Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
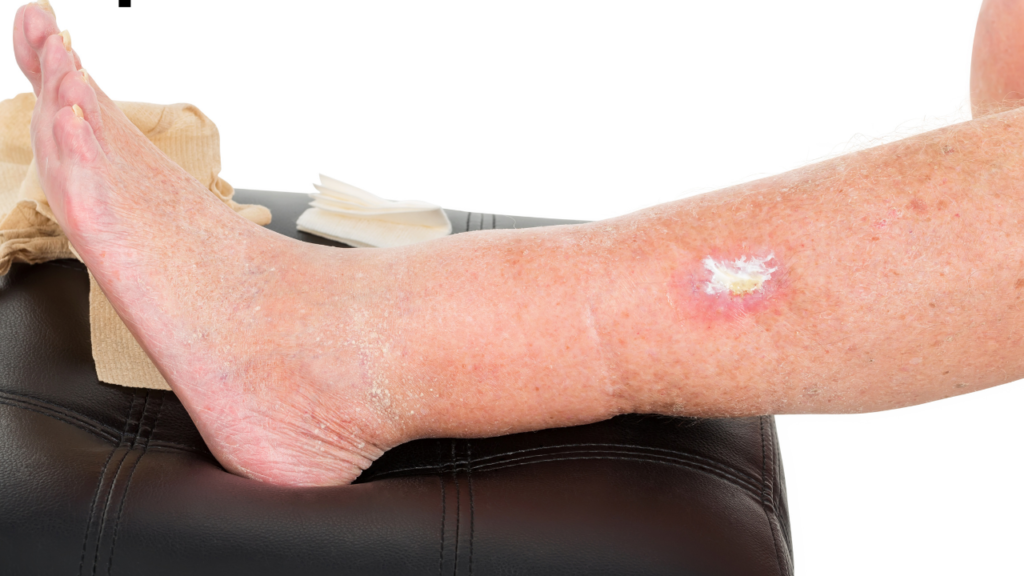
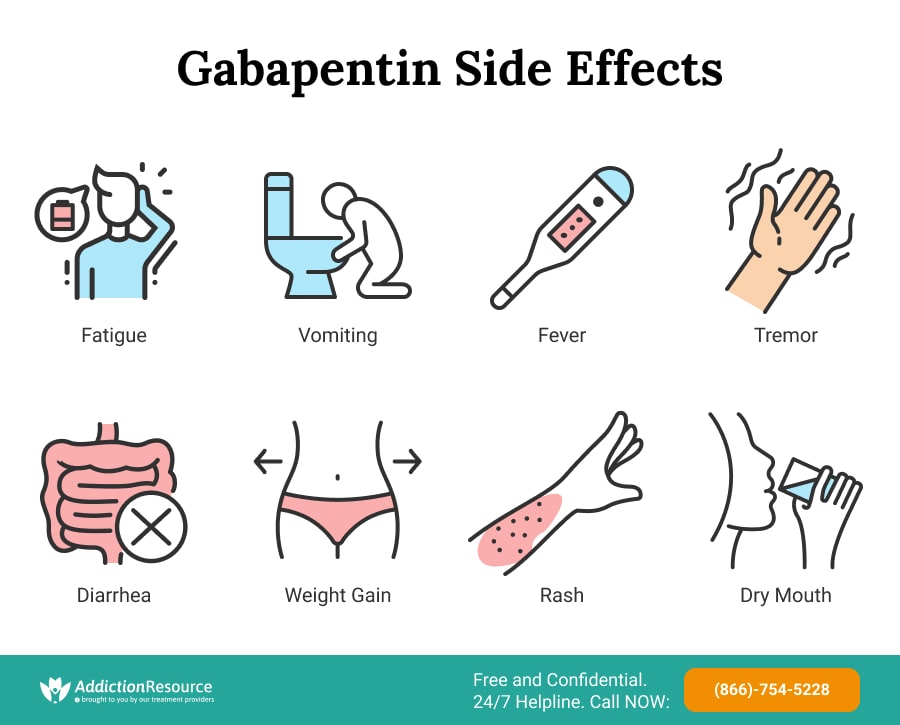
Peripheral neuropathy is difficult to treat successfully; tricyclic antidepressants are effective at reducing pain, but intolerable side effects often limit their use. Peripheral neuropathy is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are male, 50-59 old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Furosemide, and have Hiv infection. The peripheral neuropathy seen with levodopa treatment is an axonal-type sensory peripheral neuropathy that tends to be mildly symptomatic or even asymptomatic in some cases . On nerve conduction studies, a reduction in sural nerve amplitude has been noted [ 57 ]. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant and has been used to manage neuropathic pain. Gabapentin is not without side effects and there is also potential for misuse. Side effects associated with gabapentin include somnolence, dizziness, peripheral edema and gait disturbances. This has been used as a treatment for peripheral neuropathy in Europe for years and there is some evidence that it can be helpful in those with painful diabetic neuropathy. Discuss using alpha-lipoic acid with your health care professional because it can affect blood sugar levels. Painful peripheral neuropathy, especially in the hands and feet, is a common side effect. Gabapentin is a commonly used medication to relieve pain from damage to the peripheral nerves, which Gabapentin is not without side effects and there is also potential for misuse. 5 Side effects associated with gabapentin include somnolence, dizziness, peripheral edema and gait disturbances. 6 Gabapentinoids (including gabapentin) in high doses may result in sedative and psychedelic effects. 5 Gabapentin is structurally related to the The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. Side effects were more common with gabapentin (6 in 10) than with placebo (5 in 10). Dizziness, sleepiness, water retention, and problems with walking each occurred in about 1 in 10 people who took gabapentin. Serious side effects were uncommon, and not different between gabapentin and placebo. If your peripheral neuropathy stems from a condition like diabetes or vitamin deficiencies, gabapentin alone won’t resolve the root issue, and your pain may continue—or worsen—without a comprehensive treatment plan. Because these drugs have few side effects and are usually well tolerated, they are often the first medications to try for neuropathic pain. Most doctors will prescribe gabapentin first; if that doesn't work, they will try pregabalin. You may experience side effects, such as drowsiness, dizziness, confusion, or swelling in the feet and legs. However, it's best to take it at night, as one of the most frequent side effects of gabapentin is drowsiness. Most people will end up taking gabapentin three times daily. However, to ensure a consistent level of gabapentin throughout the day, it's recommended to take the medication at even intervals, approximately every eight hours. After 12 weeks, each person rated their neuropathy symptoms on a scale from 1 to 10, noted any side effects, and reported whether they had quit taking the medication due to side effects, cost, or some other reason. Though the trial is important and much needed, the results were disappointing. No medication was a clear winner or highly effective. Painful peripheral neuropathy, especially in the hands and feet, is a common side effect. Gabapentin is a commonly used medication to relieve pain from damage to the peripheral nerves, which Gabapentin is indicated for: Neuropathic pain caused by postherpetic neuralgia Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial seizures with or without secondary generalization; Neuropathic pain caused by diabetic peripheral neuropathy and spinal cord injury Restless leg syndrome (gabapentin enacarbil) Gabapentin is frequently used off-label for: Gabapentin at doses of 1800 mg to 3600 mg daily (1200 mg to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. Evidence for other types of neuropathic pain is very limited. I was just wondering if it is possible that gabapentin can sometimes make neuropathy pain worse. My EMG and biopsy results are negative for short fiber neuropathy so far. Interested in more discussions like this? Go to the Neuropathy Support Group. Among patients who were treated with gabapentin, the most common side effects were nausea and vomiting (9.7%), sleeplessness (4.1%), and imbalance (2.1%). The limitations of this study included a Key Takeaways: Gabapentin and Peripheral Neuropathy Possible Link: Gabapentin may contribute to peripheral neuropathy in some. Mixed Research Findings: Studies show varying results on gabapentin’s effects. Dosage Matters: Higher doses over time may increase risks of side effects. Check with your doctor immediately if any of the following side effects occur while taking gabapentin: More common in children. Some side effects of gabapentin may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |