Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-JulieBang-UlnarNerveEntrapment-4000x2700-fdb75872865e4898bb04fa246b43963a.png) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
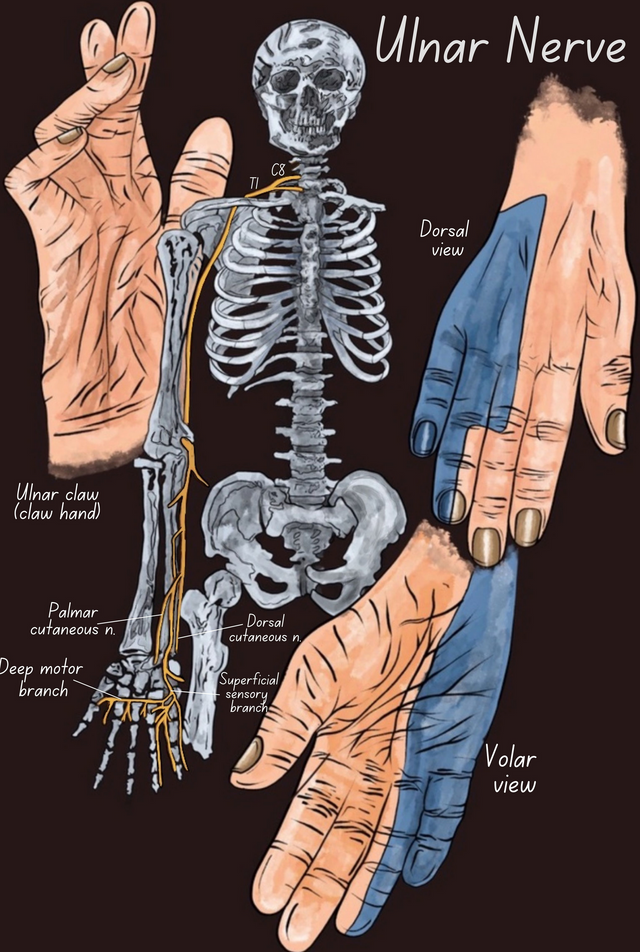 |  |
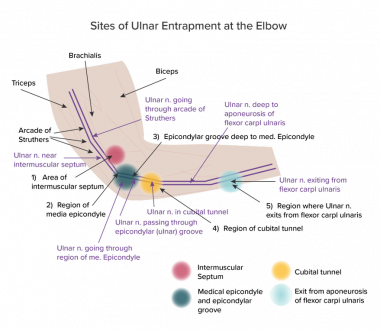
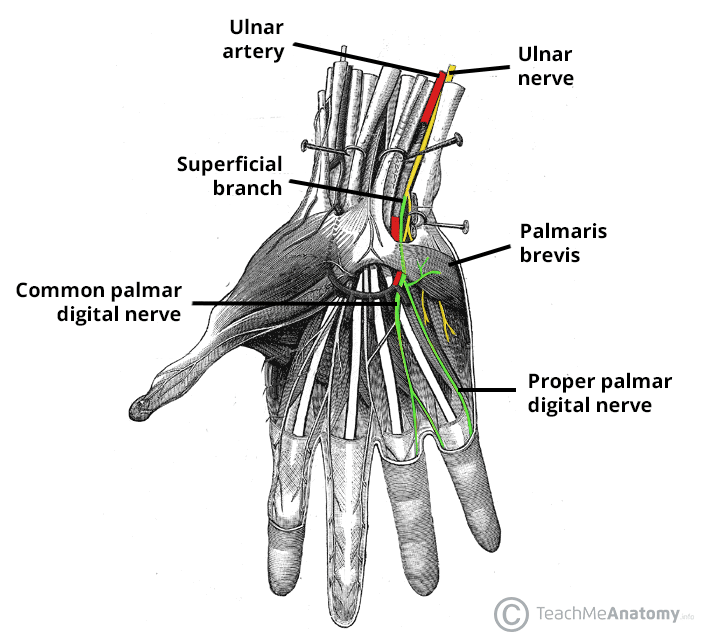
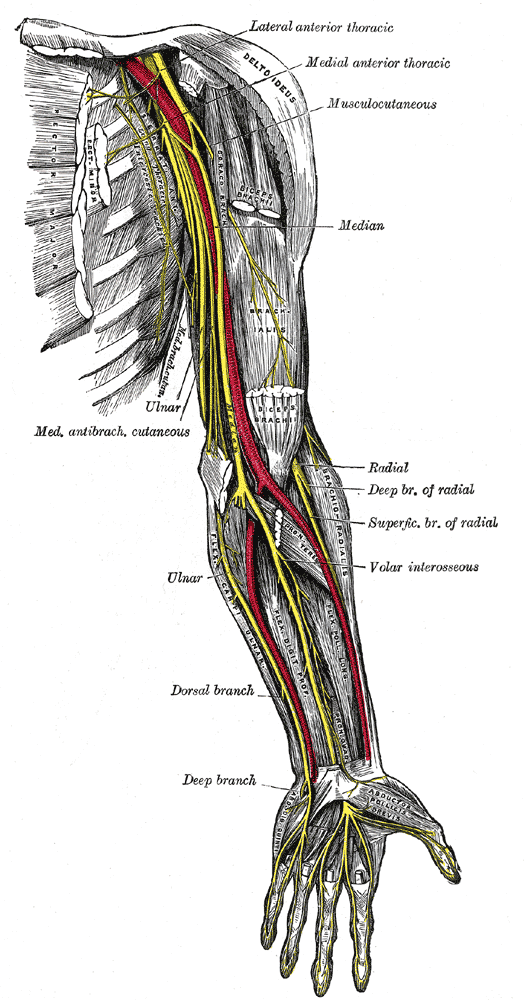
The rehabilitation implications are that gabapentin can be offered to patients experiencing chronic neuropathic pain, but with the expectations that the therapy may need to be combined with or replaced with other nonpharmacologic interventions, such as physical therapy and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation. 6 PMI-5011 normalized glycemia, improved nerve conduction slowing and sensory neuropathy, and diminished 12/15-lipoxygenase upregulation and nitrated protein expression in peripheral nervous system in rats with high-fat diet-induced neuropathy of prediabetes and obesity, potentially, by multiple mechanisms that are including the inhibition of Early peripheral neuropathy may present as sensory alterations that are often progressive, including sensory loss, numbness, pain, or burning sensations in a “stocking and glove” distribution A common type of ulnar nerve entrapment at the elbow is cubital tunnel syndrome, which can be caused by elbow injuries (e.g. fractures and dislocations), bone and joint disease (e.g. arthritis and bone spurs), repeated bending of the elbow (which is more common in some occupational settings requiring heavier work), or excessive leaning on it—especially on hard surfaces. The meta-analysis of the 2 high-quality, placebo-controlled RCTs showed positive effect of gabapentin in diabetic neuropathy and post-herpetic neuralgia. The addition of 2 low-quality, placebo-controlled RCTs did not alter the magnitude or direction of observed effect. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant and has been used to manage neuropathic pain. Gabapentin is not without side effects and there is also potential for misuse. Side effects associated with gabapentin include somnolence, dizziness, peripheral edema and gait disturbances. The median and ulnar nerves are evaluated for motor function and the median, ulnar, and sural nerves are evaluated for sensory function. The sural nerve plays an important role in the diagnosis of alcohol-induced PN because it's located in the calf and innervates sensory function in the lower legs where symptoms begin. The purpose of this report is to review the clinical evidence on the efficacy, safety and guidelines for use of gabapentin in adults with neuropathic pain, and to examine evidence on the misuse or abuse of gabapentin and other drugs for neuropathic pain. This review updates parts of two earlier Cochrane reviews investigating effects of gabapentin in chronic neuropathic pain (pain due to nerve damage). Antiepileptic drugs are used to manage pain, predominantly for chronic neuropathic pain, especially when the pain is lancinating or burning. Gabapentin at a dose of 1800 to 3600 mg daily (1200 to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. The three systematic reviews summarized in this report examined the efficacy and safety of treatments for patients with any type of neuropathic pain, 8 painful diabetic neuropathy, 9 or fibromyalgia. 10 All the reviews included gabapentin, pregabalin, TCAs, and SNRIs. In patients with neuropathic pain, this review shows that gabapentin is associated with a greater likelihood of achieving substantial or moderate pain relief vs placebo. Oral gabapentin dosed at 1,200 mg or more daily demonstrated a 50% reduction in pain intensity, with a number needed to treat (NNT) of eight for postherpetic neuralgia and an NNT of six for Pregabalin (Lyrica), gabapentin (Neurontin), amitriptyline (except in older adults), or duloxetine (Cymbalta) should be used as first-line treatment for painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. A 1 The ulnar nerve is an extension of the medial cord of the brachial plexus. It is a mixed nerve that supplies innervation to muscles in the forearm and hand and provides sensation over the medial half of the fourth digit and the entire fifth digit (the ulnar aspect of the palm) and the ulnar portion of the posterior aspect of the hand (dorsal If you've been prescribed gabapentin for nerve pain, you may begin to feel pain relief within one to two weeks of starting it, depending on your dosage. However, for some people, it can take longer to see benefits. Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a neuropathy due to the compression of the median nerve. It is shown that gabapentin in high doses is effective in treatment of CTS patients. In this study we evaluated the efficacy of low doses of gabapentin in treatment of CTS patients. Ulnar nerve entrapment occurs when something irritates or puts pressure on your ulnar nerve that runs down your arm. Cubital tunnel syndrome affects your ulnar nerve in your elbow. It’s the most common type of ulnar nerve entrapment. Guyon’s canal syndrome, which affects the nerve in your wrist, is a rare peripheral neuropathy. In a case report, two patients (1 man and 1 woman) aged 18-58 years were described.Of whom, one patient developed drowsiness during treatment with gabapentin for ulnar neuropathic pain and the another patient exhibited treatment failure during treatment with gabapentin for ulnar neuropathic pain [routes, duration of treatment to reaction onset and outcome not stated; not all dosages stated]. Surgery will take pressure off your ulnar nerve. Your surgeon may move your nerve to a different area to stop it from being stretched or pinched. He or she may remove part of your bone if it is pressing on your nerve. Treatment options. The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition. gabapentin; Qutenza
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-JulieBang-UlnarNerveEntrapment-4000x2700-fdb75872865e4898bb04fa246b43963a.png) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |