Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
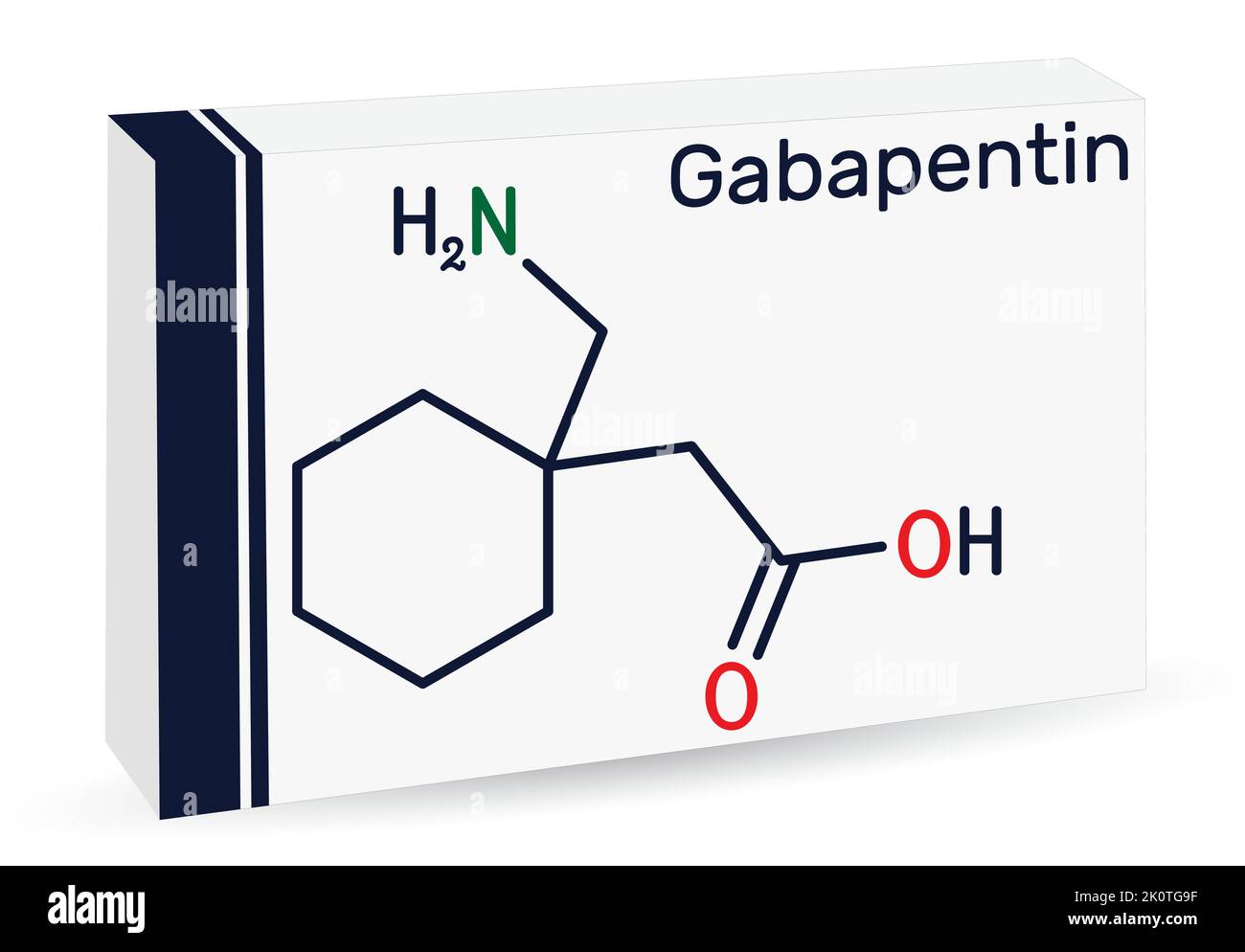
When formulated as a 10% topical gel, gabapentin is designed for localized treatment, potentially minimizing systemic absorption and reducing the likelihood of systemic drug interactions that are more common with oral administration. We performed a local retrospective observational study to assess efficacy and safety of 6% w/w gabapentin gel, manufactured by a local NHS pharmacy manufacturing unit, for the treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain conditions. Compounded Topical Analgesics for Chronic Pain Abigail E. Cline, PhD* and Jake E. Turrentine, MD† Analgesic medications compounded for topical use are gaining popularity for the management of chronic pain. The advantagesof topical painmedicationsinclude reductionof systemicadverse effects,improvedpatient acceptance, Gabapentin 40 mg/g topical cream is a semisolid preparation designed for localized treatment or absorption of active ingredients through the skin. This formulation is primarily used to manage neuropathic pain and other conditions where localized delivery of gabapentin can provide therapeutic benefits. A 10% w/w topical gabapentin gel applied thrice daily demonstrated strong antiallodynic and antihyperalgic effects in Hot-plate and von Frey test. Topical use of the gel potentially avoids dose titration in neuropathic pain patients, reduces pain similarly to systemic gabapentin, and avoids related side effects. Gabapentin: Emulsion gel- Purpose of Review Topical analgesics are a non-opioid option for the treatment of chronic pain conditions including neuropathic pain, musculoskeletal pain, and osteoarthritis. There are many topical medications available; however their efficacy is variable. This article reviews the various topical analgesics, their mechanisms of action, and their efficacy. Recent Findings Studies have found The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of Lipoderm Cream, VersaBase Gel, and Emollient Cream on the release and permeation of gabapentin formulated for neuropathic pain. Gabapentin of different strengths (1%, 5%, and 10%) was compounded with the bases, diffusion of the drug from t Compounded Topical Analgesics for Chronic Pain Abigail E. Cline, PhD* and Jake E. Turrentine, MD† Analgesic medications compounded for topical use are gaining popularity for the management of chronic pain. The advantagesof topical painmedicationsinclude reductionof systemicadverse effects,improvedpatient acceptance, Gabapentin compounded with Lipoderm cream for topical use was stable in Ecolojars for 28 days at 25°C. Under the same conditions, the drug was not stable in Versabase gel and Emollient cream. Gabapentin 6% Topical Gel is a semisolid formulation dispensed through a pump mechanism. This design allows for easy and precise application on the skin, targeting the treatment or absorption of active ingredients. Topical delivery of gabapentin is desirable to treat peripheral neuropathic pain conditions whilst avoiding systemic side effects. To date, reports of topical gabapentin delivery in vitro have been variable and dependent on the skin model employed, primarily involving rodent and porcine models. In this study a variety of topical gabapentin formulations were investigated, including Carbopol absorption • Drug concentration at the site of administration can be 30 fold higher than with an oral dose • Decreased potential for systemic side effects when targeting specific areas with a transdermal Sawynok J. Topical analgesics in neuropathic pain. Remember the dose-dependent absorption issue with gabapentin. As you get to higher dosages, there is the potential that you Gabapentin and Renal Function - Case Scenario - Med Ed 101 - [] Here’s another clinical pearl regarding gabapentin effectiveness and how this drug’s absorption can vary based upon the dose. As discussed in Chapter 2, there are potential advantages for the use of topical medications to treat pain indications, including provision of local, regional, and systemic therapeutic effects, as well as the potential for better safety profiles than oral medications.1 Owing in part to their clinical potential, topical medications are one of the most commonly compounded preparations in the Objectives: To investigate the stability and beyond-use date (BUD) of topical gabapentin in 3 commonly used bases. Methods: Lipoderm cream, Versabase gel, and Emollient cream were used to compound gabapentin (10%). Gabapentin in oral preparation is considered fairly safe, thus the risk of side effects from topical gabapentin appears low, even if there is some degree of systemic absorption. See Box 6-4 for a summary of research findings. The topical cream formulation containing Gabapentin 10%, Ketoprofen 20%, and Lidocaine HCl 5% is designed for localized treatment and may be used to manage conditions such as neuropathic pain, inflammatory pain, or certain types of chronic pain syndromes. Each sample then was mounted on a diffusion cell with 10 mL sterile PBS in its receptor chamber and placed in a warm water bath at 39°C as described in experiments evaluating topical gabapentin formulations. 3 Transdermal gabapentin (10% or 20% in a Lipoderm base) was applied using a gloved finger to the mounted cadaver skin at 0 and 12 hours Skin concentrations increased with a longer 1-hour pre-treatment. Minimal skin and deeper tissue levels were found following a 4-hour pre-treatment. These results suggest that topical gabapentin may be antinociceptive in a rodent formalin model at specific doses and pre-treatment intervals. Topical delivery of gabapentin could provide an alternative treatment to oral delivery of the active for neuropathic pain conditions, with associated reduced systemic side effects; this is supported by in vivo studies and observational clinical evidence.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |