Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
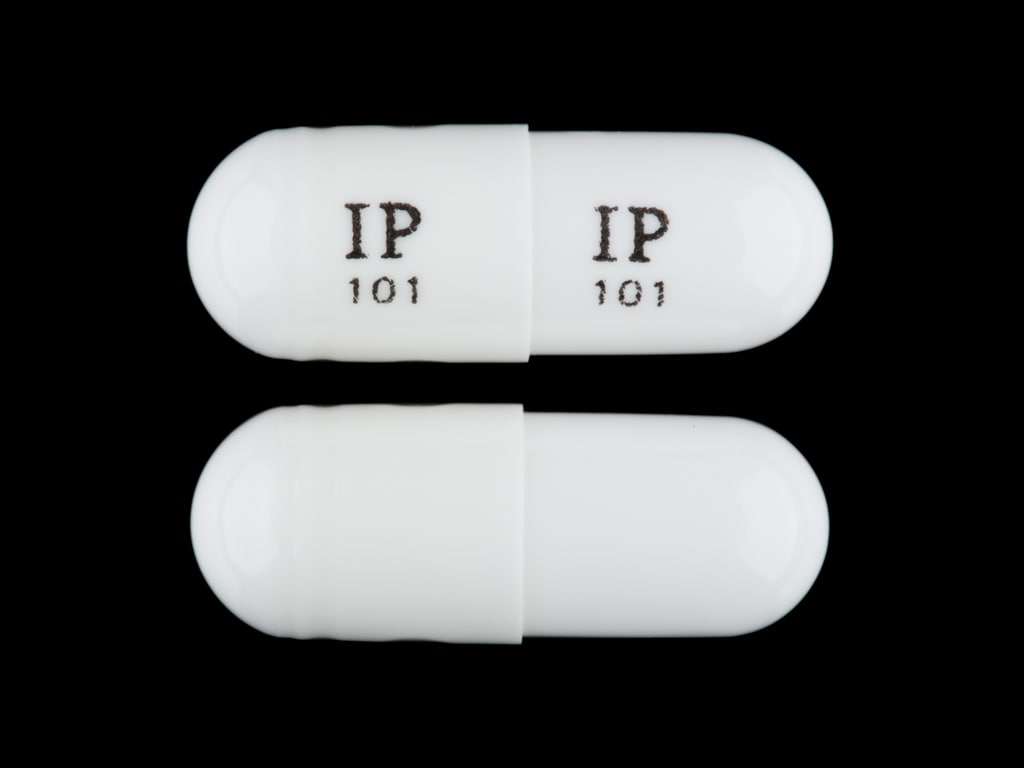
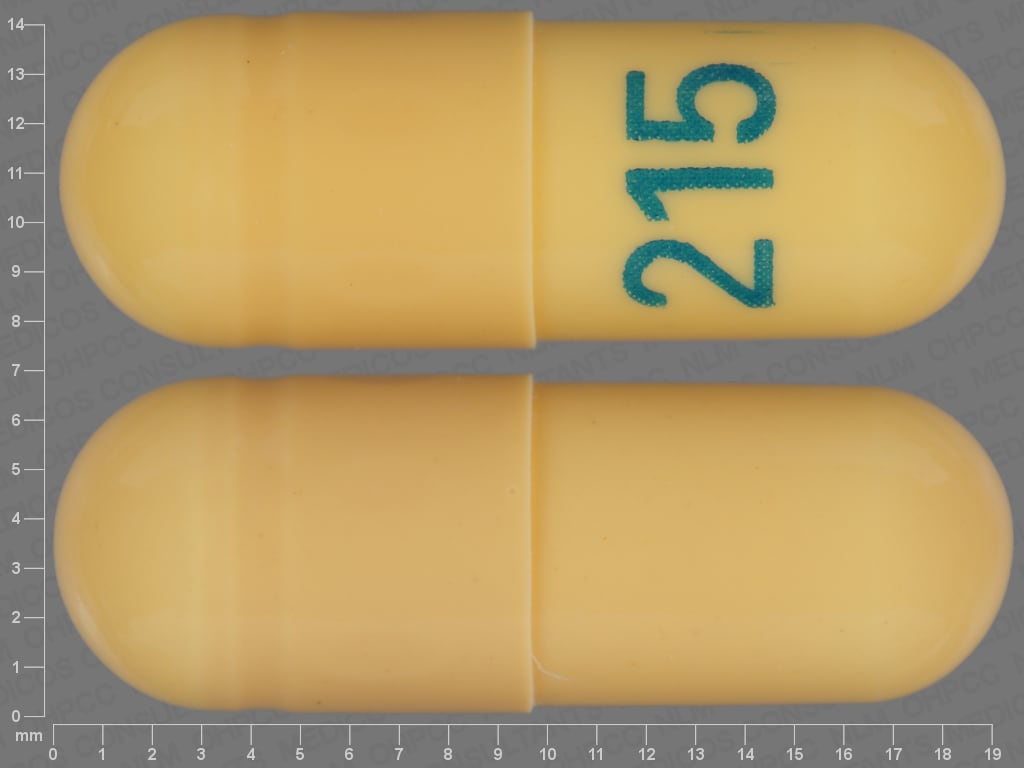
Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. NIH-funded study finds that gabapentin may treat alcohol dependence. Promising results from a randomized, controlled clinical trial of the medication. The generic anticonvulsant medication gabapentin shows promise as an effective treatment for alcohol dependence, based on the results of a 150-patient clinical trial of the medication. • Taking medicine for an alcohol use disorder is not substituting one drug for another. How should I take gabapentin? • The recommended dose of gabapentin for the treatment of alcohol use disorder is 300–600 milligrams (mg) three times daily. • Gabapentin can be taken with or without food. If you take an antacid containing aluminum Benzodiazepines Carbamazepine Gabapentin Clonidine Concurrent Alcohol Use Potentiates effects of alcohol; can lead to serious safety risks, incl. over sedation, falls, delirium, respiratory depression (e.g., non-fatal or fatal overdose), and prolonged hospitalization No well-described safety risk Abstinence recommended after txdue to Gabapentin is effective at reducing drinking among people with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and strong withdrawal symptoms, according to a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine. Evidence from single-site studies lend support to the safety and efficacy of gabapentin as a novel treatment for alcohol use disorder, with unique benefits for alcohol-related insomnia and negative affect, relative to available treatments. In practice, gabapentin is best reserved for treating bipolar disorder in patients with comorbidities like anxiety and alcohol or cannabis use disorders. Table: Off-Label Dosing of Gabapentin (Click to view full-size PDF.) Restless legs syndrome and pain Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. with alcohol or benzodiazepine use disorderkeep these considerations in mind in addressing clinical issues. CNS Drugs. 2015 Apr;29(4):293-311. doi: 10.1007/s40263-015-0240-4. Anticonvulsants for the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome and alcohol use disorders. Hammond CJ. 1, Niciu MJ, Drew S, Arias AJ. Author information Abstract • The recommended dose of gabapentin for the treatment of alcohol use disorder is 300–600 milligrams (mg) three times daily. • Gabapentin can be taken with or without food. Is gabapentin an effective treatment for alcohol use disorder (AUD)? Bottom line. Gabapentin treatment avoided more heavy drinking days (> 5 standard drinks/day) than placebo (27% vs 9%). Gabapentin can be a second-line, off-label option to treat AUD. However, there is mixed evidence and concerns about abuse-misuse, and drug-related harms. Evidence Is gabapentin an effective treatment for alcohol use disorder (AUD)? Gabapentin treatment avoided more heavy drinking days (> 5 standard drinks/day) than placebo (27% vs 9%). Gabapentin can be a second-line, off-label option to treat AUD. However, there is mixed evidence and concerns about abuse- Three medications are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for AUD treatment: disulfiram, oral and extended-release injectable naltrexone and acamprosate. Two other agents, gamma-hydroxybutyric acid and nalmefene, are approved in Europe. Several other agents are used off-label to treat the symptoms of AUD. In sustained remission: After full criteria for alcohol use disorder were previously met, none of the criteria for alcohol use disorder have been met at any time during a period of 12 months or longer (with the exception that Criterion A4, "Craving, or a strong desire or urge to use alcohol," may be met). Specify if: -Opioid use disorder, prescribed opioids – For patients with alcohol use disorder and co-occurring opioid use disorder, our preference is to address both disorders with naltrexone (algorithm 1). However, naltrexone can only be started after a sufficient time has elapsed since last opioid exposure. Some research shows that gabapentin has promise as an alcohol withdrawal treatment, possibly in combination with other medications. Gabapentin can: A clinical trial showed that people with Gabapentin can be a second-line, off-label option to treat AUD. However, there is mixed evidence and concerns about abuse-misuse, and drug-related harms. Results are statistically significant unless indicated. In summary, the studies showed a significant reduction in the number of weekly drinks among patients receiving gabapentin monotherapy, 4 as well as reduced alcohol craving, positively affected mood and sleep symptoms, and increased rates of abstinence with an 1800-mg daily dose of gabapentin. 5 Both studies also suggest favorable safety • The use of medications to treat substance use disorders – Typically accompanied by psychosocial interventions (counseling, mutual support groups or AA, etc.) – Plus other clinical support (resources, care management) • For alcohol use disorder (AUD), medications focus on altering the reinforcing effects of alcohol use
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |