Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
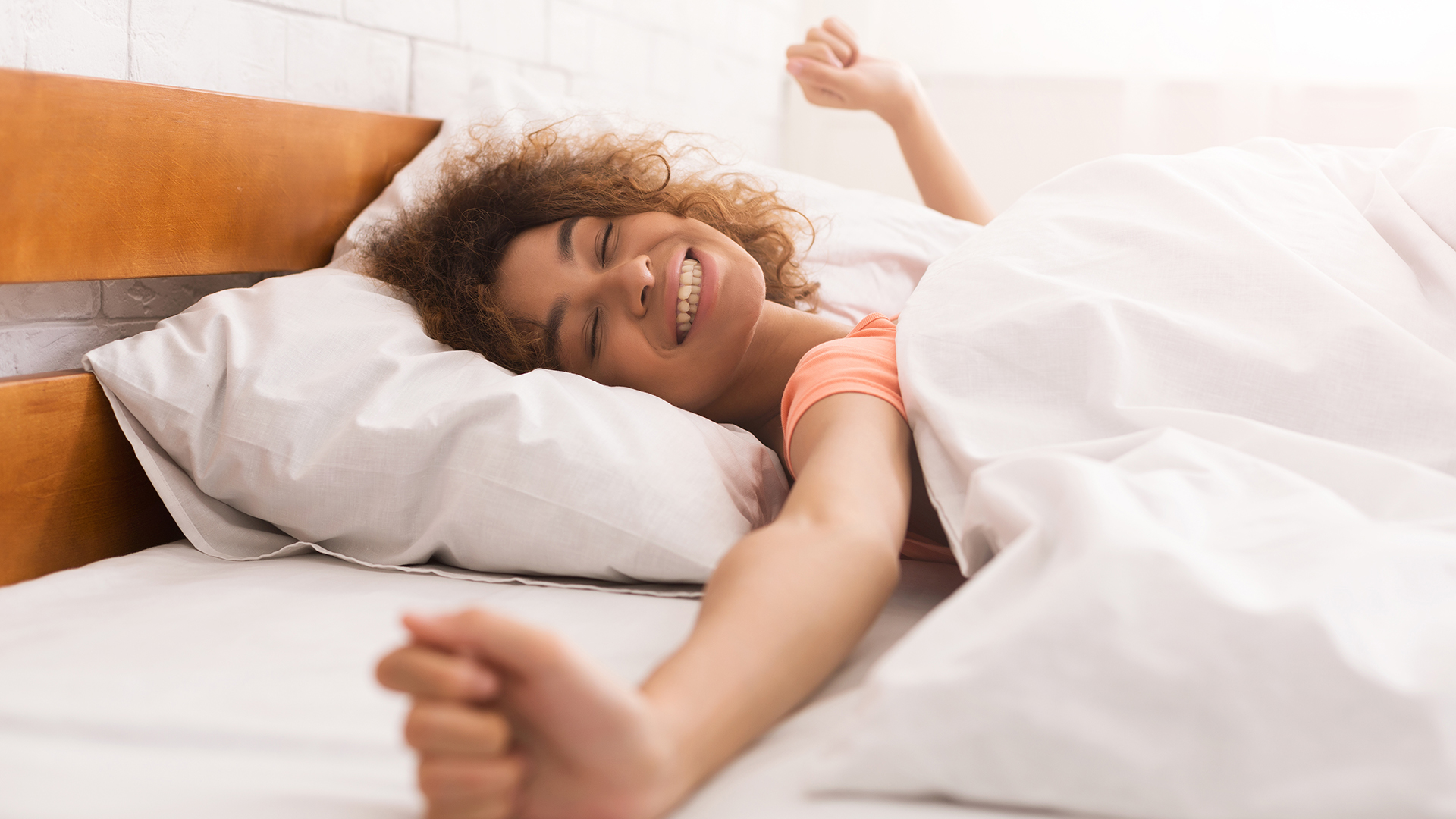
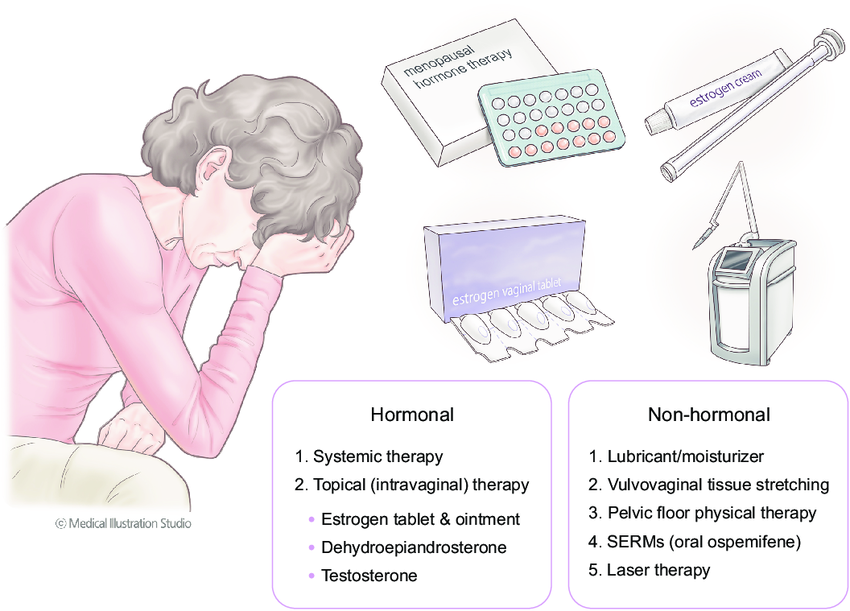
By reducing the intensity and frequency of hot flashes, Gabapentin can help improve the overall quality of life. Patients often report better sleep, less anxiety, and an increase in daily functioning. Better sleep quality: Reduces night sweats and nighttime disturbances. Less psychological stress: Decrease in hot flash-induced anxiety and The researchers compared the effects of extended-release gabapentin vs. a placebo on sleep problems in postmenopausal women using data from the Breeze 1 study, which was a phase III, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted at 48 sites. Gabapentin doses range from 100 to 2700 mg daily. Begin treatment with gabapentin IR at 100- 300 mg nightly and slowly titrate up to 900-1200 nightly, and use lower doses during the day to minimize side effects. By targeting the underlying causes of sleep disruption, gabapentin can help women achieve a more restful and rejuvenating sleep. This improvement in sleep quality can have a positive impact on their overall well-being and quality of life during the menopausal transition. Therefore, by improving sleep quality, gabapentin can contribute to better overall health for menopausal women. Conclusion. Gabapentin offers a promising solution for menopausal women experiencing sleep disturbances. By targeting the underlying causes of sleep disruption, gabapentin can help women achieve a more restful and rejuvenating sleep. Three cases are presented here of late premenopausal women experiencing frequent nighttime awakenings that responded well to bedtime treatment with gabapentin. In one case, what started as isolated nighttime awakenings slowly progressed to awakenings accompanied by typical menopausal night sweats. Gabapentin may improve sleep quality in menopausal women with hot flashes. These results warrant further prospective investigation, with an emphasis on measuring subjective sleep quality and maintenance. Gabapentin may be a better choice for women with predominant nocturnal HFs for its added benefit on the maintenance of sleep cycle. It is as effective as venlafaxine, but patients often prefer venlafaxine due to better tolerance profile of later. The dosage of gabapentin needs to be individualized. Navigating menopause can be challenging, with symptoms like hot flashes, mood swings, and sleep disturbances affecting daily life. While hormone replacement therapy is a common treatment, some women seek alternatives. Gabapentin, traditionally used for nerve pain, has emerged as a promising option for managing menopaus isorder is most common associated manifestations. Sleep disorders and insomnia largely remain a clinical diagnosis based on the subjective complaints of patients. Benzodiazepines remain the mainstay of the treatment in majority of the sleep disorders including chronic or acute insomnia. Treatment of associated anxiety, depression, or psychosis is most important. Tricyclic antidepressant Clinicians have been using gabapentin off-label to help relieve hot flashes in postmenopausal women. A new extended-release formulation of gabapentin has also shown efficacy in treating hot flashes and improving sleep quality with potentially fewer side effects than regular gabapentin. 12–18. Gabapentin may cause side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and dizziness. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and seek medical attention if experiencing serious side effects or changes in mood or behavior. Gabapentin is prescribed by healthcare professionals and should only be taken under medical supervision. To fully appreciate the potential role of gabapentin in addressing menopause-related sleep issues, it’s crucial to understand the nature of these disturbances. Menopause and sleep disturbances are intricately linked, with hormonal changes playing a significant role in disrupting sleep patterns. Yurcheshen et al. demonstrated that gabapentin improved sleep quality in menopausal women with HFs at a dose of 300 mg, three times daily, in a RCT , and positive effects of gabapentin on nighttime awakenings and sleep-enhancing actions were also observed in the hypothesized novel sleep disorder, LUNA, associated with low serum estradiol Discussion. This study revealed that without consideration of the type of sleep outcomes, gabapentin was significantly superior to placebos for the treatment for sleep disorders secondary to RLS, neuropathic pain, alcohol dependence, hot flashes in menopause, fibromyalgia, phantom limb pain, HIV-associated sensory neuropathies, and bipolar disorder. Gabapentin. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant (an analogue of gamma-aminobutyric acid). It is approved to treat neurological disorders such as seizures and neuropathic pain. Research: A systematic review has confirmed that Gabapentin 900mg per day reduces hot flushes more effectively than placebo 11. The most common side effect of gabapentin is
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |