Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
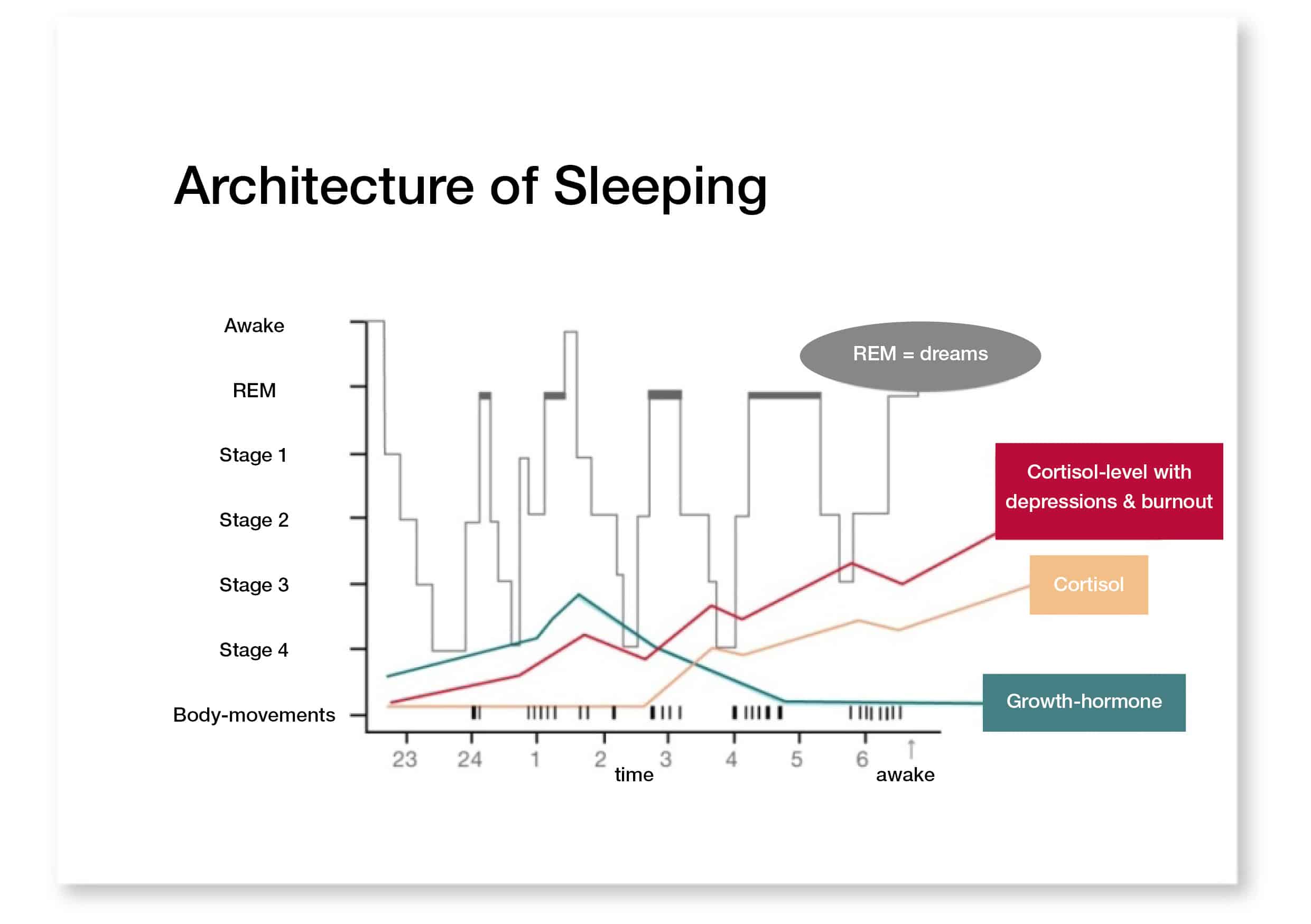
When comparing gabapentin to other sleep medications, it’s important to note that its effects on sleep architecture differ from those of traditional sleep aids. For instance, Gabapentin vs Ambien for Sleep: Comparing Effectiveness and Safety reveals distinct mechanisms of action and potential outcomes. Key Words: Gabapentin—Sleep architecture—Polysomnography—Antiepileptic drugs— Daytime sleepiness. purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of GBP on sleep architecture and daytime vigilance in nor-mal adults. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Cleveland Clinic Foundation. Discussion. This study revealed that without consideration of the type of sleep outcomes, gabapentin was significantly superior to placebos for the treatment for sleep disorders secondary to RLS, neuropathic pain, alcohol dependence, hot flashes in menopause, fibromyalgia, phantom limb pain, HIV-associated sensory neuropathies, and bipolar disorder. By enhancing GABA’s effects, gabapentin may help to calm overactive neural circuits, potentially leading to a more relaxed state conducive to sleep. Research has shown that gabapentin can have significant effects on sleep architecture, the pattern and structure of sleep stages throughout the night. The sleep questionnaire included the average number of hours of sleep per night, sleep latency, number of awakenings and their cause, napping habits, caffeine use, and sleep disorder symptoms such as snoring, witnessed apnea, difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep, restlessness, and uncomfortable sensations in the legs in the evening • Improved sleep quality: By enhancing sleep architecture, Gabapentin can help improve the overall quality of sleep, leading to more restful and rejuvenating sleep. • Reduction of sleep disturbances: Gabapentin can help reduce the frequency and severity of sleep disturbances, such as waking up during the night or experiencing fragmented sleep. Results: Polysomnographic study revealed increased sleep efficiency and slow-wave sleep, decreased wake after sleep onset, and spontaneous arousal index after gabapentin treatment. The biochemical blood test revealed decreased prolactin levels in the morning after treatment. Most studies show that gabapentin improves slow wave sleep (“deep sleep”) and total sleep time. Two small studies showed that gabapentin may help people with primary insomnia and occasional sleep disturbance improve total sleep time and wakefulness in the morning. We have demonstrated that gabapentin can produce dose-dependent increases in slow wave sleep and ameliorate the effects of chronic alcohol on sleep fragmentation, in an adult rat model of alcohol-induced sleep disturbance (Sanchez-Alavez et al. 2018). In the present study, we extend those findings to an adolescent model of alcohol exposure and Like baclofen, some studies have shown that gabapentin might be of interest in alcohol dependence management [2]. In this context, baclofen is linked to sleep apnea syndrome [3, 4], aggravating sleep-disordered breathing by depressing central ventilatory drive and/or increasing upper airway obstruction. Regardless the type of sleep outcomes, gabapentin showed stable efficacy in the treatment for sleep disturbance in patients with medical illness with a relatively high risk of treatment discontinuation and drug withdrawal when used at an average dose of approximately 1,800 mg/day. Finally, a GABA A agonist appears to both increase stage 3 and 4 sleep and improve various measures of insomnia, and a GABA B agonist increases stage 3 and 4 sleep, consolidates sleep by reducing sleep stage shifts and awakenings and improves the daytime sleepiness associated with narcolepsy. No difference in total sleep time was seen for any of the groups (baseline vs alcohol or alcohol-placebo vs alcohol-gabapentin). Effects of alcohol on sleep are shown in the Table 1. There was no significant change in any of the studied parameters. The effects of gabapentin on sleep are shown in the Figure 1. When all gabapen- In the present study, gabapentin produced only modest changes in sleep architecture that were directionally consistent across the 2 sleep phase advance periods. Architecture: Gabapentin appears to improve sleep architecture by increasing slow-wave sleep and decreasing fast-wave sleep. Specifically, EEG readings indicate that gabapentin increases delta-2 waves and theta waves in Stage 1 of sleep and decreases sigma waves Stages N2 and N3. To appreciate how gabapentin influences sleep, it’s essential to delve into the intricate architecture of our nightly rest. Sleep is not a uniform state but rather a complex cycle of different stages, each playing a vital role in physical and mental restoration. Gabapentin appears to have a multifaceted impact on this sleep structure Keywords: Antiepileptic drugs; Sleep architecture; Pilot study 1. Introduction Two of the most prevalent complaints of patients with epilepsy are disturbed sleep and excessive daytime drowsi-ness [1]. These symptoms have several possible causes, including coexisting sleep disorders, effects of seizures, and effects of anticonvulsant drugs. Gabapentin 250 and 500 mg also affected sleep architecture; percent slow wave sleep (stages 3 and 4 combined) was significantly greater and percent stage 1 significantly lower versus placebo (p ≤ 0.05). The 2 gabapentin doses were not significantly different from each other. Gabapentin enhances slow-wave sleep in patients with primary insomnia. It also improves sleep quality by elevating sleep efficiency and decreasing spontaneous arousal. The results suggest that gabapentin may be beneficial in the treatment of primary insomnia. Areas of particular interest include the long-term effects of gabapentin use on sleep architecture in sleep apnea patients, the potential for developing gabapentin formulations with reduced impact on respiratory function, and the exploration of novel combination therapies that can address both pain and sleep disorders effectively.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |