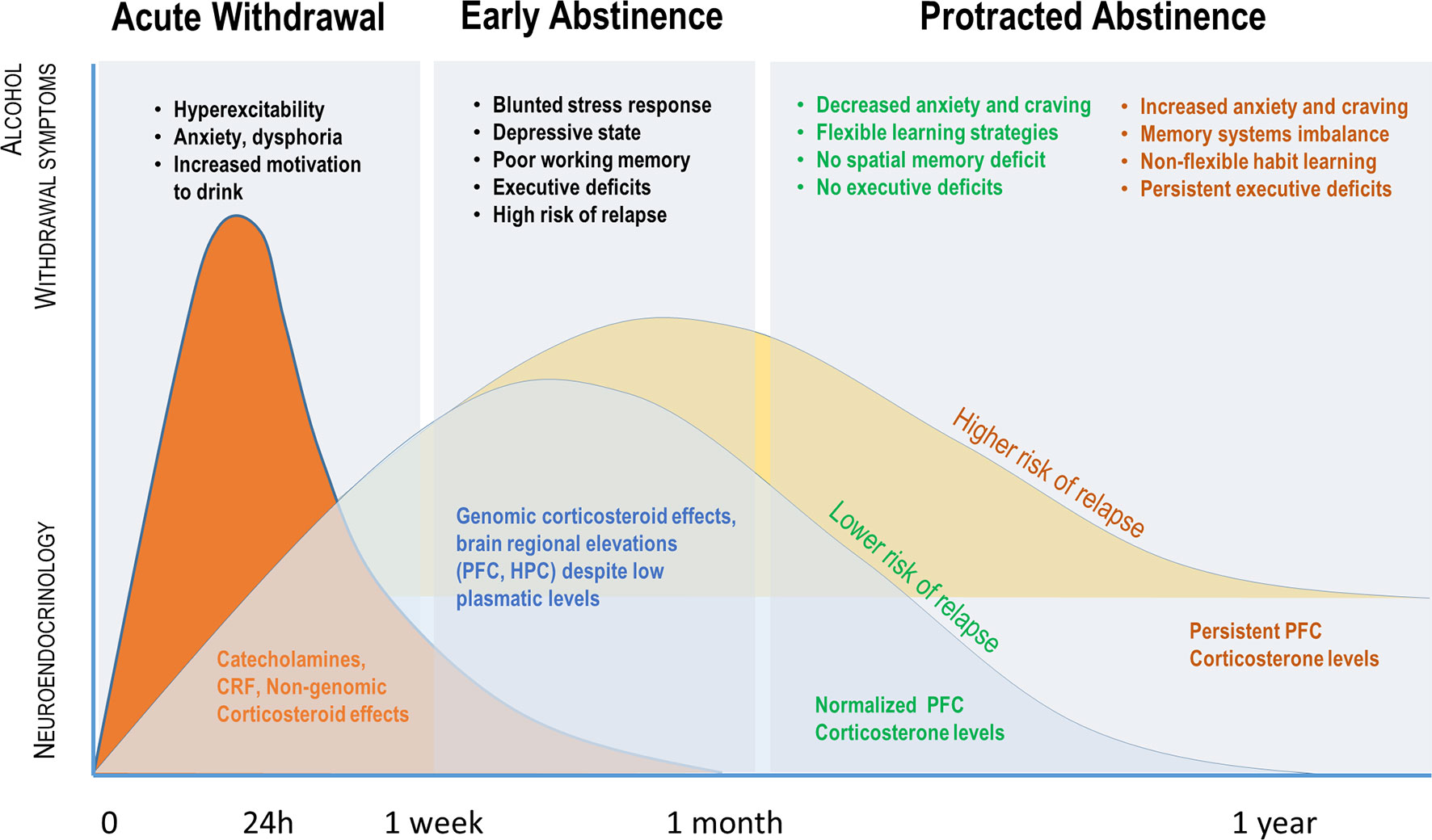
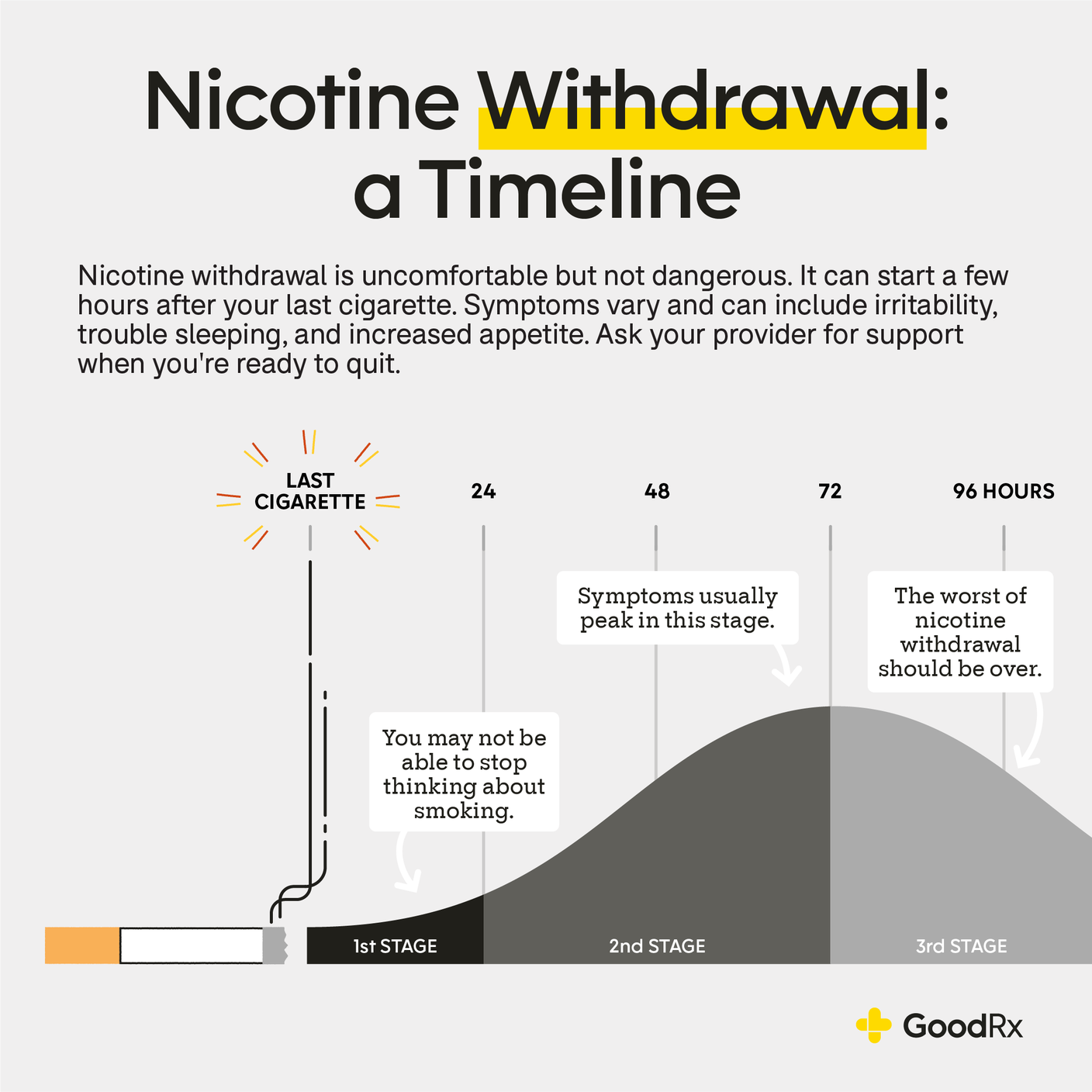
When a person stops taking gabapentin, especially after long-term use, they may experience a range of withdrawal symptoms. These symptoms can vary in intensity and duration, depending on several factors such as the duration of use, dosage, and individual physiology. Among the documented cases, gabapentin withdrawal began between 12 hours and 7 days after the last dose. The majority saw withdrawal symptoms within 24 to 48 hours. Among the cases reported, gabapentin withdrawal symptoms typically peaked three days after someone’s last dose. Case reports have shown that gabapentin withdrawal often lasts for 5 to 10 days, but some people have taken as long as 18 weeks to completely taper off gabapentin while managing withdrawal symptoms. Symptoms may start within 12 hours to 7 days after stopping gabapentin and may be severe. Gabapentin withdrawal syndrome can manifest with a variety of physical and psychological symptoms. Managing symptoms during Gabapentin detox is crucial due to the range of withdrawal symptoms that can vary from mild discomfort to potentially life-threatening conditions. A comprehensive symptom management approach typically involves medical and non-medical interventions tailored to the individual’s specific needs. Gabapentin Withdrawal Symptoms. What are the withdrawal symptoms of gabapentin? Dependence is when a person’s body requires a drug to function properly. Regular use of neurontin can result in dependence. If the drug is suddenly stopped “cold turkey” rather than tapering off it, withdrawal symptoms can result. 9 Withdrawal symptoms can begin within 12 hours to 7 days after quitting the medication and last up to 10 days. Symptoms of gabapentin withdrawal may include nausea, dizziness, headaches, insomnia, and anxiety. Long-Term Use: Taking gabapentin for over six months can increase dependency risks. Concurrent Medications: People using opioids or benzodiazepines alongside gabapentin have a higher withdrawal risk. The best way to minimize withdrawal symptoms is through **gradual tapering**. However, like many medications, gabapentin does have some negative side effects, along with withdrawal symptoms, some of which may be experienced after just one use, and some of which may arise as a result of long-term use. These effects can range from mild to severe. 1 Using gabapentin over a long period can lead to more dramatic health risks. While it can be effective for managing pain or seizures, prolonged use increases the chance of developing serious side effects. Some of the most common Gabapentin long-term side effects include: Memory loss: Long-term gabapentin use has been linked to problems with Gabapentin withdrawal symptoms can vary in intensity depending on factors such as the duration of use, dosage, and individual physiology. Common signs and symptoms include: Psychological Symptoms: Anxiety, depression, irritability, mood swings, and difficulty concentrating. People who take high doses of gabapentin or use it long-term may experience more severe withdrawal symptoms. Within 2 to 7 days after the last dose, withdrawal symptoms may peak. Common symptoms include anxiety disorders, insomnia, stomach pain, abdominal pain, muscle pain, and light sensitivity. To minimize withdrawal symptoms, it is generally recommended to taper off gabapentin gradually under medical supervision. Gabapentin withdrawal symptoms can mimic those of benzodiazepine withdrawal due to similar mechanisms of action affecting GABA levels, indicating a potential for cross-dependence or distress in patients with long-term use. Some people can become addicted to gabapentin. If this happens, you’ll have withdrawal symptoms after you stop taking the medicine. When you stop taking gabapentin, you'll need to reduce your dose gradually to avoid withdrawal symptoms. Do not stop taking gabapentin without talking to your doctor. When abruptly stopping gabapentin (Neurontin), withdrawal symptoms are likely to occur within the first 1-2 days. If the medication is gradually reduced, withdrawal symptoms may begin within this time or may take slightly longer to emerge, if at all. [2] [5] Generally, withdrawal symptoms will last for up to two weeks. Gabapentin withdrawal happens when a person stops taking the medication abruptly, which may lead to symptoms such as confusion, disorientation, and seizures. The duration of these symptoms can vary, but preventive steps can limit the impact. It is important to discuss medication withdrawal risks with your prescriber. If you want to What Are the Symptoms of Gabapentin Withdrawal? The main symptoms of gabapentin withdrawal are nausea, anxiety, headaches, and seizures. According to the study titled “Gabapentin Withdrawal Syndrome” by Tran et al., published in Pharmacotherapy in 2005, gabapentin withdrawal occurs in patients who abruptly discontinue the medication, particularly after long-term use or high doses. What Are the Long-Term Effects of Taking Gabapentin? The fact that gabapentin is associated with withdrawal symptoms suggests that users may develop physiological dependence. Physiological dependence occurs when neurons in the brain adapt to account for the regular use of a substance. Gabapentin Taper Plan: Gradually reducing the dosage according to a structured gabapentin taper chart can significantly lower the risk of severe withdrawal symptoms. Medical Supervision : Healthcare professionals can prescribe short-term anxiety relief or adjust gabapentin doses more gradually to reduce severe withdrawal. Even if you’ve taken gabapentin for a short period, like two weeks, you might still experience withdrawal symptoms when you try to quit. These symptoms may include bloating, mood changes, and difficulty sleeping. But don’t worry, we’ve got you covered!
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |