Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
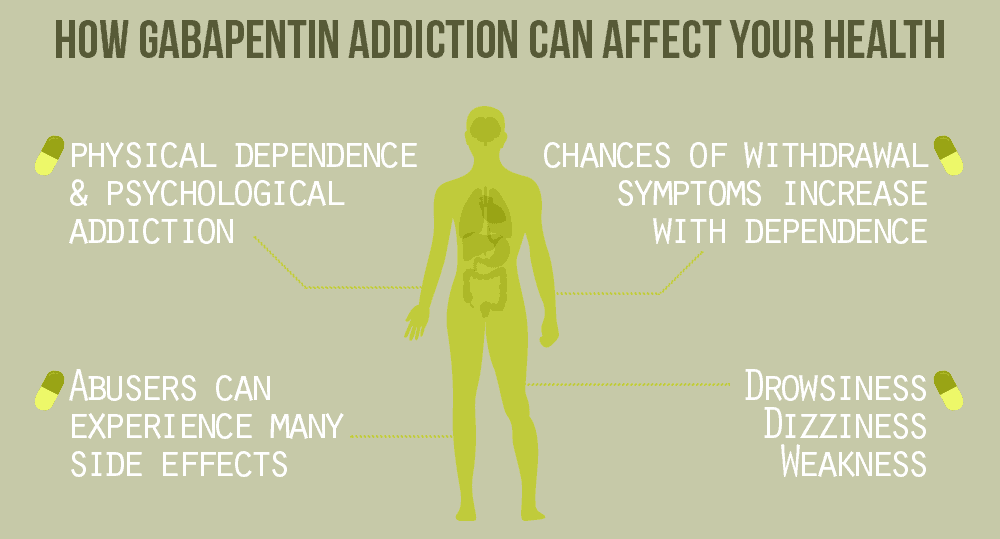
A population-based cohort study of more than 10,000 persons using gabapentinoids found that their use was associated with an increased risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbation. Montreal—A new cohort study has identified an association between use of gabapentinoids and an increased risk of severe exacerbation in patients with COPD. Common side effects of gabapentinoids include drowsiness, dizziness, blurry or double vision, difficulty with coordination and concentration, and swelling of the hands, legs, and feet. Gabapentinoid use was associated with a significantly increased COPD exacerbation risk for each group of users compared with nonusers, with hazard ratios of 1.58, 1.35, and 1.49 for epilepsy Use of gabapentinoids (gabapentin, pregabalin) by people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) was associated with a 39% increased risk for severe disease exacerbation, according to investigators from McGill University and Lady Davis Institute for Medial Research in Montreal, Canada. The authors reported about gabapentin side effects: “perioperative gabapentin use was associated with modestly increased risk of delirium, new antipsychotic use, and pneumonia but not with in-hospital death among adults aged 65 years or older after major surgery. Health care professionals and patients should report side effects from gabapentin, pregabalin or other medicines to the FDA’s MedWatch program. Additional Resources Opioid Medications Neurology > General Neurology FDA Warns of Breathing Problems With Gabapentinoids — Updated labeling for gabapentin, pregabalin, and new trials required. by Judy George, Senior Staff Writer Gabapentin and pregabalin, commonly known as gabapentinoids, have been widely used globally. This paper highlights the serious breathing problems due to using gabapentin and pregabalin which was warned by the United States Food and Drug One RCT found side effects in 31% of gabapentin group while 10% of patients taking placebo, including confusion, dizziness, nausea, dry mouth, fatigue, headache, blurred vision, and memory loss17. The other RCT reported adverse events in 40% of gabapentin group vs 23.1% in the placebo group, with similar side effects as Ryan et al. 17 reported. Side effects of gabapentin. Common side effects of gabapentin include: drowsiness or dizziness; headache or blurred vision; nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation; dry mouth; weight gain; swelling of the hands, feet, or ankles; back or joint pain; flulike symptoms such as fever or body aches. Rare but serious side effects. Rare but serious Still, gabapentin’s cardiac side effects sometimes include a severe alteration of the heart rhythm called atrial fibrillation and other types of arrhythmia. Gabapentin can also have long-term side effects when administered for an extended period. Neurontin side effects in the long long-term include: Compared with nonuse, gabapentinoid use was associated with increased risk for severe COPD exacerbation across the indications of epilepsy (HR, 1.58 [95% CI, 1.08 to 2.30]), neuropathic pain (HR, 1.35 [CI, 1.24 to 1.48]), and other chronic pain (HR, 1.49 [CI, 1.27 to 1.73]) and overall (HR, 1.39 [CI, 1.29 to 1.50]). Can gabapentin be fatal to people with COPD? Gabapentin can lead to respiratory depression in people with reduced lung function due to COPD. That’s when your breathing is too slow and What are the more common side effects of gabapentin? Common side effects of gabapentin include: Feeling tired. Dizziness. Headache. Nausea and vomiting. Fever. Difficulty speaking. Recurring infections. Memory loss. Weight gain. Movement problems: coordination problems, being unsteady, tremors, jerky movements. Listen to an audio podcast of the December 19, 2019 FDA Drug Safety Communication warning that serious breathing difficulties may occur in patients using seizure and nerve pain medicines Gabapentinoids are associated with an increased risk of severe exacerbation in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), a study of more than 10 000 people has reported. 1 Gabapentinoid use, namely gabapentin and pregabalin, was associated with increased risk for severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbation in patients with epilepsy, Gabapentinoid use was associated with significantly higher risk for severe COPD exacerbations requiring hospitalization (15.1% vs. 8.3% annually; adjusted hazard ratio, 1.4). Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who use gabapentinoids for epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and other chronic pain have an increased risk for severe COPD exacerbations, researchers reported in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |