Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
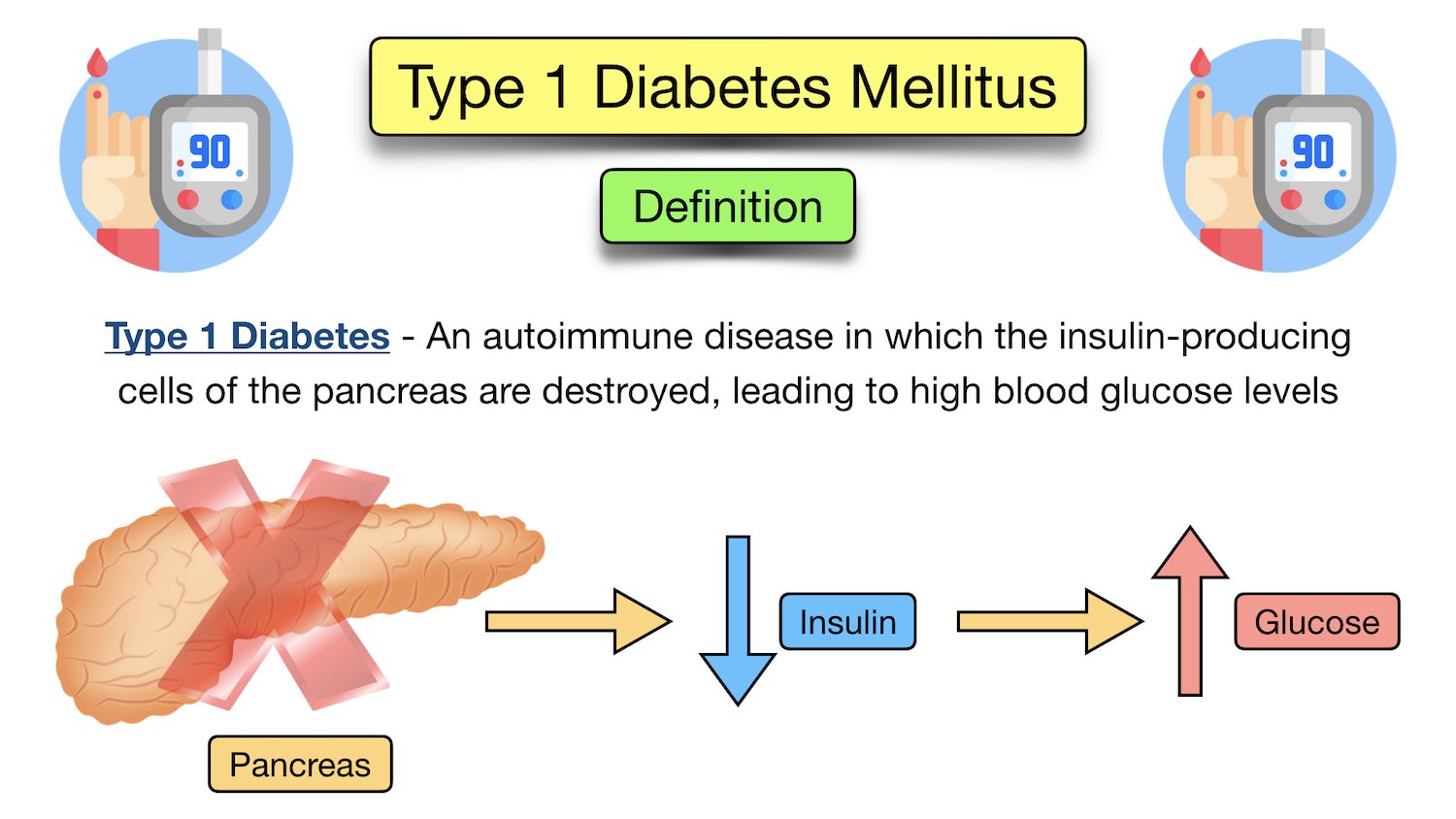
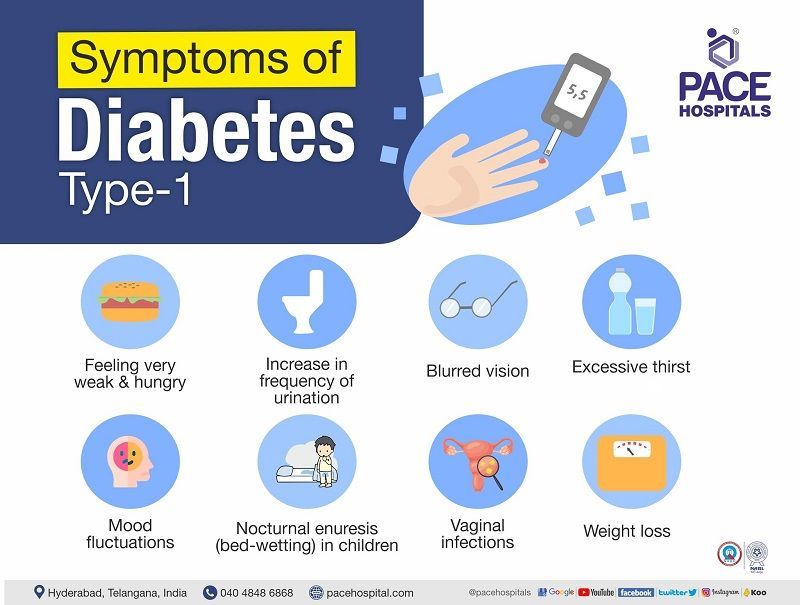
Gabapentin can cause mild disorders of blood glucose due to an unknown mechanism of action. In the absence of other factors, clinicians can accept gabapentin as a contributing factor to glucose fluctuations. Based on these principles, insulin therapy should be modified. hyperglycemia in a diabetic patient. Gabapentin is an analgesic at lower doses and an anticonvulsant at higher doses. Other than drowsiness, it has few noticeable side effects. Galliprant is an anti-inflammatory and will likely provide more analgesia for arthritis than gabapentin, but we often use Galliprant and gabapentin together. Medication Interaction; Pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin) May increase toxic effects of CNS depressants,* SSRIs, thiazolidinediones Toxic effects may be increased by CNS depressants The inclusion criteria were: (i) patients with type 1 diabetes receiving gabapentin at doses up to 900 mg (n = 30) or pregabalin at doses up to 300 mg (n = 32) daily Yes, a diabetic can take Gabapentin, but it's crucial to consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice. Diabetes is a condition that requires careful management of various aspects of health, from diet to medication. The pain descriptors of the SF-MPQ were similar between the placebo and gabapentin groups and between patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes at baseline. Fifty-six gabapentin-treated patients (67%) achieved the 3600 mg/d dosage. Type 1 diabetes is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are male, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for 2 - 5 years also take Seroquel, and have Depression. Relieving pain. Many prescription medications are available for diabetes-related nerve pain, but they don't work for everyone. When considering any medication, talk to your health care provider about the benefits and possible side effects to find what might work best for you. Diabetic neuropathy is one of the most prevalent chronic complications in adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes while also affecting individuals with prediabetes and young people with diabetes, with an estimated lifetime prevalence exceeding 50% (1 – 4). The prevalence of CAN increases with diabetes duration in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. In the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Intervention and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) study, prevalence rates of at least 30% were observed after 20 years of type 1 diabetes . We conducted a double-blind, controlled trial that compared gabapentin with placebo in the treatment of 32 diabetic patients referred for the management of neuropathic pain (visual pain score >60 on a 100-point scale) after conventional treatment failed. Diet and exercise in type 2 diabetes — The American Diabetes Association recommends lifestyle interventions, specifically diet and exercise, as the first line in treating diabetic neuropathy in type 2 diabetes . The goal is to achieve and maintain a normal body weight with a nutrient-dense diet low in saturated fats and high in whole grains A 63-year-old Caucasian gentleman with type 2 diabetes mellitus developed a possible case of gabapentin-induced mild hyperglycemia after receiving gabapentin for several months with a dose titration. Gabapentin could be considered as a cause for otherwise unexplained hyperglycemia in a patient. I have had diabetic neuropathy for many years now, and for a few years I was on Pregabelin then Gabapentin. They certainly helped with the foot pain, but I found my brain turning to mush, so I decided to stop taking this type of drug. Do NOT suddenly stop - you need to come off these medications slowly. diabetes; gabapentin; pregabalin Introduction Diabetic neuropathy is the most common complication of diabetes type 1 and type 2 and as many as 50% of patients develop neuropathy in the course of the disease [1]. According to a definition of the Special Interest Group on Neuropathic Pain (NeuPSIG), neuropathic pain In patients with type 1 diabetes, intensive glycemic control with an A1C goal of approximately 7% reduces the risk of symptomatic neuropathy by up to 60%. 7 Only modest reductions in neuropathy Gabapentin use may cause hypoglycemia in both diabetic and non-diabetic patients, requiring monitoring and informed patients about the risk. Gabapentin may cause mild hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, but this case was not considered due to adequate pain control. Diabetes mellitus is the most common cause of peripheral neuropathy, with 45 percent of patients affected at some time during the course of their disease. Gabapentin is a fairly new The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends that screening for diabetic neuropathy begin immediately after someone is diagnosed with type 2 diabetes or five years after diagnosis with type 1 diabetes. After that, screening is recommended once a year. We received six cases of (severe) hypoglycaemia in both diabetic and non-diabetic patients exposed to gabapentin, which occurred between July 2002 and July 2012. Two cases are described in more detail below. Patient A, a 36-year-old female with a history of a complex regional pain syndrome, presented to the hospital after syncope.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |