Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
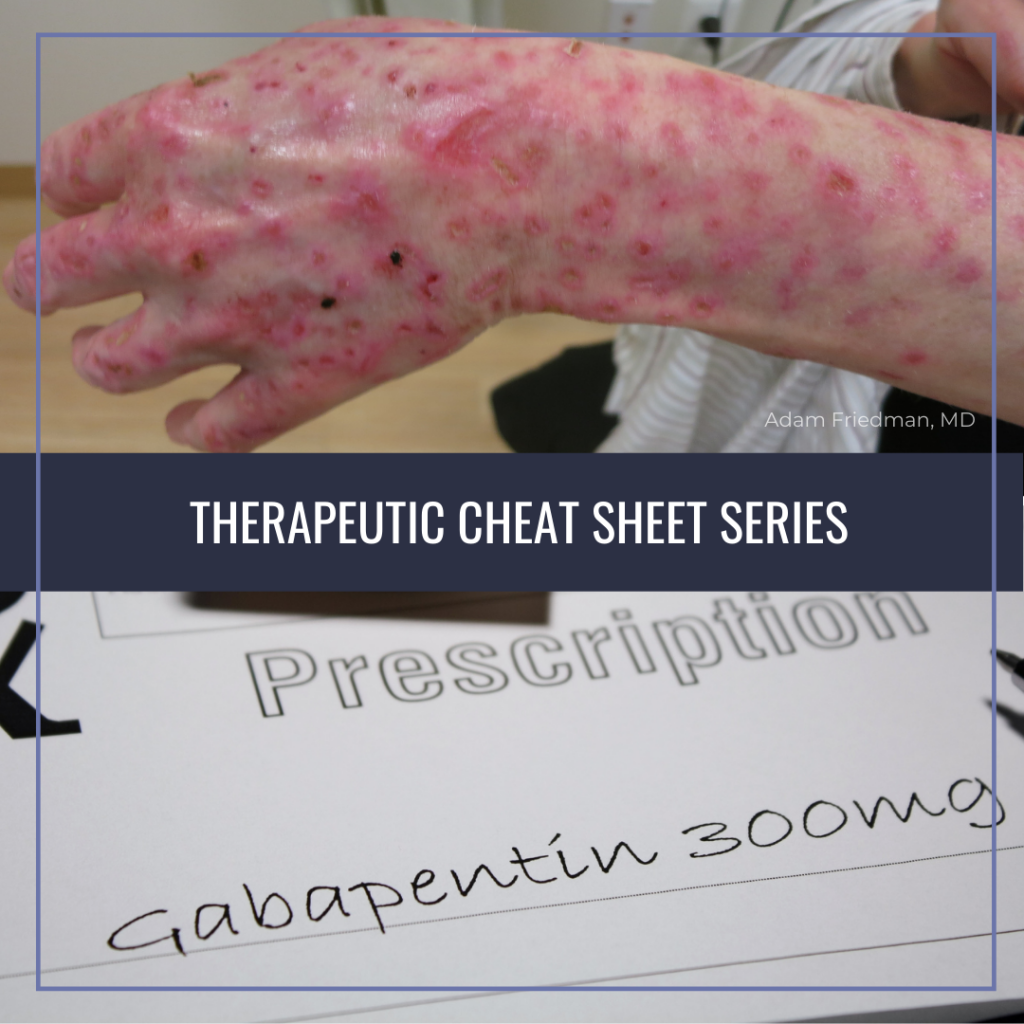
Gabapentin has few side effects and can be administered in certain disorders, being a good option for very sick cats. Occasionally, cat owners may report increased drowsiness, which may give their It is crucial for nurses to be familiar with the potential side effects and nursing implications of medications like Gabapentin to ensure safe and effective care for their patients. By staying informed and proactive, nurses can play a vital role in managing the adverse effects associated with Gabapentin and provide optimal patient care. It is thought that Gabapentin may play a role in neural membranes. We use Gabapentin for the prevention of seizures for peripheral neuropathy, for neuropathic pain and for the prevention of migraines. So some of the side effects that we see with Gabapentin are things like drowsiness, facial edema, hypertension, and confusion. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. The most significant or serious side effects are suicidal ideation, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, rhabdomyolysis, and hypersensitivity reactions including angioedema and anaphylaxis. Nursing implications When starting therapy or increasing the dosage, patients should be monitored for depression and suicidal thoughts. Read this chapter of Davis's Drug Guide for Rehabilitation Professionals online now, exclusively on F.A. Davis PT Collection. F.A. Davis PT Collection is a subscription-based resource from McGraw Hill that features trusted content from the best minds in PT. Some side effects of gabapentin may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects. What are the side-effects of gabapentin (Neurontin)? Pharmacologic class: gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue. Therapeutic class: anticonvulsant, antineuralgic. Pregnancy category: C. Epilepsy dosage. Adults: PO: 300mg TDS. Maintenance dose: 900 – 1800mg/day in 2 to 3 divided doses. Children (3-12yrs): PO: 10 – 15mg/day in 3 divided doses. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Ultimately, this results in decreased seizure activity. The most common side effects are gastrointestinal problems, such as dyspepsia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. Some clients might also experience hematologic side effects, like thrombocytopenia and leukopenia; while others can develop DRESS. Patient/caregiver was educated on side effects of gabapentin as follows: General allergic reactions: Gabapentin use can result in general allergic reactions, such as, skin rashes, hives, and itching. Managing Gabapentin Side Effects. Successfully managing gabapentin side effects in elderly loved ones often involves a multi-faceted approach. The first step is regular monitoring. Keep track of any physical, emotional, or cognitive changes and keep an open line of communication with your loved one’s healthcare team. You may experience these side effects: Dizziness, blurred vision (avoid driving or performing other tasks requiring alertness or visual acuity); GI upset (take drug with food or milk, eat frequent small meals); headache, nervousness, insomnia; fatigue (periodic rest periods may help). Inform to take gabapentin at bedtime to minimize adverse effects. Do not suddenly stop gabapentin due to the increased risk of seizure. Teach the patient to avoid driving and activities that require concentration until the effects have been evaluated. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. Assess for and document side effects. Monitor for signs of abuse or dependence. Provide emotional support and frequent monitoring for patients at risk for suicidal ideation. Ensure proper hydration. Monitor weight regularly. Take gabapentin exactly as prescribed, at evenly spaced intervals. Educate patients about potential side effects of gabapentin, such as drowsiness, dizziness, or gastrointestinal symptoms. Being aware of potential side effects helps patients recognize and attribute these symptoms to the medication, promoting early reporting and appropriate management. Three infants who were 2 to 3 weeks of age and one who was 14 weeks of age were breastfed during maternal use of gabapentin in an average daily dosages of 1575 mg (range 600 mg to 2.1 grams daily). Serum levels were measured after the morning nursing before the mothers' morning dose of gabapentin (10 to 15 hours after the prior evening's dose). All drugs may cause side effects. However, many people have no side effects or only have minor side effects. Call your doctor or get medical help if any of these side effects or any other side effects bother you or do not go away: Feeling dizzy, sleepy, tired, or weak. Diarrhea, upset stomach, or throwing up. Dry mouth. These are not all of the Find information on Gabapentin (Gralise, Horizant) in Davis’s Drug Guide including dosage, side effects, interactions, nursing implications, mechanism of action, half life, administration, and more. Davis Drug Guide PDF.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |