Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cervical-radiculopathy-physical-therapy-5199243_final-01-a732057be7c14ac0a3be1a7dc75325f0.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
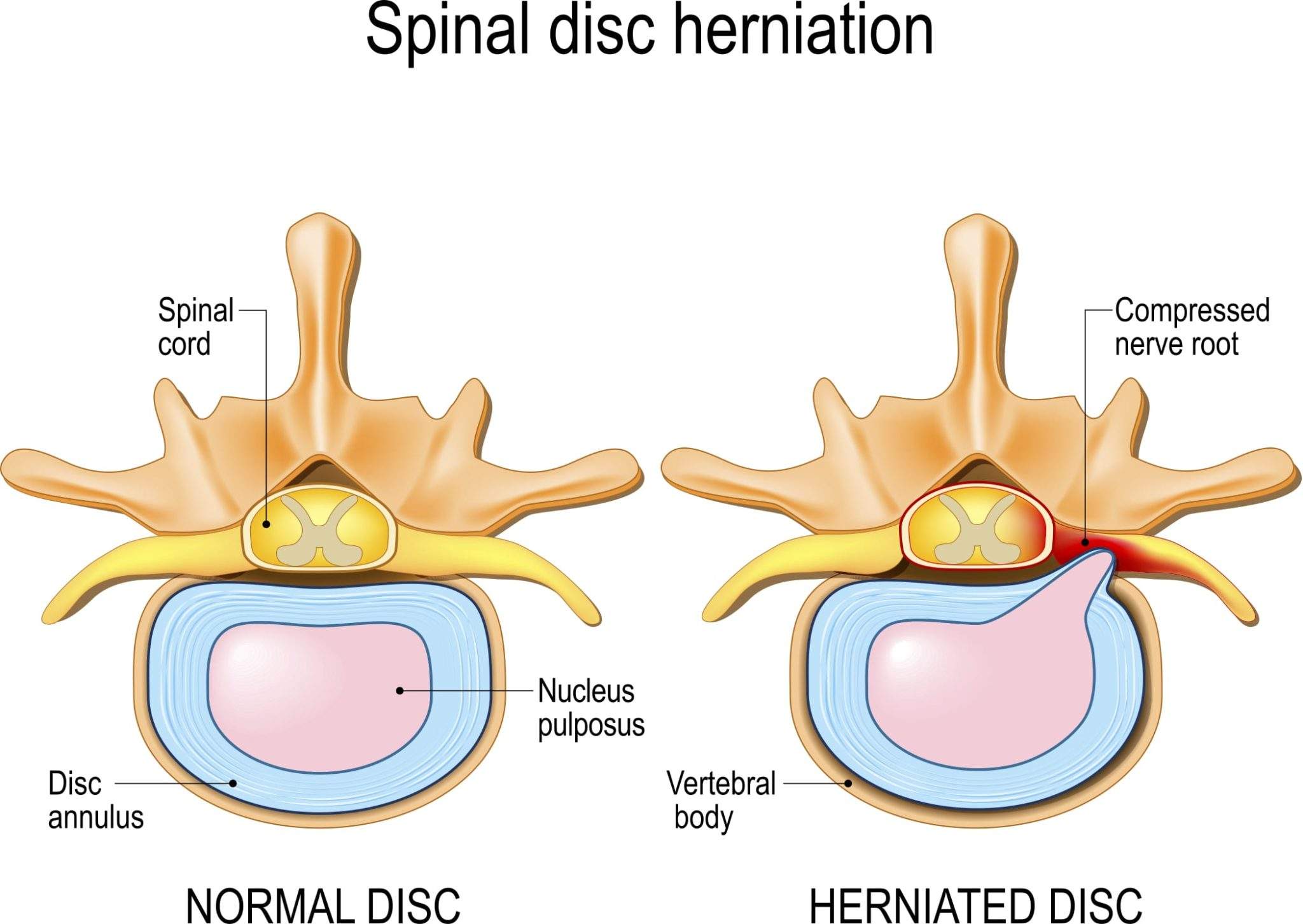 |  |
UpToDate Learn the difference between lumbar and cervical radiculopathy. Important Updates so gabapentin is that type of medication I talked about that relaxes the nerve Tricyclic antidepressants and drugs such as gabapentin are useful adjuncts in the treatment of cervical radiculopathy. Opioid pain medications are not recommended for routine use, but they can be useful in managing radicular pain. Cervical radiculopathy treatments include nonsurgical therapies such as anti-inflammatory drugs, physical therapy and epidural steroid injections. (prednisone), neuropathic agents (gabapentin In the case of cervical radiculopathy, gabapentin can be helpful in relieving the symptoms associated with nerve compression in the neck. It can reduce the intensity and frequency of pain, as well as alleviate the tingling and burning sensations that often accompany this condition. Among many medications available for managing neuropathic pain, gabapentinoids, including gabapentin (GBP) and pregabalin (PGB), are considered as the first-line treatment in most clinical guidelines. PGB is commonly used to alleviate radicular pain and accompanying symptoms in patients with cervical or lumbar radiculopathy. What is Gabapentin? Gabapentin has active ingredients of gabapentin. It is often used in neuralgia. eHealthMe is studying from 322,822 Gabapentin users for the drug's side effects, drug interactions, effectiveness and more. Check Gabapentin in the real world. What is Herniated nucleus pulposus (slipped disk)? Cervical radiculopathy most commonly involves C6 and C7 nerve roots. Cervical nerve roots exit above their corresponding pedicles (except C8) ventrolaterally through the neuroforamen which makes them vulnerable to injury. Radiculopathy may cause severe pain that significantly reduces quality of life for some people. Treatment options vary based on the severity of symptoms and the degree of damage to the affected spinal nerves. Medications: Some medications, such as gabapentin (Neurontin®) or pregabalin (Lyirca®) may treat the pain caused by radiculopathy. It Tricyclic antidepressants, gabapentin, and pregabalin can be useful adjuncts in controlling radicular pain. []Opioid medications are generally not necessary for pain relief, but these drugs can be used when other medications fail to provide adequate relief or if other agents are contraindicated. Abstract. Lumbar radiculopathy can be presented as low back pain and radiating pain. Transforaminal epidural steroid injection (TFESI) has been used to treat radicular pain, and after the injection, additional medications such as gabapentinoids including pregabalin (PGB) and gabapentin (GBP) can be administered to relieve remnant pain. Although they are approved by the FDA to treat seizures, anticonvulsant drugs such as gabapentin , carbamazepine , and pregabalin may help with nerve-related neck pain. Nonoperative treatment includes physical therapy involving strengthening, stretching, and potentially traction, as well as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, and massage. When it comes to neck pain, gabapentin is commonly prescribed for conditions such as cervical radiculopathy, in which the nerves in the neck become compressed or irritated, causing pain, numbness, and weakness. By taking gabapentin, patients can experience significant relief from these symptoms. Gabapentin is not effective for the treatment of radicular low back pain and is associated with adverse effects. (Strength of Recommendation: B, based on a systematic review of Medications that include gabapentin and pregabalin are frequently used to relieve radiculopathy related pain symptoms. These medications work differently than anti-inflammatory medications. (They are also used, though less frequently, for patients suffering seizure disorders.) In a study by Yildirim and colleagues, 50 patients with lumbosacral radiculopathy who were randomly assigned to oral gabapentin ranging from 900 to 3600 mg/d or to placebo for 8 weeks were described. Those who received gabapentin were shown to have improved motor and sensory function, lumbar flexion range of motion ( P <.001), and pain at rest Reference: Enke O, New HA, New CH, et al. Anti-convulsants in the treatment of low back pain and lumbar radicular pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis.CMAJ. 2018;190(26):E786–E793. Methods: Thirty-five patients with radicular pain and diagnosed as L4, L5 or S1 radiculopathy were treated with oral gabapentin from a total of 300 mg per day once up to a total of 1800 mg per day divided in 3 doses for eight-week trial period. This is a phase IV clinical study of how effective Gabapentin (gabapentin) is for Cervical radiculopathy and for what kind of people. The study is created by eHealthMe from 35 Gabapentin users and is updated continuously.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cervical-radiculopathy-physical-therapy-5199243_final-01-a732057be7c14ac0a3be1a7dc75325f0.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |