Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
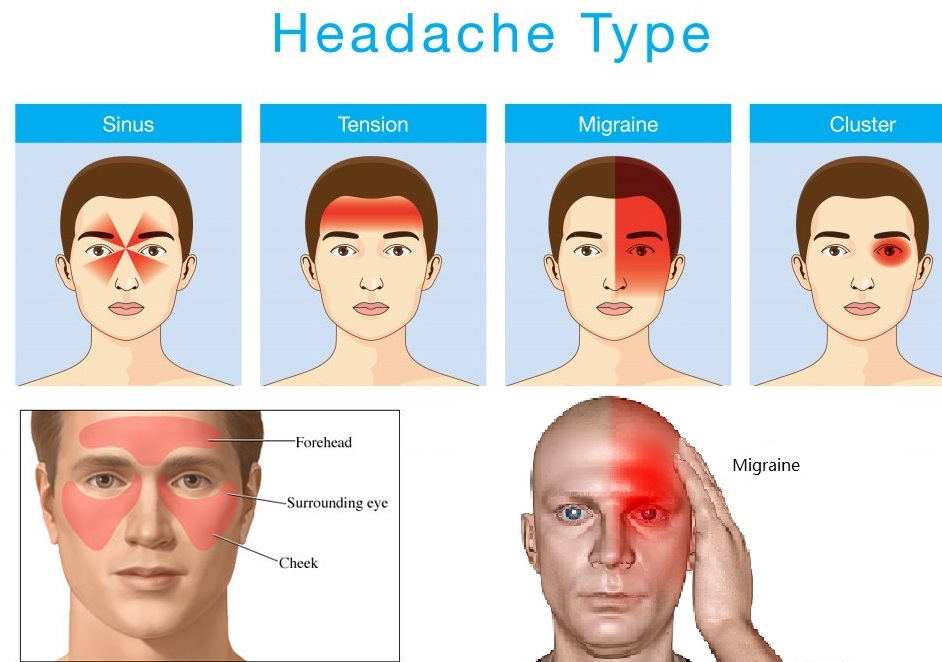 |  |
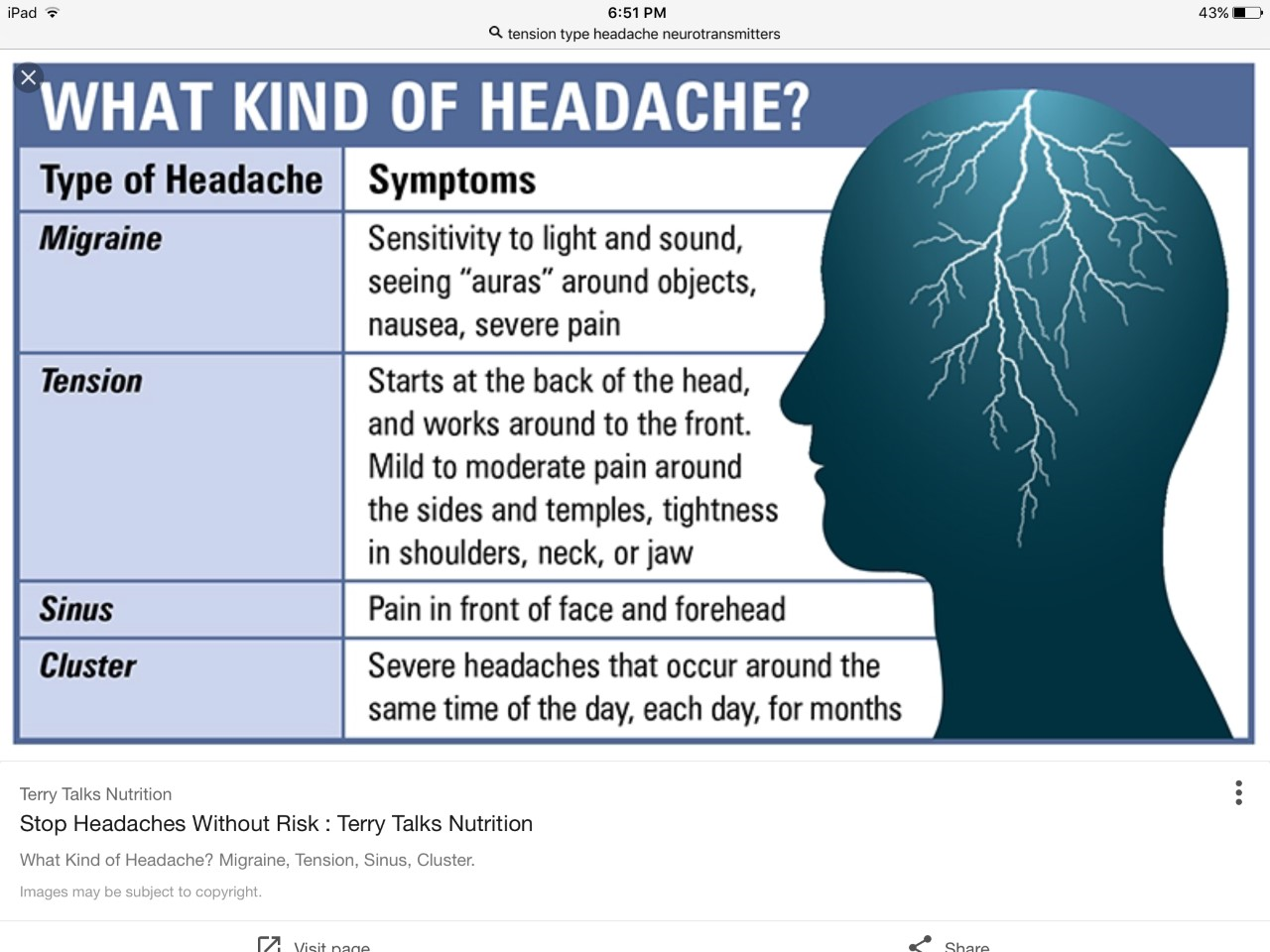
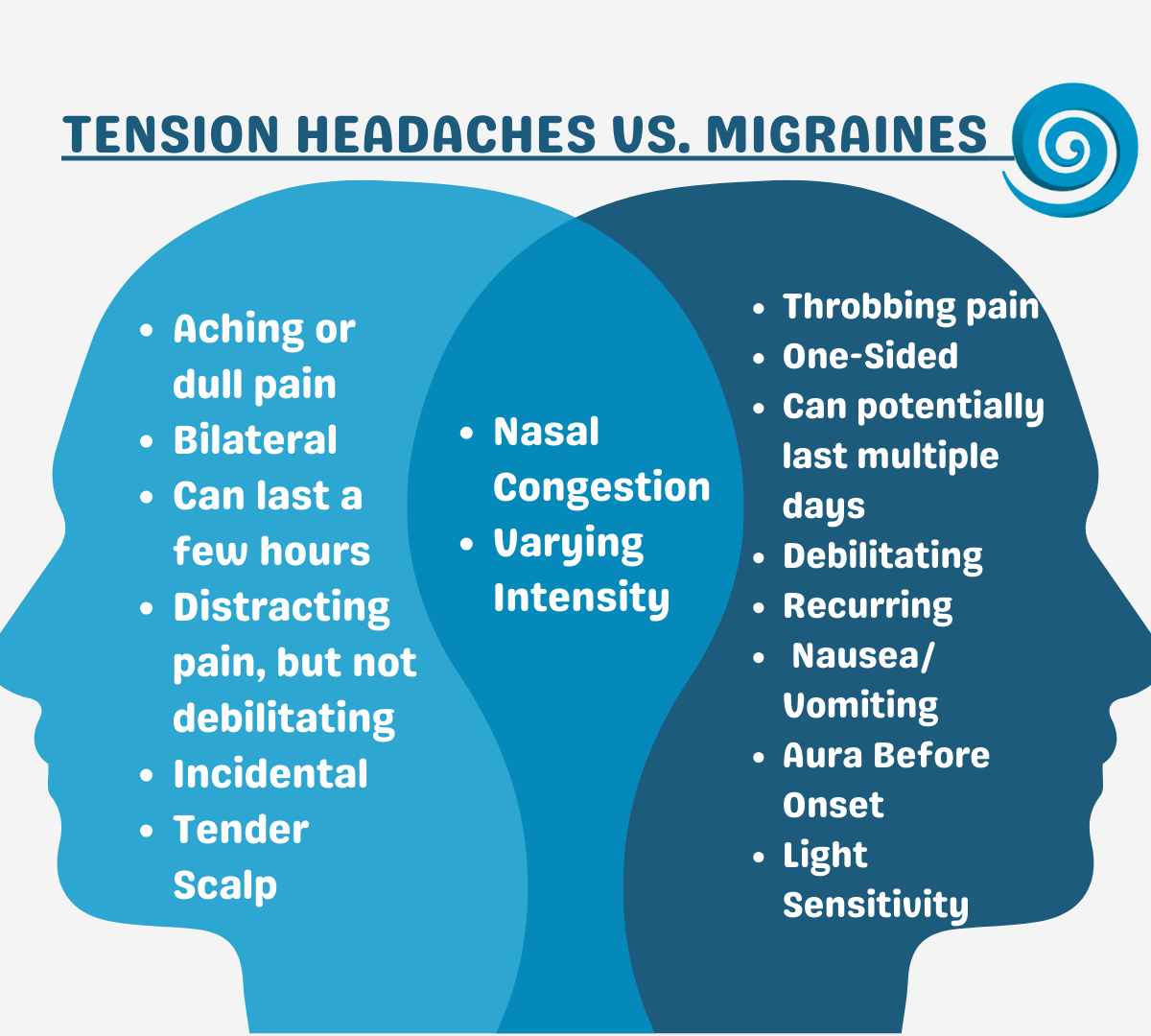
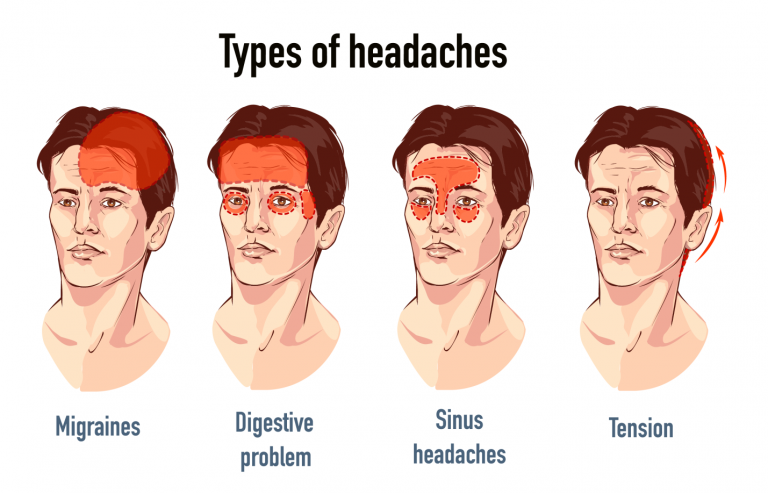
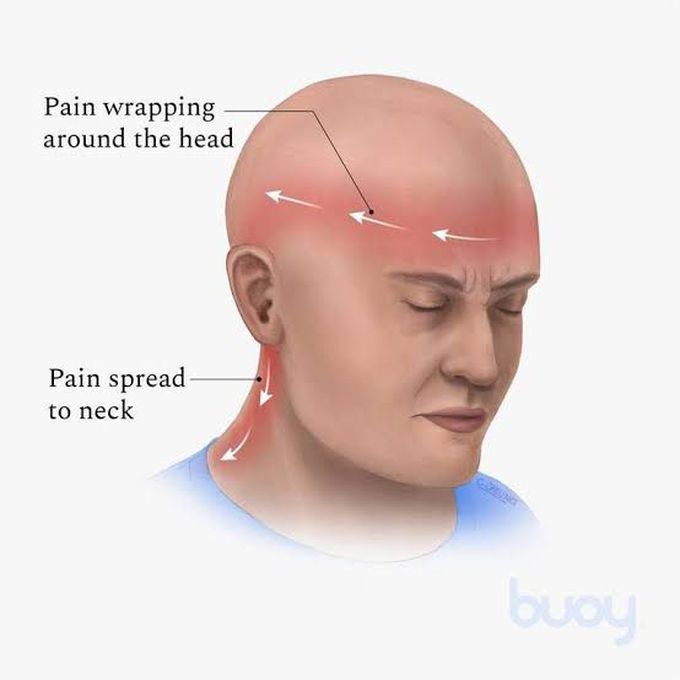
Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. WebMD explains the treatments for tension headaches, including over-the-counter drugs, biofeedback, cognitive behavioral therapy, and stress reduction techniques. Objective: To compare efficacy and safety of gabapentin (GPT) versus placebo for prophylaxis of chronic daily headache (CDH) (headache at least 15 days/month of greater than 4 hours duration over preceding 6 months). Methods: This is a multicenter randomized placebo-controlled crossover study. The anti-seizure medicines gabapentin (Gralise, Horizant, Neurontin) and topiramate (Topamax, Qsymia, others) may help prevent headache pain. But more study is needed to understand how well they work to prevent tension-type headaches. Tension-type headaches affect more than one-half of adults and last from 30 minutes to seven days. They present with at least two of the following characteristics: bilateral location, a Tension headaches can interrupt concentration but are usually not bad enough to send people to bed. Most people can work through a tension headache if they really need to. A tension headache can last from 30 minutes to seven days. Most last a few hours. Tension headaches tend to become worse as the day goes on and are often mildest in the morning. Tension-type headaches are divided into two main categories — episodic and chronic. Episodic tension-type headaches. Episodic tension-type headaches can last from 30 minutes to a week. Frequent episodic tension-type headaches occur less than 15 days a month for at least three months. This type of headache can become chronic. Gabapentin is used to control seizures, to treat nerve pain that can happen after having had shingles, and to treat a condition called restless legs syndrome. In addition to these FDA-approved uses, doctors sometimes prescribe gabapentin off-label. Off-label, gabapentin has been used in the treatment of migraine and other types of headache, including cluster and tension headaches. It shows potential as an option for those living with migraine and other headache disorders. Drugs in tension type headaches can either be used for acute episodes or for prophylaxis (1). Episodic tension headaches happening on fewer than 2 days per week can be treated symptomatically with over the counter analgesics (2). The drug treatment of episodic tension-type headaches consists of: paracetamol - appears to be less effective (2) Tension-type headache (TTH) is characterized by a bilateral, nonthrobbing headache of a mild to moderate intensity, typically without other associated features. TTH is the most common headache and prevalent neurologic disorder in the population. Somnolence and dizziness accounted for many of the premature withdrawals among those taking gabapentin. Conclusion: Gabapentin is an effective prophylactic agent for patients with migraine. In addition, gabapentin appears generally well tolerated with mild to moderate somnolence and dizziness. Migraines impose significant health and financial burdens. Approximately 38% of patients with episodic migraines would benefit from preventive therapy, but less than 13% take prophylactic medications. Gabapentin (Neurontin) increases the number of headache-free days in patients with chronic daily headache when compared with placebo. Valproate (Depacon) and topiramate (Topamax) reduce the Gabapentin is a drug that’s approved to help prevent seizures in people with epilepsy and treat nerve pain from shingles. It’s also sometimes used off-label for migraine prevention . What is a tension headache? A tension headache is a headache that feels like there’s a tight band wrapped around your head that puts pressure on your forehead and temples. Healthcare providers may call them tension-type headaches. Many factors cause tension headaches, and you may be unable to avoid all potential triggers. We offer a panoramic view of nociception, from a central perspective, and discuss various pharmacological options available to treat headache and neck pain. We also debate the role of a new antiepileptic drug, gabapentin, in the management of headache and neck pain. It is now considered to be an emergent treatment for pain syndrome. "I have been having chronic migraines for 5 years now and probably 50 other prescriptions written for me, and finally, gabapentin is like a miracle for me. My migraines were 24/7 with tension in shoulders and neck. Felt a little tired and strange the first day, but great relief now. Amitriptyline is efective at preventing tension-type headaches after three months of treatment. Triptans, ibuprofen, naproxen, aspirin, and high-dose acetaminophen are efective treatments for Objective: Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |