Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
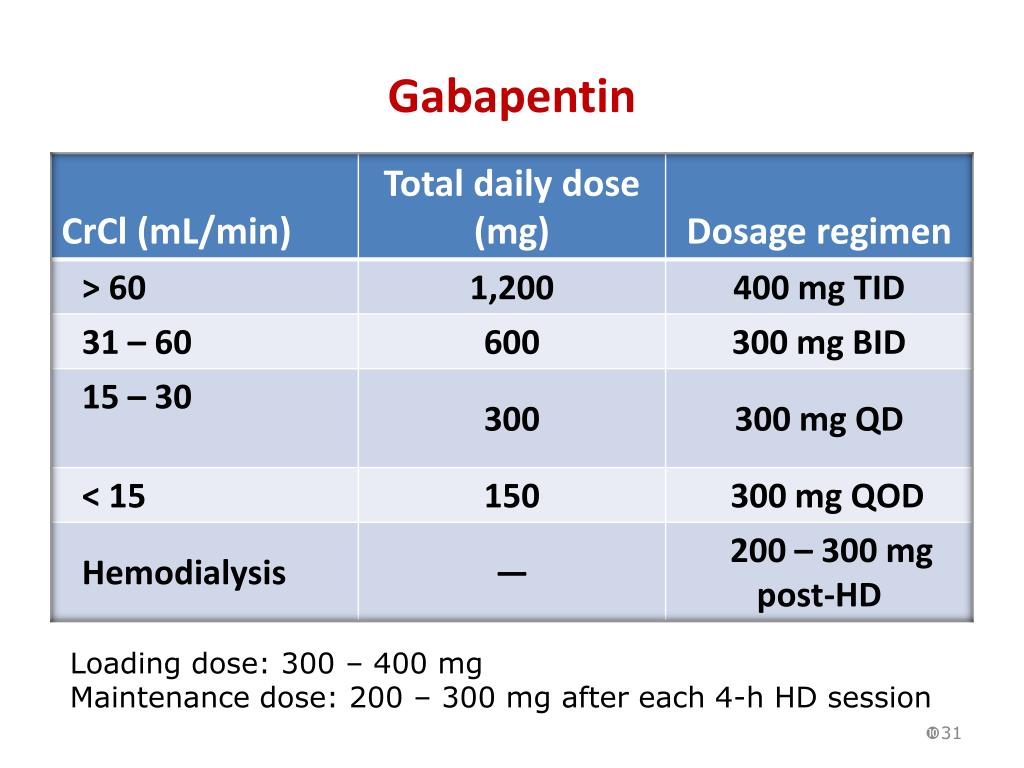
If you have diabetes and chronic kidney disease, check with your physician to see if any dosing changes need to be made based on your level of kidney function. Upset stomach/antacid medications. This group of over-the-counter medications can disrupt the body's electrolyte balance if you have chronic kidney disease. Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Majority drugs, including Gabapentin, are eliminated by the kidneys and will accumulate to a toxic level in renally compromised patients as in this case. Per Lexicomp, Gabapentin’s recommended dose in patients with renal impairment is as follows: CrCl >15 to 29 mL/minute: 200 to 700 mg once daily. CrCl 15 mL/minute: 100 to 300 mg once daily In most cases, gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys, though proper dosing is important to prevent side effects. Learn how gabapentin affects the liver and kidneys here. Gabapentin can be used long-term in cats with kidney disease, as long as it is monitored regularly by a veterinarian for any potential side effects or changes in kidney function. 5. Are there any side effects of gabapentin in cats with kidney disease? Common side effects of gabapentin in cats may include sedation, dizziness, and It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Some cats may experience no side effects at all, while others may have more severe reactions. It is important for pet owners to monitor their cat closely when starting Gabapentin to watch for any adverse effects. Trend #4: Gabapentin as a Pre-Anesthetic Medication. Gabapentin is also being increasingly used as a pre-anesthetic medication in Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Gabapentin is used for muscular symptoms in motor neurone disease, E but is not licensed for this indication. Important safety information The levels of propylene glycol, acesulfame K and saccharin sodium may exceed the recommended WHO daily intake limits if high doses of gabapentin oral solution (Rosemont brand) are given to adolescents or Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. When it comes to gabapentin and kidney disease, kidney disease sufferers should be aware of the risks that are involved in taking gabapentin with kidney disease. Gabapentin is actually toxic to the kidneys. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. The second case was for a 55-year-old man with a history of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) on peritoneal dialysis (PD), diabetes mellitus, neuropathic pain, and peripheral vascular disease who was evaluated for acute worsening severe upper extremity tremor and altered mental status shortly after initiation of gabapentin 600 mg total daily dose Does gabapentin have any cardiac side effects I should be aware of with kidney disease? Some studies suggest a potential link between short-term gabapentin use and increased risks of cardiac issues like heart failure, which is more concerning for patients with kidney disease and may further compromise their health. The straightforward answer is yes, you can potentially take gabapentin if you have stage 3 kidney disease, but with significant caveats. It’s crucial to understand that gabapentin is primarily eliminated by the kidneys, meaning that impaired kidney function can lead to a buildup of the drug in your system. Some of its most common side effects include the following: ataxia, nystagmus, drowsiness, headaches, diplopia, fatigue and myoclonic twitches. 1 All of these effects appear quite often in patients with chronic kidney disease, especially if they are undergoing dialysis and their doses are not adjusted to their glomerular filtration rates. 2 We The short answer is: yes, gabapentin can be problematic for individuals with kidney failure and chronic kidney disease (CKD). While gabapentin is often prescribed for pain management, particularly nerve pain, and sometimes for seizures, its primary elimination pathway is through the kidneys. With a growing chronic kidney disease epidemic, 22, 23 an increasing number of patients with chronic kidney disease will be exposed to gabapentin. This study demonstrates that gabapentin dosage for patients with chronic kidney disease has been insufficiently adjusted and that the risk of gabapentin toxicity has been underrecognized. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used for neuropathic pain in CKD patients but are not fully understood as this population remains excluded from efficacy and safety trials. Renal adjustments for the gabapentinoids are prodigiously recommended in the literature. However, when kidney function is impaired, gabapentin can accumulate in the body, leading to potential side effects like excessive sedation, dizziness, and confusion. Therefore, cautious dosing, usually significantly lower than what might be given to a cat with healthy kidneys, is essential.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |