Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 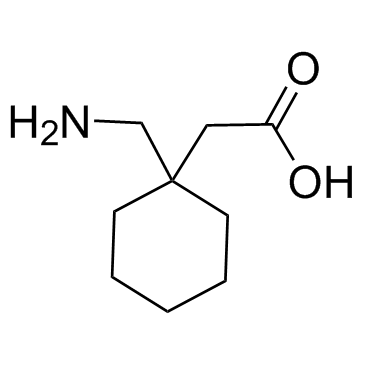 |
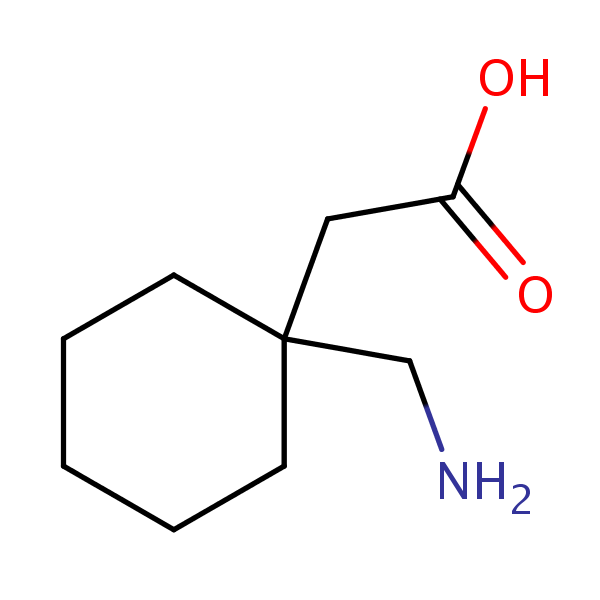
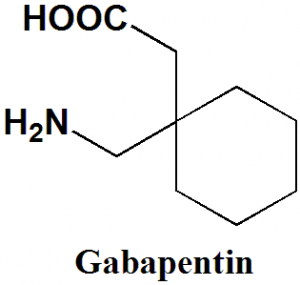
Use of Gabapentin Gabapentin (Neurontin) is a pharmaceutical drug, specifically a GABA analog. It was originally developed to treat epilepsy, and currently is also used to relieve neuropathic pain.IC50 Value: 140 nM (α2δ subunit of calcium channel) [1]Target: Calcium Channelin vitro: Gabapentin, baclofen and CGP 44532 all reduced the electrically stimulated release of [3H]glutamic acid (IC50 Gabapentin hydrochloride | C9H18ClNO2 | CID 6453919 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological Gabapentin is like carbamazepine and phenytoin with respect to effects on excitatory mechanisms and segmental inhibition in the trigeminal complex, but it differs in its effects on inhibitory pathways descending from the reticular formation. Gabapentin is a neuroprotective agent by inhibition of glutamate synthesis. Gabapentin Enacarbil | C16H27NO6 | CID 9883933 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological The 2D chemical structure image of gabapentin is also called skeletal formula, which is the standard notation for organic molecules. The carbon atoms in the chemical structure of gabapentin are implied to be located at the corner(s) and hydrogen atoms attached to carbon atoms are not indicated – each carbon atom is considered to be associated Four crystalline forms of gabapentin have been reported [4, 5, 6], attesting to its flexibility in forming supramolecular structures. Form I is gabapentin monohydrate, and Forms II, III, and Chemical structures of GABA and gabapentin, with commonalities highlighted. Gabapentin is a 3,3-disubstituted derivative of GABA. Therefore, it is a GABA analogue, as well as a γ-amino acid. [102] [103] It is similar to several other compounds that collectively are called gabapentinoids. Gabapentin is a structural analogue of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid that was first approved for use in the United States in 1993. 16 It was originally developed as a novel anti-epileptic for the treatment of certain types of seizures 14,5 - today it is also widely used to treat neuropathic pain. 8,10 Gabapentin has Gabapentin is a 3,3-disubstituted derivative of GABA. Therefore, it is a GABA analogue, as well as a γ-amino acid. Specifically, it is a derivative of GABA with a pentyl disubstitution at 3 position, hence, the name - gabapentin, in such a way as to form a six-membered ring. After formation of the ring, the amine and carboxylic groups are not Brand name: Neurontin. Structure and Mechanism. 1-(aminomethyl)cyclohexaneacetic acid (C9H17NO2) Gabapentin is widely used off-label for various chronic pain Know about technical details of Gabapentin like: chemical name, chemistry structure, formulation, uses, toxicity, action, side effects and more at Pharmacompass.com. Gabapentin (CAS 60142-96-3) information, including chemical properties, structure, melting point, boiling point, density, formula, molecular weight, uses, prices, suppliers, SDS and more, available at Chemicalbook. The ligand structures were readied utilizing Discovery Studio 4.1 through plan ligand protocol. All the tautomers and isomers of the ligand were regarded, and the ligands possessing the lowest energy has approved for docking. Table 1: Selected candidates for in-silico docking studies SI. NO Name Chemical structure 1 Gabapentin 2 ChemSpider record containing structure, synonyms, properties, vendors and database links for Gabapentin, 60142-96-3, UGJMXCAKCUNAIE-UHFFFAOYSA-N The chemical structures for gabapentin [1-(aminomethyl) cyclohexaneacetic acid], gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and pregabalin are shown below. Gabapentin closely resembles pregabalin, a schedule V drug under the Controlled Substances Act in its chemical structure and pharmacological activity. Novel antiepileptic drugs have been developed at an unparalleled rate during the past 15 years. Gabapentin (GBP), which was approved for the treatment of refractory localization-related epilepsies in the U.K. and Europe in 1993, was one of the first drugs to come out of this era. Since then, GBP has become well-known across the world, not only for its antiepileptic qualities but also for its Chemical structures of GABA and gabapentin, with commonalities highlighted. Gabapentin is a 3,3-disubstituted derivative of GABA. Therefore, it is a GABA analogue, as well as a γ-amino acid. [102] [103] It is similar to several other compounds that collectively are called gabapentinoids. consists of a gamma amino butyric acid molecule covalently bound to a lipophilic cyclohexane ring (C 9 H 17 NO 2 ) [ Figure 1]. It is a centrally active gamma amino butyric acid Gabapentin monohydrate | C9H19NO3 | CID 14598836 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological Gabapentin is a structural analogue of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid that was first approved for use in the United States in 1993. It was originally developed as a novel anti-epileptic for the treatment of certain types of seizures - today it is also widely used to treat neuropathic pain.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |